If a mother's____________ cell contains mutated DNA, this mutation can be passed to her offspring. Which of the following options correctly completes the sentence above?
A. somatic
B. white blood
C. germ.
D. Stem
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
The correct answer is c. germ. If a mother's germ cell contains mutated DNA, this mutation can be passed to her offspring. Germ cells are the reproductive cells (eggs in females and sperm in males) that carry genetic information from one generation to the next.
a. Somatic cells are all the other cells in the body that are not germ cells. Mutations in somatic cells are not passed on to offspring.
b.White blood cells are a type of somatic cell that plays a role in the immune system.
d. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the
body.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 3
Question 1:
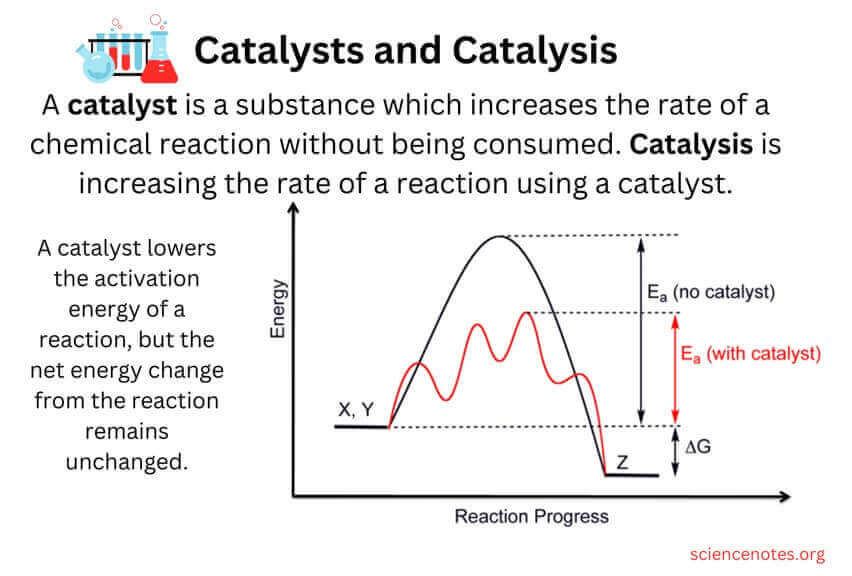
Which of the following best describes the result of using a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
A. A more desirable product is often formed.
B. The reaction is completed in a shorter amount of time.
C. A greater amount of heat energy is released by the reaction.
D. The yield of product is increased.
The Correct Answer is B.The result of using a catalyst in a chemical reaction is that the reaction is completed in a shorter amount of time ¹. A catalyst is a chemical substance that affects the rate of a chemical reaction by altering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed ¹. This process is called catalysis ¹. A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction, one that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed pathway .
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe the result of using a catalyst in a chemical reaction. A more desirable product is not necessarily formed, a greater amount of heat energy is not necessarily released by the reaction, and the yield of product is not necessarily increased as a result of using a catalyst.
Question 2:
If a mother's____________ cell contains mutated DNA, this mutation can be passed to her offspring. Which of the following options correctly completes the sentence above?
A. somatic
B. white blood
C. germ.
D. Stem
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is c. germ. If a mother's germ cell contains mutated DNA, this mutation can be passed to her offspring. Germ cells are the reproductive cells (eggs in females and sperm in males) that carry genetic information from one generation to the next.
a. Somatic cells are all the other cells in the body that are not germ cells. Mutations in somatic cells are not passed on to offspring.
b.White blood cells are a type of somatic cell that plays a role in the immune system.
d. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the
body.

Question 3:
Hikers who found a human body at high altitude in the Italian Alps thought the man had died recently, but tests indicated he was shot with an arrow more than 5,300 years ago. Which of the following would be the best reason for prolonged preservation of the body?
A. The ultraviolet rays at such a high altitude caused all his molecules to be preserved.
B. The food that the person ate contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body.
C. The body was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found.
D. The arrow wound caused blood to flow out of the body which led the enzymes that would break down tissue to be cleared from the body.
The Correct Answer is C.The best reason for the prolonged preservation of the body is that it was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after death and remained frozen until it was found. Freezing can preserve a body by slowing down or stopping the decomposition process.
The other options are not as likely to have caused prolonged preservation.
Ultraviolet rays can damage molecules rather than preserve them. Toxins in food would not necessarily kill all bacteria that could cause decomposition. Blood loss from an arrow wound would not necessarily clear all enzymes that could break down tissue.
Question 4:
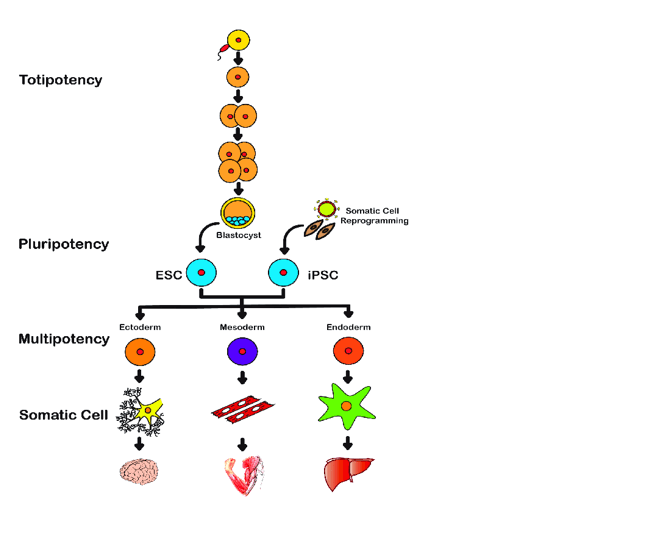
Which of the following is the function of a totipotent cell?
A. Develops into any kind of cell
B. Fights infectious diseases
C. Aids in the maturation of sex cells
D. Carries electrical impulses
The Correct Answer is A.The function of a totipotent cell is to develop into any kind of cell ¹. Totipotent cells have the capacity to produce all adult cell types and can enter the germ line, contributing genetic material to succeeding generations ?. They have the ability to self-replicate, producing daughter cells that are identical to the parent ?.
The other options are incorrect because they do not accurately describe the function of a totipotent cell. Fighting infectious diseases, aiding in the maturation of sex cells, and carrying electrical impulses are not functions performed by totipotent cells.
Question 5:
Which of the following ions binds to the troponin complex, initiating the contraction of a muscle?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Calcium
D. Phosphorus
The Correct Answer is C.When a muscle cell is stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm. The calcium ions bind to the troponin complex, which is a protein that regulates the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. The binding of calcium to troponin causes a conformational change that exposes the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments. This allows the myosin heads to attach to the actin and pull the filaments past each other, resulting in muscle contraction.
Question 6:
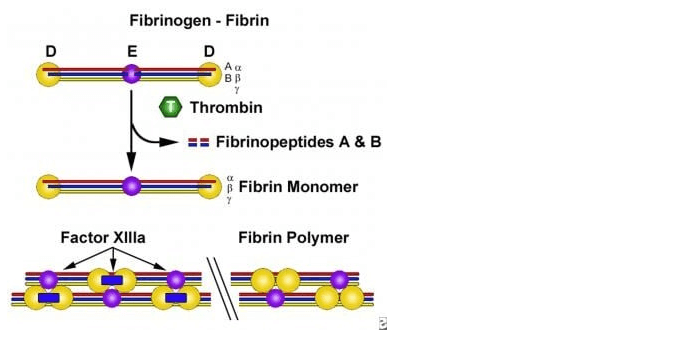
Which of the following is a protein present in blood plasma?
A. Monocytes
B. Platelets
C. Fibrinogen
D. Lymphocytes
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is c. Fibrinogen. Fibrinogen is a protein present in blood plasma that plays a key role in blood clotting. When an injury occurs and bleeding begins, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin, which forms a mesh-like structure that helps to trap blood cells and form a clot.
A. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell, not a protein present in blood plasma.
B. Platelets are cell fragments that play a role in blood clotting, but they are not a protein present in blood plasma.
D. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell, not a protein present in blood plasma.
Question 7:
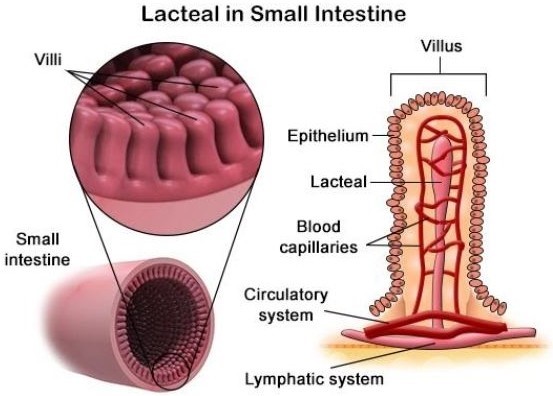
Lipids absorbed in the small intestine will first enter which of the following structures?
A. Veins
B. Arteries
C. Lacteal vessels
D. Interstitial spaces
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is c. Lacteal vessels. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine will first enter lacteal vessels, which are small lymphatic vessels located in the villi of the small intestine. These vessels transport the absorbed lipids to the lymphatic system, where they eventually enter the bloodstream.
a. Veins and b. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood throughout the body. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine do not directly enter these vessels.
d. Interstitial spaces are spaces between cells and tissues that contain interstitial fluid. Lipids absorbed in the small intestine do not directly enter these spaces.
Question 8:
Which of the following classes of biological molecules includes enzymes?
A. Lipids
B. Vitamins
C. Carbohydrates
D. Proteins
The Correct Answer is D.Enzymes are a type of protein that catalyze chemical reactions in the body. Proteins are one of the four main classes of biological molecules, along with lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
The other options are not classes of biological molecules that include enzymes. Lipids are a class of molecules that includes fats and oils, vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for normal growth and nutrition, and carbohydrates are a class of molecules that includes sugars and starches.
Question 9:
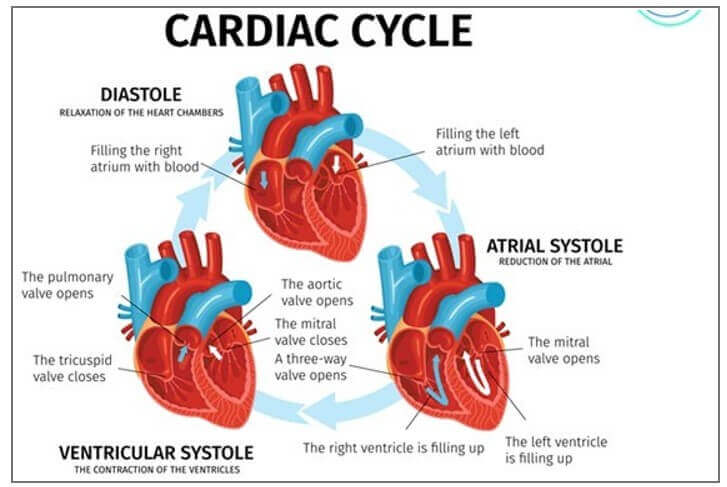
Which of the following terms describes the relaxation of the chambers of the heart during the cardiac cycle?
A. Tachycardia
B. Diastole
C. Systole
D. Bradycardia
The Correct Answer is B.The relaxation of the chambers of the heart during the cardiac cycle is called diastole ¹. The cardiac cycle is a sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats ². It consists of two phases: systole, when the heart contracts and pumps blood into circulation, and diastole, when the heart relaxes and fills with blood ².
The other options are not correct because they do not accurately describe the relaxation of the chambers of the heart during the cardiac cycle. Tachycardia is a rapid heart rate, bradycardia is a slow heart rate, and systole is the contraction of the heart chambers.
Question 10:
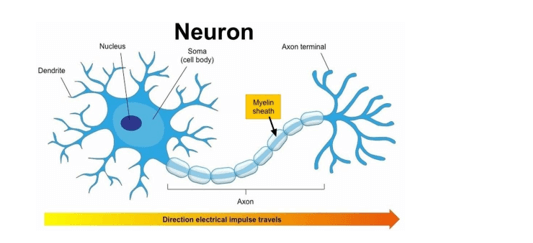
Which of the following functions does the myelin sheath perform for a nerve cell?
A. Insulation
B. Regeneration
C. Sensory perception
D. Nutrition
The Correct Answer is A.The myelin sheath is a protective membrane that wraps around parts of certain nerve cells.
Its fatty-protein coating provides protective insulation for your nerve cell like the plastic insulation covering that encases the wires of an electrical cord ².
This allows the electrical impulses to travel quickly and efficiently between one nerve cell and the next. The other options are incorrect because they do not describe the functions of the myelin sheath.
Regeneration, sensory perception, and nutrition are not functions performed by the myelin sheath for a nerve cell.