Properties of Matter
- Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It can exist in various forms, including solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
- Properties of matter are characteristics that help describe and identify different substances. These properties can be classified into two main categories: physical properties and chemical properties.
Physical Properties of Matter:
1. Mass: The amount of matter in an object. It is measured in units such as grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
2. Volume: The amount of space occupied by an object or substance. It can be measured in cubic units such as cubic centimeters (cm³) or liters (L).
3. Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance. It indicates how tightly packed the particles of a substance are. Density = Mass/Volume.
4. State (Solid, Liquid, Gas): The physical form in which matter exists. It is determined by the arrangement and movement of particles.
5. Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid substance changes into a liquid state.
6. Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid substance changes into a gaseous state.
7. Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture (solution).
8. Conductivity: The ability of a substance to conduct heat or electricity. Substances can be classified as conductors, insulators, or semiconductors based on their conductivity.
9. Magnetism: The property of attracting certain materials such as iron or steel when exposed to a magnetic field.
10. Color: The visual appearance of a substance due to the wavelengths of light it reflects.
Chemical Properties of Matter:
1. Flammability: The ability of a substance to burn or ignite when exposed to heat or flames.
2. Reactivity: The tendency of a substance to undergo chemical reactions with other substances to form new products.
3. Corrosivity: The ability of a substance to cause damage or deterioration to other materials through chemical reactions, such as rusting or tarnishing.
4. Toxicity: The degree to which a substance can cause harm or poison living organisms upon exposure.
5. pH: A measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity.
More on AmplifyGlobe
States of Matter
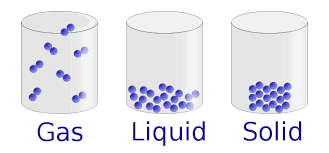 Matter exists in four primary states: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. These stat Read More
Matter exists in four primary states: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. These stat Read More
Solubility
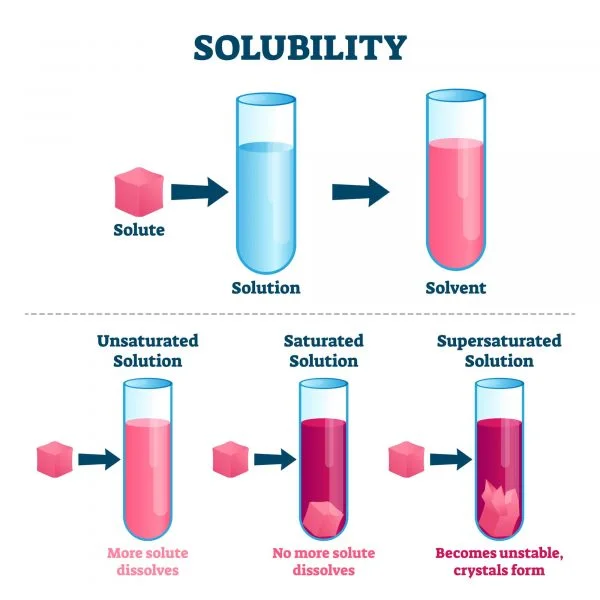 Solubility refers to the ability of a substance, known as the solute, to dissolv Read More
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance, known as the solute, to dissolv Read More
Separation of Mixtures
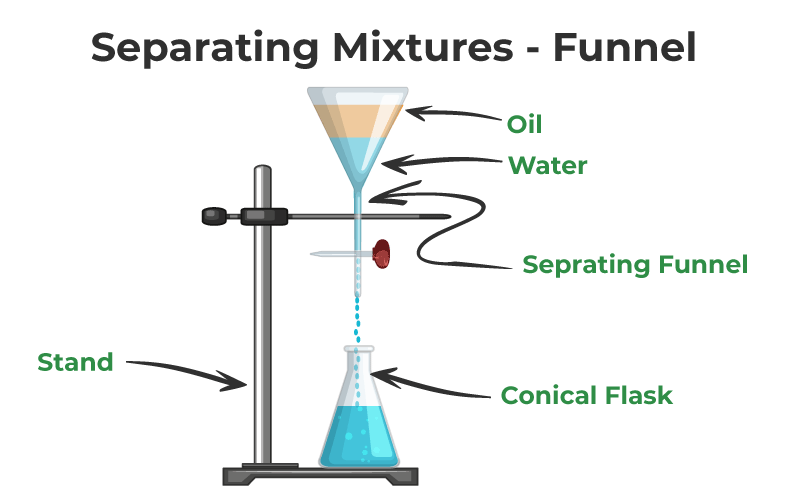 Mixtures of substances are not chemically bonded (joined) to each other so they Read More
Mixtures of substances are not chemically bonded (joined) to each other so they Read More