If a person was unable to break down food particles into molecules that could be absorbed by the body, you would predict
A. there is a malfunction with the digestive system
B. there is a malfunction with the excretory system
C. there is a malfunction with the reproductive system
D. there is a malfunction with the circulatory system
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
A) there is a malfunction with the digestive system
- Correct: Inability to break down food particles into molecules that can be absorbed by the body suggests a malfunction with the digestive system. The digestive system is responsible for the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller molecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, that can be absorbed by the intestines and utilized by the body for energy, growth, and repair. If the digestive system is not functioning properly, it can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, resulting in nutritional deficiencies and related health issues.
B) there is a malfunction with the excretory system
- Incorrect: The excretory system is responsible for removing waste products from the body, primarily through the kidneys, urinary tract, and skin. While the excretory system plays a role in eliminating some metabolic waste products generated from the breakdown of nutrients, it is not primarily responsible for the breakdown of food particles into absorbable molecules.
C) there is a malfunction with the reproductive system
- Incorrect: The reproductive system is responsible for the production of gametes (sperm and eggs) and the facilitation of reproduction. It is not directly involved in the breakdown and absorption of food particles in the digestive process.
D) there is a malfunction with the circulatory system
- Incorrect: The circulatory system, comprising the heart, blood vessels, and blood, is responsible for transporting nutrients, oxygen, and other substances throughout the body. While the circulatory system transports nutrients absorbed by the digestive system to various tissues and organs, it does not directly participate in the breakdown of food particles into absorbable molecules.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on Digestive System Practice Exam 1
Question 1:
Which process is represented by the diagram below?

A. emulsification
B. excretion
C. absorption
D. peristalsis
The Correct Answer is A.Emulsification is a process by which large fat globules are broken down into smaller droplets. This process is facilitated by substances called emulsifiers, with bile being one of the most common emulsifiers in the human body.
Question 2:
Which disorder would most directly interfere with the emulsification of fats?
A. bronchitis
B. gout
C. goiter
D. gallstones
The Correct Answer is D.D) gallstones
- Correct: Gallstones would most directly interfere with the emulsification of fats. Emulsification of fats is primarily facilitated by bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, often consisting of cholesterol or bilirubin. These stones can obstruct the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the small intestine, impairing the emulsification of fats and leading to difficulties in fat digestion and absorption. This obstruction can result in symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and indigestion.
A) bronchitis
- Incorrect: Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchial tubes in the lungs and does not directly interfere with the emulsification of fats in the digestive system.
B) gout
- Incorrect: Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, typically affecting the feet. It does not directly interfere with the emulsification of fats in the digestive system.
C) goiter
- Incorrect: Goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck, often due to iodine deficiency or thyroid disorders. It does not directly interfere with the emulsification of fats in the digestive system.
Question 3:
Which foods should be included in a balanced diet as a good source of roughage?
A. red meat and poultry
B. fresh fruits and vegetables
C. eggs and milk products
D. animal fat and plant oil
The Correct Answer is B.B) fresh fruits and vegetables
- Correct: Fresh fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of roughage, also known as dietary fiber. These foods provide insoluble fiber, soluble fiber, or a combination of both, which adds bulk to the stool and promotes healthy digestion. Insoluble fiber, found in foods like leafy greens, celery, and broccoli, helps to move food through the digestive tract, preventing constipation. Soluble fiber, found in foods like apples, oats, and beans, can help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels.
A) red meat and poultry
- Incorrect: While red meat and poultry are good sources of protein and other nutrients, they are not significant sources of dietary fiber or roughage. These foods do not contribute to the fiber content of the diet.
C) eggs and milk products
- Incorrect: Eggs and milk products are valuable sources of protein, vitamins, and minerals, but they are not significant sources of dietary fiber or roughage. These foods do not provide the fiber needed for healthy digestion.
D) animal fat and plant oil
- Incorrect: Animal fat and plant oils are sources of dietary fat, which is important for providing energy and essential fatty acids in the diet. However, they do not contain significant amounts of dietary fiber or roughage. These foods do not contribute to the fiber content of the diet.
Question 4:
In humans, chemical digestion is accomplished
A. by enzyme action that begins in the mouth and ends in the
B. esophagus
C. stomach
D. small intestine
The Correct Answer is C.C) small intestine
- Correct: Chemical digestion in humans is a complex process involving various enzymes acting on different nutrients. While digestion does begin in the mouth with the action of enzymes like salivary amylase on carbohydrates, the majority of chemical digestion occurs in the small intestine. Enzymes secreted by the pancreas (such as pancreatic amylase, lipase, and proteases) and the small intestine itself (such as maltase, sucrase, lactase, and peptidases) break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules. Additionally, bile salts produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder aid in the emulsification and digestion of fats in the small intestine. Therefore, chemical digestion largely concludes in the small intestine before nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
A) esophagus
- Incorrect: The esophagus is primarily involved in the mechanical process of swallowing, which pushes food down into the stomach. While some minor enzymatic activity may occur due to saliva coating the food during swallowing, significant chemical digestion does not occur in the esophagus.
B) stomach
- Incorrect: While the stomach does play a role in chemical digestion, particularly in the breakdown of proteins by the enzyme pepsin and the denaturation of proteins by hydrochloric acid, the majority of chemical digestion occurs in the small intestine. The stomach mainly serves to mechanically churn food and begin the process of protein digestion.
D) gallbladder
- Incorrect: The gallbladder stores and releases bile produced by the liver, which aids in the emulsification and digestion of fats in the small intestine. However, the gallbladder itself is not directly involved in chemical digestion, and the majority of digestive enzymes are not secreted or stored in the gallbladder.
Question 5:
Which structures secrete chemicals utilized for the completion of digestion within the small intestine?
A. liver and pancreas
B. glomerulus and villi
C. esophagus and alveoli
D. gallbladder and pharynx
The Correct Answer is A.A) liver and pancreas
- Correct: The liver and pancreas both secrete chemicals that are utilized for the completion of digestion within the small intestine. The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to aid in the emulsification and digestion of fats. The pancreas secretes pancreatic enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, and proteases) into the small intestine to further break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules that can be absorbed.
B) glomerulus and villi
- Incorrect: The glomerulus is a part of the kidney involved in the filtration of blood, and villi are finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption. While villi play a role in absorption within the small intestine, they do not secrete chemicals for digestion. The glomerulus is not involved in digestion.
C) esophagus and alveoli
- Incorrect: The esophagus is involved in swallowing and does not secrete chemicals for digestion. Alveoli are air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs during respiration and are not involved in digestion.
D) gallbladder and pharynx
- Incorrect: The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver but does not secrete chemicals directly into the small intestine. The pharynx is involved in swallowing and does not secrete chemicals for digestion.
Question 6:
In humans, structures that release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine include both the
A. salivary glands and the pancreas
B. gall bladder and the lacteals
C. villi and the salivary glands
D. pancreas and the gall bladder
The Correct Answer is D.D) pancreas and the gallbladder
- Correct: Both the pancreas and the gallbladder release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine. The pancreas secretes pancreatic enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, and proteases) into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver, which is released into the small intestine to aid in the emulsification and digestion of fats.
A) salivary glands and the pancreas
- Incorrect: While the pancreas releases digestive secretions directly into the small intestine, the salivary glands secrete saliva into the mouth, which contains enzymes (such as amylase) that begin the digestion of carbohydrates. Salivary glands do not release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine.
B) gall bladder and the lacteals
- Incorrect: The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver, which is released into the small intestine to aid in fat digestion. Lacteals are lymphatic vessels found in the villi of the small intestine and are involved in the absorption of fats, but they do not release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine.
C) villi and the salivary glands
- Incorrect: Villi are finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients but do not release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine. Salivary glands secrete saliva into the mouth to initiate the digestion of carbohydrates but do not release digestive secretions directly into the small intestine.
Question 7:
Hardened deposits of cholesterol that accumulate in the structure that stores bile are known as
A. gallstones
B. ulcers
C. goiters
D. allergies
The Correct Answer is A.A) gallstones
- Correct: Hardened deposits of cholesterol that accumulate in the structure that stores bile, which is the gallbladder, are known as gallstones. Gallstones can also contain other substances, such as bilirubin or calcium salts, in addition to cholesterol. These stones can vary in size and may cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. In severe cases, gallstones may require medical intervention, including surgery, to remove them.
B) ulcers
- Incorrect: Ulcers are sores or lesions that develop in the lining of the digestive tract, commonly in the stomach (gastric ulcers) or the upper part of the small intestine (duodenal ulcers). They are not related to hardened deposits of cholesterol in the gallbladder.
C) goiters
- Incorrect: Goiters are abnormal enlargements of the thyroid gland in the neck. They can be caused by iodine deficiency, thyroid disorders, or other factors, but they are not related to gallstones.
D) allergies
- Incorrect: Allergies are immune responses to specific substances (allergens) that the body perceives as harmful, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, itching, or anaphylaxis. They are not related to hardened deposits of cholesterol in the gallbladder.
Question 8:
Which of these nutrients is absorbed mainly in the duodenum?
A. glucose
B. iron
C. sodium
D. water
The Correct Answer is B.b) iron
- Correct: Iron is mainly absorbed in the duodenum, particularly in its proximal portion. Iron absorption occurs through active transport mechanisms facilitated by specialized transport proteins in the duodenal epithelial cells. Once absorbed, iron can be transported into the bloodstream and utilized for various physiological functions, including the production of hemoglobin and other iron-containing proteins.
a) glucose
- Incorrect: Glucose is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, but its absorption occurs mainly in the jejunum and ileum rather than the duodenum. Glucose is absorbed through facilitated diffusion and active transport mechanisms in the epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
c) sodium
- Incorrect: Sodium is absorbed throughout the small intestine, including the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Its absorption occurs through active transport mechanisms in the epithelial cells lining the intestinal mucosa, primarily in conjunction with glucose and other nutrients.
d) water
- Incorrect: Absorption of water indeed takes place in the large intestine, particularly in the colon.
Question 9:
What occurs during the digestion of proteins?
A. Specific enzymes break down proteins into amino acids.
B. Specific hormones break down proteins into simple sugars.
C. Specific hormones break down proteins into complex starches.
D. Specific enzymes break down proteins into simple sugars.
The Correct Answer is A.A) Specific enzymes break down proteins into amino acids.
- Correct: This is the correct answer. Proteins are broken down into their constituent amino acids by specific enzymes during the process of digestion. Enzymes like pepsin in the stomach and various proteases in the small intestine facilitate this breakdown.
B) Specific hormones break down proteins into simple sugars.
- Incorrect: Hormones are not directly involved in breaking down proteins into simple sugars. Hormones are signaling molecules that regulate various processes in the body, including metabolism, but they don't directly participate in the breakdown of proteins into sugars.
C) Specific hormones break down proteins into complex starches.
- Incorrect: Hormones do not break down proteins into complex starches. Proteins are broken down into amino acids by enzymes, not hormones. Starches are complex carbohydrates and are broken down into simple sugars by enzymes like amylase, not proteins.
D) Specific enzymes break down proteins into simple sugars.
- Incorrect: Proteins are not broken down into simple sugars. They are broken down into amino acids by specific enzymes. Simple sugars come from the breakdown of carbohydrates, not proteins.
Question 10:
Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below of some human digestive organs and on your knowledge of biology.
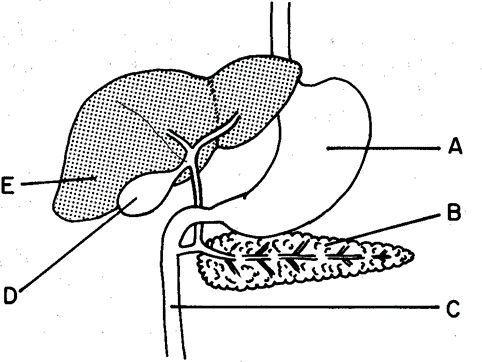
Which organ synthesizes both urea and bile?
A. A
B. E
C. C
D. D
The Correct Answer is B.The organ that synthesizes both urea and bile is the liver (E).
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolism and detoxification in the body. It synthesizes urea as a waste product of protein metabolism through the process of the urea cycle. Urea is then excreted by the kidneys in urine.
Additionally, the liver produces bile, a substance that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. Bile is synthesized in hepatocytes (liver cells) and then stored and concentrated in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine to emulsify fats.