Animal cell
- Animal cells are the fundamental units of structure and function in animals.
- They are eukaryotic cells, characterized by a well-defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane.
Structure of Animal Cell
|
Organelle |
Function |
|
1) Cell Membrane |
A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. |
|
2) Lysosome |
Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. |
|
3) Cytoplasm |
Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. |
|
4) Nucleus |
The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA |
|
5) Nuclear Membrane |
Surrounds the nucleus. |
|
6) Nucleolus |
A round structure in the nucleus that makes ribosomes. |
|
7) Vacuole |
Stores food and water. |
|
8) Golgi Body |
Processes and packages materials for the cell. |
|
9) Mitochondria |
The “Powerhouse”. Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP. |
|
10) Rough E.R. |
Builds and transports substances through the cell. Has ribosomes on it. |
|
11) Smooth E.R. |
Builds and transports substances through the cell. Does not have ribosomes. |
|
12) Ribosome |
Helps make protein for the cell. |
Functions of Animal Cells
a) Cellular Respiration: Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration, providing energy for cellular processes.
b) Protein Synthesis: Endoplasmic reticulum (both rough and smooth) and Golgi apparatus are involved in the synthesis, modification, and packaging of proteins.
c) Genetic Regulation: Nucleus contains genetic material and regulates cell activities based on genetic instructions.
d) Cellular Transport: Cell membrane regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
e) Waste Management: Lysosomes break down waste materials and cellular debris.
f) Cell Division: Centrioles play a role in organizing the spindle fibers during cell division (mitosis).
More on AmplifyGlobe
Plant Cell
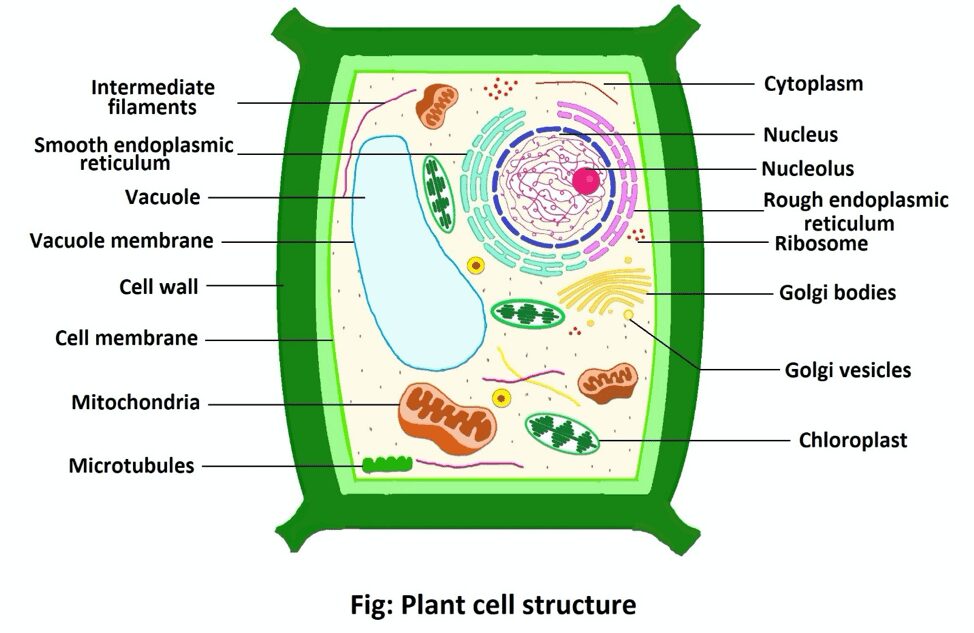 Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants. They are eu Read More
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants. They are eu Read More