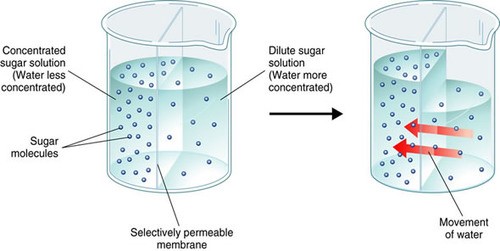
In a hypertonic solution, water flows through aquaporins embedded in the plasma membrane of the cell. This type of transport is best known as which of the following?
A. Facilitated diffusion
B. Active transport
C. Osmosis
D. Diffusion
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell, so water flows out of the cell through aquaporins embedded in the plasma membrane to balance the concentration gradient.
Choice A.
Facilitated diffusion is not correct because it is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of molecules across a membrane through specific transport proteins, but it does not specifically refer to the movement of water molecules.
Choice B.
Active transport is not correct because it is a type of transport that involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient and requires energy in the form of ATP, but osmosis is a passive process that does not require energy.
Choice D.
Diffusion is not correct because it refers to the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, but it does not specifically refer to the movement of water molecules.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 2
Question 1:
Which of the following represents the complementary strand of a DNA sequence 3' TCGATCGCA 5'?
A. 3' AGCTAGCGT 5'
B. 5’ AGCTAGCGT 3’
C. 5' UCGAUCGCA 3'
D. 3' TCGUTCGCU 3'
The Correct Answer is B.In DNA, the nitrogenous bases adenine (A) and thymine (T) pair together, while cytosine (C) and guanine (G) pair together.
Therefore, the complementary strand of the given DNA sequence 3' TCGATCGCA 5' would have the complementary nitrogenous bases as:
5’ AGCTAGCGT 3’
NOTE: The 5’ to 3’ direction of the complementary strand is opposite to that of the given strand.
Choice A.
3’ AGCTAGCGT 5’ is not correct because it is not complementary to the given strand.
Choice C.
5’ UCGAUCGCA 3’ is not correct because it contains uracil (U), which is a nitrogenous base found in RNA, not DNA.
Choice D.
3’ TCGUTCGCU 3’ is not correct because it also contains uracil (U), which is a nitrogenous base found in RNA, not DNA.
Question 2:
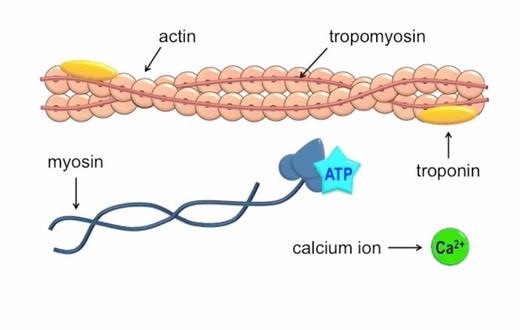
Which of the following ions binds to the troponin complex, initiating contraction of a muscle?
A. Potassium.
B. Calcium.
C. Phosphorus.
D. Sodium
The Correct Answer is B.Calcium ions play a crucial role in initiating muscle contraction.
When a muscle cell is stimulated to contract by an action potential, calcium channels open in the sarcoplasmic membrane and release calcium into the sarcoplasm.
Some of this calcium attaches to troponin, which causes it to change shape.
This shape change exposes binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
Myosin’s binding to actin causes crossbridge formation, and contraction of the muscle begins.
The other ions mentioned in the question do not have this specific role in muscle contraction.
Potassium ions are important for maintaining the resting membrane potential of cells, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Phosphorus ions are important for energy metabolism, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Sodium ions are important for generating action potentials, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Question 3:
In a plant in which fuzzy leaves (F) are dominant over smooth leaves (f), which of the following crosses will produce only offspring with smooth leaves?
A. FF x FF
B. Ff x Ff
C. ff x ff
D. Ff x ff
The Correct Answer is C.ff.
In this cross, both parents are homozygous recessive for the smooth leaf trait
(ff).
This means that all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the recessive allele (f) and will therefore have smooth leaves.
Choice A.
FF x FF is not correct because both parents are homozygous dominant for the fuzzy leaf trait (FF) and all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the dominant allele (F) and will therefore have fuzzy leaves.
Choice B.
Ff x Ff is not correct because both parents are heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) and their offspring can inherit either one dominant allele (F) or one recessive allele (f) from each parent, resulting in a 3:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves. Choice D.
Ff x ff is not correct because one parent is heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) while the other is homozygous recessive (ff), resulting in a 1:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves in their offspring.
Question 4:
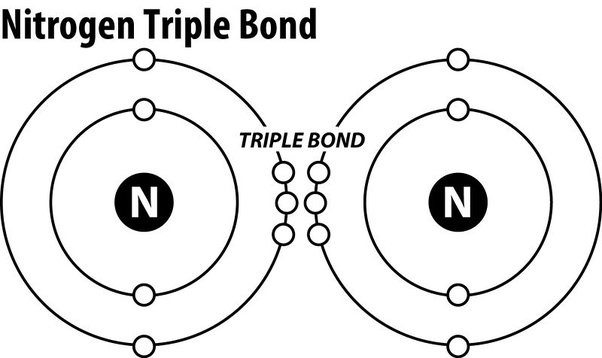
Nitrogen gas is an extremely stable molecule because of which of the following?
A. Ionic bonds
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Resonance bonds
D. Triple covalent bonds
The Correct Answer is D.Triple covalent bonds.
Nitrogen gas (N2) is an extremely stable molecule because it consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together by a triple covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons to form a molecule.
In a triple covalent bond, three pairs of electrons are shared between the two atoms, resulting in a very strong bond that makes the molecule extremely stable.
Choice A.
Ionic bonds is not correct because ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another to form ions, which are then attracted to each other due to their opposite charges.
Nitrogen gas does not contain ions and is not held together by ionic bonds.
Choice B.
Hydrogen bonds is not correct because hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between molecules that contain hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Nitrogen gas does not contain hydrogen atoms and is not held together by hydrogen bonds.
Choice C.
Resonance bonds is not correct because resonance refers to the delocalization of electrons in a molecule where multiple Lewis structures can be drawn to represent the molecule.
Nitrogen gas has a single Lewis structure and does not exhibit resonance.
Question 5:
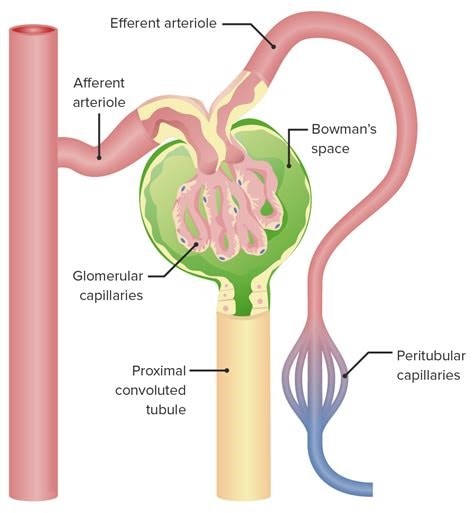
Which of the following is the structure through which blood exits the glomerulus?
A. Efferent arteriole
B. Proximal tubule
C. Distal tubule
D. Afferent arteriole
The Correct Answer is A.The glomerulus is the main filtering unit of the kidney.
It is formed by a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) enclosed within a sac called the Bowman’s capsule.
The blood supply to the glomerulus is provided via the afferent arteriole.
The blood then flows through the capillary network, where it gets filtered, and then leaves the glomerulus via the efferent arteriole.
Choice B.
Proximal tubule is not correct because it is where the ultrafiltrate collected in the Bowman’s space drains directly into.
Choice C.
Distal tubule is not correct because it is not mentioned in relation to blood exiting the glomerulus.
Choice D.
Afferent arteriole is not correct because it provides blood supply to the glomerulus.
Question 6:
Which of the following microorganisms lack their own metabolic pathways and can only reproduce inside of a host cell?
A. Bacteria
B. Protozoa
C. Helminths
D. Viruses
The Correct Answer is D.Viruses.
Viruses lack essential machinery needed to reproduce by themselves.
In fact, viruses can only reproduce after infecting a living cell - a process called viral replication.
Once inside a living cell, viruses re-program the cell’s machinery to produce viral proteins and genetic material to make new copies of themselves.
Choice A, Bacteria, is not the correct answer because bacteria have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice B, Protozoa, is also not the correct answer because protozoa are singlecelled eukaryotes that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice C, Helminths, is not the correct answer because helminths are multicellular parasitic worms that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Question 7:
In the following data table of an experiment carried out at 4°C (39.2 F) over 4 hours
|
Solution in bag |
Solution outside bag |
Bag mass change (g): |
|
water |
Water |
-0.2 |
|
20% sucrose |
Water |
+2.4 |
|
, 40% sucrose |
Water |
+4.3 |
|
, 60% sucrose |
water |
+5.8 |
Which of the following options represents the dependent variable?
A. Duration
B. Temperature
C. Bag mass change
D. Solution used outside
The Correct Answer is C.Bag mass change is the dependent variable in this experiment.
In an experiment, the dependent variable is the variable that is being measured and is expected to change in response to changes in the independent variable(s).
In this case, the bag mass change is being measured and is expected to change in response to changes in the independent variable (sucrose concentration).
Choice A is incorrect because duration is not a variable in this experiment.
Choice B is incorrect because temperature is not a variable in this experiment.
Choice D is incorrect because sucrose concentration is an independent variable, not a dependent variable.
An independent variable is a variable that is manipulated by the experimenter to see how it affects the dependent
Question 8:
Which of the following allows the AIDS virus, which contains RNA, to insert viral DNA into the DNA of a host cell after the AIDS virus enters the cell?
A. The phospholipids found on the envelope of the virus.
B. Reverse transcriptase, an enzyme encoded by the virus.
C. Receptor proteins located on the surface of the virus.
D. The protein that makes up the capsid of the virus.
The Correct Answer is B.Reverse transcriptase, an enzyme encoded by the virus.
Reverse transcriptase is a virus-specific enzyme that transcribes an RNA template to DNA1.
This allows the AIDS virus, which contains RNA, to insert viral DNA into the DNA of a host cell after the AIDS virus enters the cell.
Choice A, The phospholipids found on the envelope of the virus, is not the correct answer because phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and do not play a direct role in inserting viral DNA into the DNA of a host cell.
Choice C, Receptor proteins located on the surface of the virus, is not the correct answer because receptor proteins located on the surface of the virus play a role in attachment and fusion of HIV virons to host cells, but do not play a direct role in inserting viral DNA into the DNA of a host cell.
Choice D, The protein that makes up the capsid of the virus, is not the correct answer because capsid is the outer protein shell of a virus and does not play a direct role in inserting viral DNA into the DNA of a host cell.
Question 9:
Which of the following is the function of a totipotent cell?
A. Fights infectious diseases.
B. Aids in the maturation of sex cells.
C. Carries electrical impulses.
D. Develops into any kind of cell.
The Correct Answer is D.A totipotent cell can self-renew by dividing and develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo and into extra-embryonic tissues such as the placenta.
A fertilized egg is a totipotent stem cell and as such can develop into any specialized cell found in the organism.
Choice A is not correct because totipotent cells do not fight infectious diseases.
Choice B is not correct because totipotent cells do not aid in the maturation of sex cells.
Choice C is not correct because totipotent cells do not carry electrical impulses.
Question 10:
Which of the following structures is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Cell membrane
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Chloroplasts
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The cell membrane is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment.
It is composed of a lipid bilayer and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
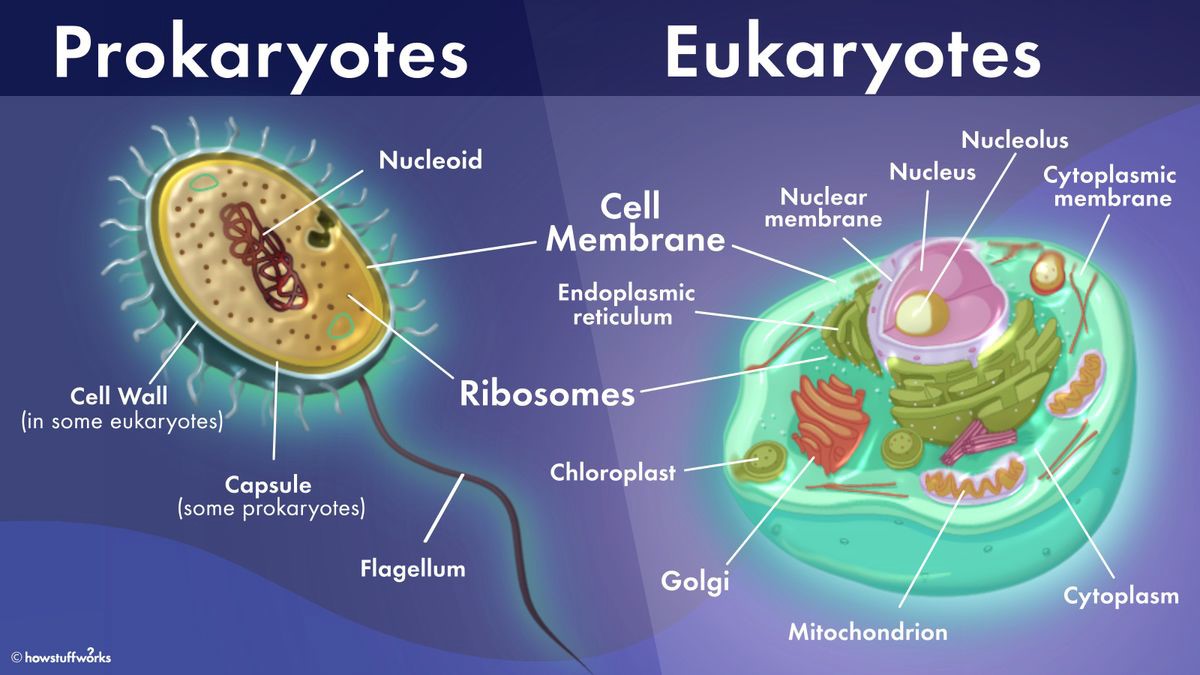
Choice B is incorrect because the Golgi apparatus is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to other parts of the cell or to be secreted outside the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because chloroplasts are not present in prokaryotic cells.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae that are responsible for photosynthesis.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.