A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis. What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
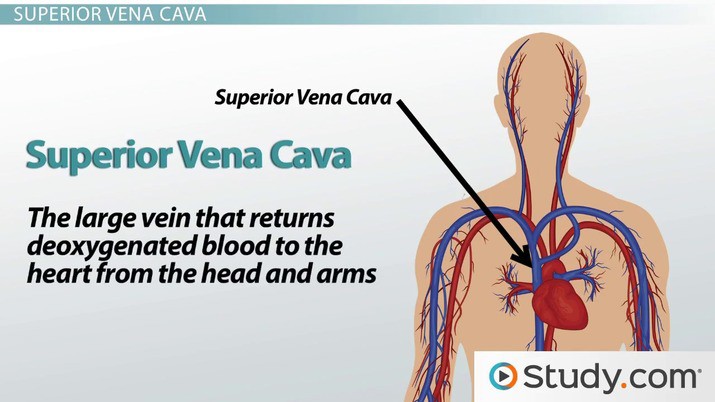
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
Question 2:
A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis.
What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
The Correct Answer is C.Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
Question 3:
What are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA?
A. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
B. Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine.
C. Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine.
D. Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine.
The Correct Answer is A.These are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA1.
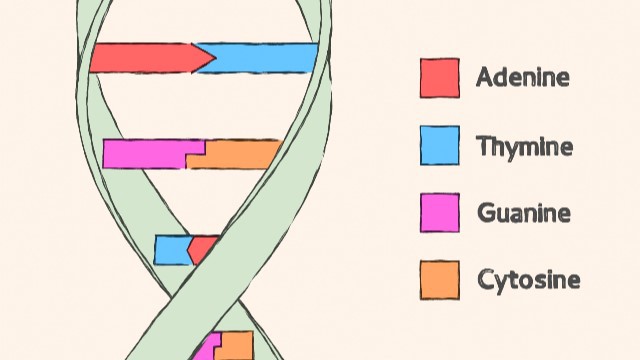
Choice B) Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine is incorrect because Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice C) Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine and Guanosine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice D) Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine, Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Question 4:
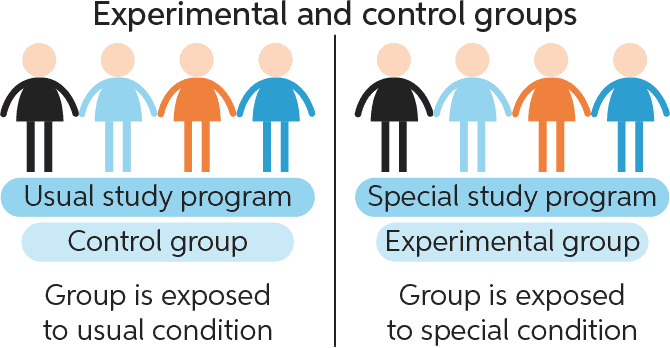
In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between what?.
A. Control group and treatment group.
B. Independent variable and dependent variable.
C. Experimental group and non-experimental group.
D. High level and low level of the independent variable.
The Correct Answer is A.In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between the control group and treatment group.
This means researchers can correctly measure the entire effect of the treatment without interference from confounding variables.
Choice B) Independent variable and dependent variable is incorrect because these are not groups but rather variables.
The independent variable is manipulated by the experimenters while the dependent variable is measured to see if it changes as a result of the manipulation.
Choice C) Experimental group and non-experimental group is incorrect because a non-experimental group is not a term used in experimental design.
The correct term for the group that does not receive the treatment is control group.
Choice D) High level and low level of the independent variable is incorrect because these are levels of the independent variable, not groups.
In an experiment, there can be multiple levels of the independent variable, but they are applied to different groups (e.g.
control group, treatment group).
Question 5:
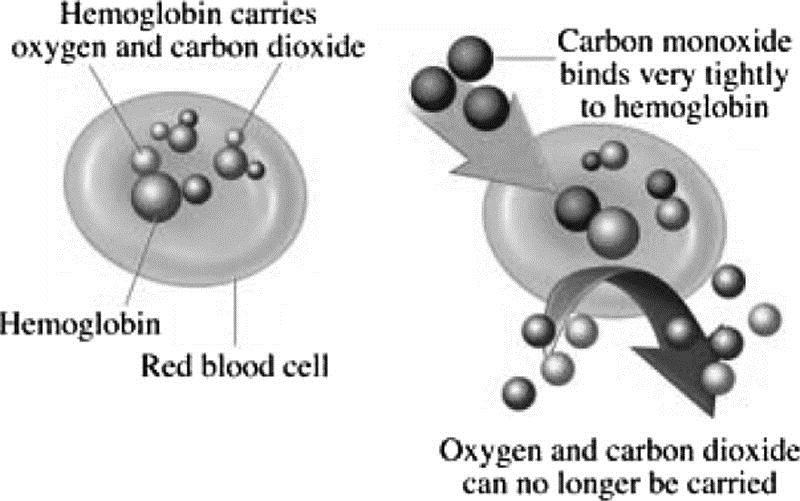
Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
The Correct Answer is B.Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
 |
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 6:
A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder.
The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
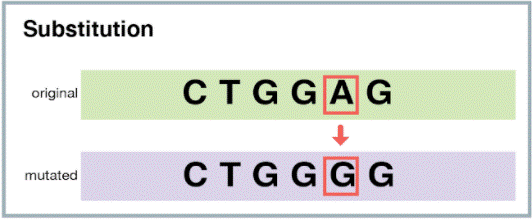 |
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
Question 7:
What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
The Correct Answer is C.Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.
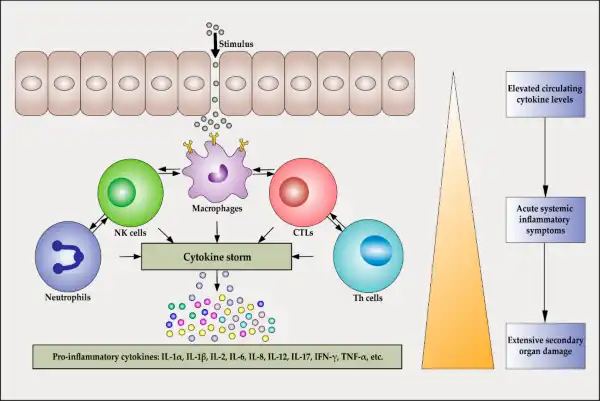
Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
Question 8:
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
A. Decrease in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus.
B. Increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
C. Decrease in the concentration of sodium in the blood.
D. Increase in the concentration of magnesium in the blood.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing an increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
The kidneys play a pivotal role in the regulation of electrolyte balance.
With progressive loss of kidney function, derangements in electrolytes inevitably occur and contribute to poor patient outcomes123.
Choice A is incorrect because calcium concentration is not regulated in the glomerulus.
Choice C is incorrect because chronic kidney disease can result in either an increase or decrease in sodium concentration in the blood.
Choice D is incorrect because chronic kidney disease does not necessarily result in an increase in magnesium concentration in the blood.
Question 9:
What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
The Correct Answer is C.Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Question 10:
During the menstrual cycle, which structure in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation?
A. Corpus luteum.
B. Fimbriae
C. Follicle
D. Ovarian ligament.
The Correct Answer is A.Corpus luteum.
During the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation.
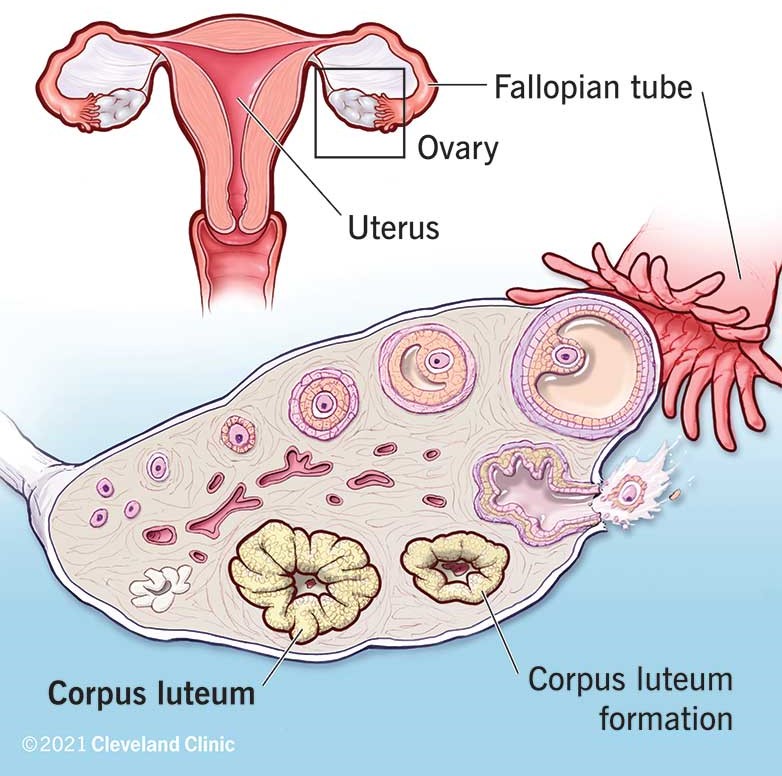
Choice B is incorrect because fimbriae are finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube.
Choice C is incorrect because a follicle is a sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Choice D is incorrect because the ovarian ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the uterus.