In a plant in which fuzzy leaves (F) are dominant over smooth leaves (f), which of the following crosses will produce only offspring with smooth leaves?
A. FF x FF
B. Ff x Ff
C. ff x ff
D. Ff x ff
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
ff.
In this cross, both parents are homozygous recessive for the smooth leaf trait
(ff).
This means that all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the recessive allele (f) and will therefore have smooth leaves.
Choice A.
FF x FF is not correct because both parents are homozygous dominant for the fuzzy leaf trait (FF) and all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the dominant allele (F) and will therefore have fuzzy leaves.
Choice B.
Ff x Ff is not correct because both parents are heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) and their offspring can inherit either one dominant allele (F) or one recessive allele (f) from each parent, resulting in a 3:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves. Choice D.
Ff x ff is not correct because one parent is heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) while the other is homozygous recessive (ff), resulting in a 1:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves in their offspring.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 2
Question 1:
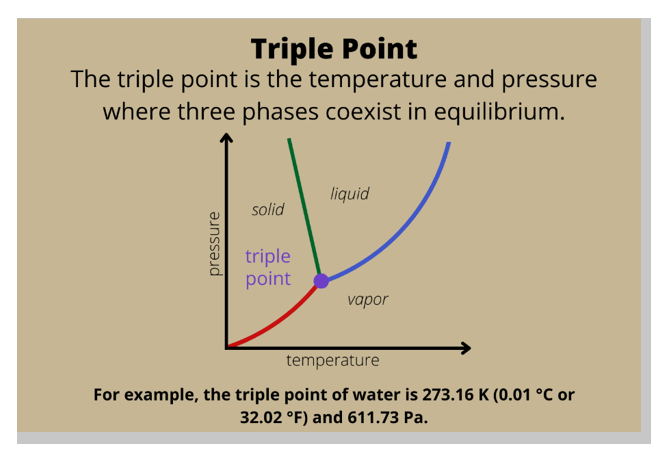
In a phase diagram, which of the following is the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously?
A. Triple point
B. Critical temperature
C. Critical point
D. Absolute zero
The Correct Answer is A.Triple point.
In a phase diagram, the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously is the triple point.
The triple point is a unique point on a phase diagram where the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) can coexist in equilibrium.
At the triple point, the temperature and pressure of the substance are fixed.
Option B, critical temperature, is the temperature at which a gas cannot be liquefied, regardless of the pressure applied.
It is a characteristic property of a substance and is typically higher than the boiling point of the liquid at standard pressure.
Option C, critical point, is the point on a phase diagram where the liquid and gas phases of a substance become indistinguishable.
At the critical point, the distinction between the liquid and gas phases disappears, and the substance becomes a supercritical fluid.
Option D, absolute zero, is the theoretical temperature at which all matter has zero thermal energy.
At absolute zero, all substances are in their solid state, but it is not relevant to a phase diagram, as it is a temperature where no transitions between states occur.
In summary, the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously in a phase diagram is the triple point, whereas the other options provided are not relevant or are characteristic properties of substances in different contexts.
Question 2:
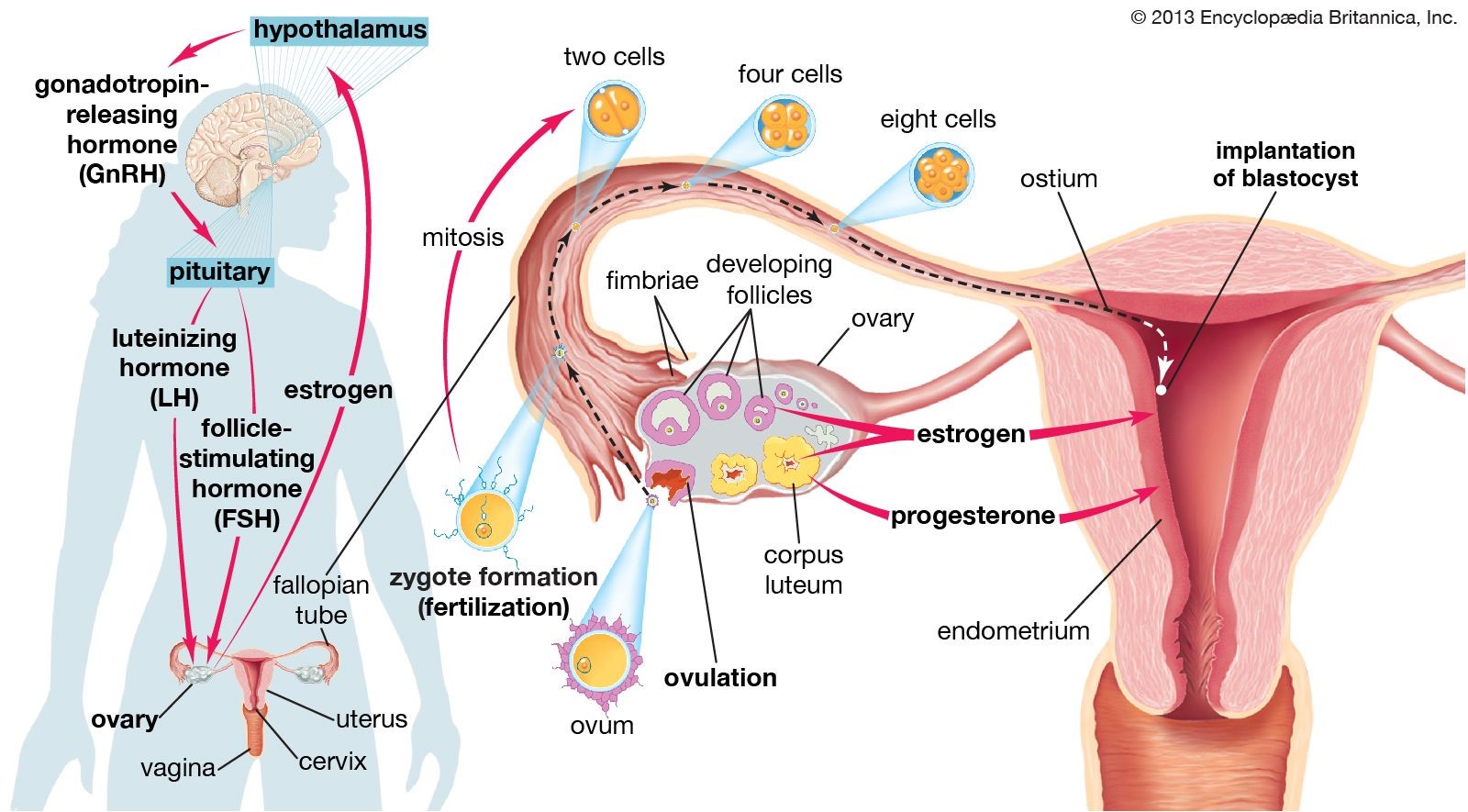
Which of the following is the process in which an ovarian follicle matures and releases a reproductive egg?
A. Menstruation
B. Fertilization
C. Ovulation
D. Oogenesis
The Correct Answer is C.Ovulation is the process in which an ovarian follicle matures and releases a reproductive egg.
During ovulation, a mature egg is released from the female ovary, enabling it to be fertilized by male sperm cells 1.
Choice A is incorrect because menstruation is the process of shedding the uterine lining, which occurs when an egg is not fertilized.
Choice B is incorrect because fertilization is the process of a sperm cell joining with an egg cell to form a zygote.
Choice D is incorrect because oogenesis is the process of forming female gametes (eggs) in the ovaries.
Question 3:
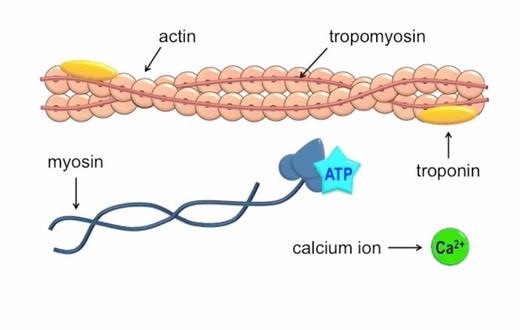
Which of the following ions binds to the troponin complex, initiating contraction of a muscle?
A. Potassium.
B. Calcium.
C. Phosphorus.
D. Sodium
The Correct Answer is B.Calcium ions play a crucial role in initiating muscle contraction.
When a muscle cell is stimulated to contract by an action potential, calcium channels open in the sarcoplasmic membrane and release calcium into the sarcoplasm.
Some of this calcium attaches to troponin, which causes it to change shape.
This shape change exposes binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
Myosin’s binding to actin causes crossbridge formation, and contraction of the muscle begins.
The other ions mentioned in the question do not have this specific role in muscle contraction.
Potassium ions are important for maintaining the resting membrane potential of cells, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Phosphorus ions are important for energy metabolism, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Sodium ions are important for generating action potentials, but they do not bind to the troponin complex.
Question 4:
Which of the following statements best supports the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer?
A. Cancerous and normal cells share genetic sequences
B. Cellular DNA has sequences related to viral sequences
C. Viruses and cancer cells both replicate rapidly.
D. Genes that regulate cell division are found in some viruses
The Correct Answer is D.Genes that regulate cell division are found in some viruses.
When viruses cause an infection, they spread their DNA, affecting healthy cells’ genetic makeup and potentially causing them to turn into cancer.
For instance, HPV infections cause the virus’ DNA to combine with the host’s DNA, disrupting the normal function of cells.
Choice A is not correct because cancerous and normal cells sharing genetic sequences does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Choice B is not correct because cellular DNA having sequences related to viral sequences does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Choice C is not correct because viruses and cancer cells both replicating rapidly does not support the hypothesis that viruses can cause cancer.
Question 5:
Hikers who found a human body at high altitude in the Italian Alps thought the man had died recently, but tests indicated he was shot with an arrow more than 5,300 years ago.
Which of the following would be the best reason for prolonged preservation of the body? .
A. The food that the person ate contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body
B. The arrow wound caused blood to flow out of the body, which led the enzymes that would break down tissue to be cleared from the body
C. The body was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found
D. The ultraviolet rays at such a high altitude caused all the body's molecules to be preserved.
The Correct Answer is C.The best reason for the prolonged preservation of the body is that it was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found.
Freezing can preserve a body by slowing down or stopping the decomposition process.
Choice A is not correct because the food that the person ate would not have contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body.
Choice B is not correct because the arrow wound would not have caused blood to flow out of the body in a way that would have cleared enzymes that break down tissue from the body.
Choice D is not correct because ultraviolet rays at high altitude would not have caused all of the body’s molecules to be preserved.
Question 6:
Which of the following is the main function of centrosomes in animal cells?
A. . Organelle trafficking.
B. Pathogen digestion.
C. Cytoplasm formation
D. Microtubule organization
The Correct Answer is D.Microtubule organization.
Centrosomes are organelles that serve as the main microtubule-organizing centers for animal cells.
They regulate the movement of microtubules and other cytoskeletal structures, thereby facilitating changes in the shapes of the membranes of animal cells.
Choice A, Organelle trafficking, is not the correct answer because while centrosomes do play a role in intracellular trafficking during interphase by organizing an astral ray of microtubules, their main function is microtubule organization.
Choice B, Pathogen digestion, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in pathogen digestion.
Choice C, Cytoplasm formation, is not the correct answer because centrosomes do not play a direct role in cytoplasm formation.
Question 7:
Which of the following organic molecules contain both an amine and carboxyl group?
A. Lipids
B. Chitin
C. Cellulose
D. Proteins
The Correct Answer is D.Proteins.
Proteins are made up of amino acids which are organic molecules that contain both an amine functional group (–NH2) and a carboxylic acid functional group (– COOH).
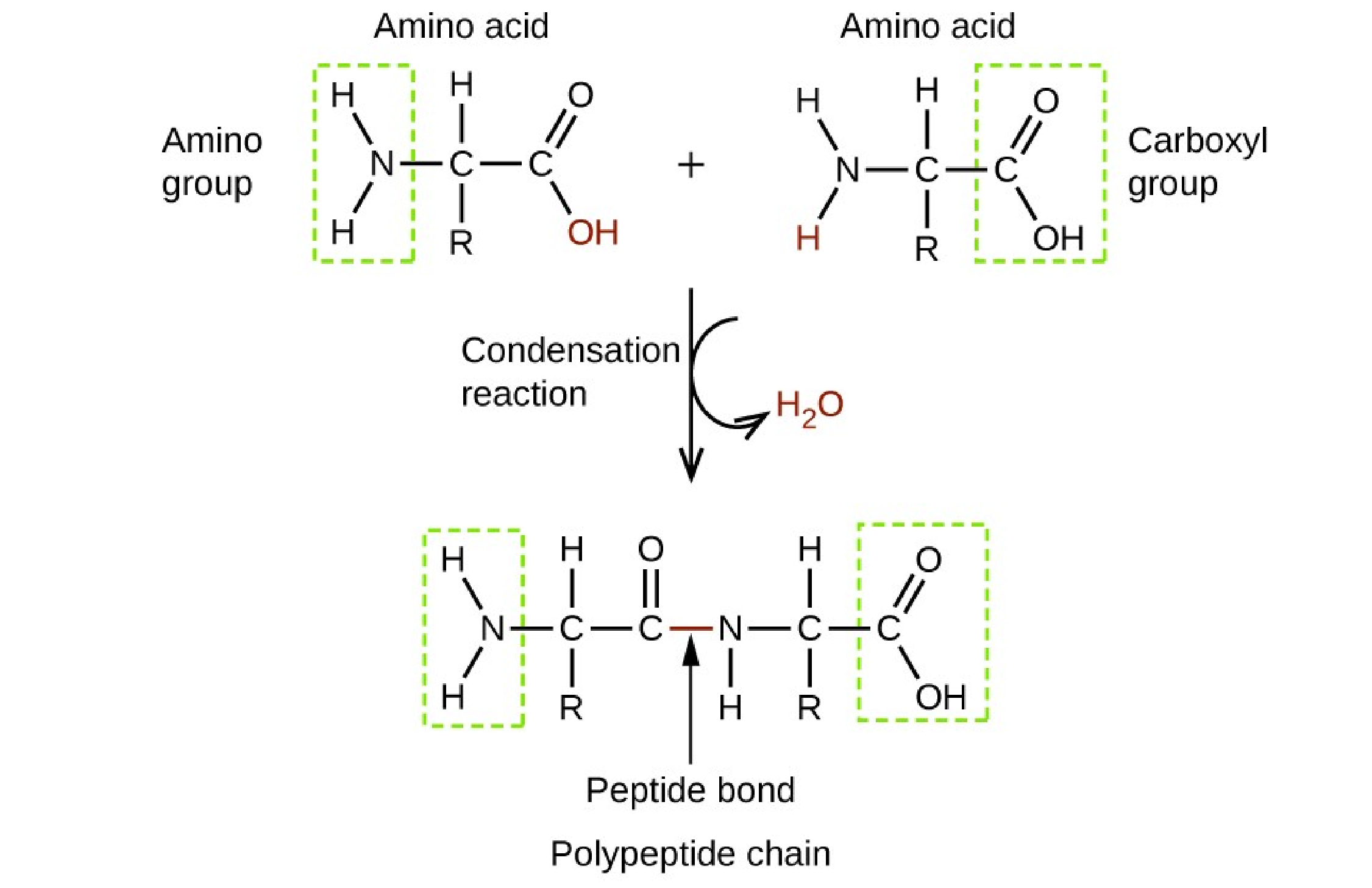 |
Choice A, Lipids, is not the correct answer because lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others.
They do not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice B, Chitin, is not the correct answer because chitin is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice C, Cellulose, is not the correct answer because cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C6H10O5)n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Question 8:
Which of the following structures is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Cell membrane
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Chloroplasts
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The cell membrane is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment.
It is composed of a lipid bilayer and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
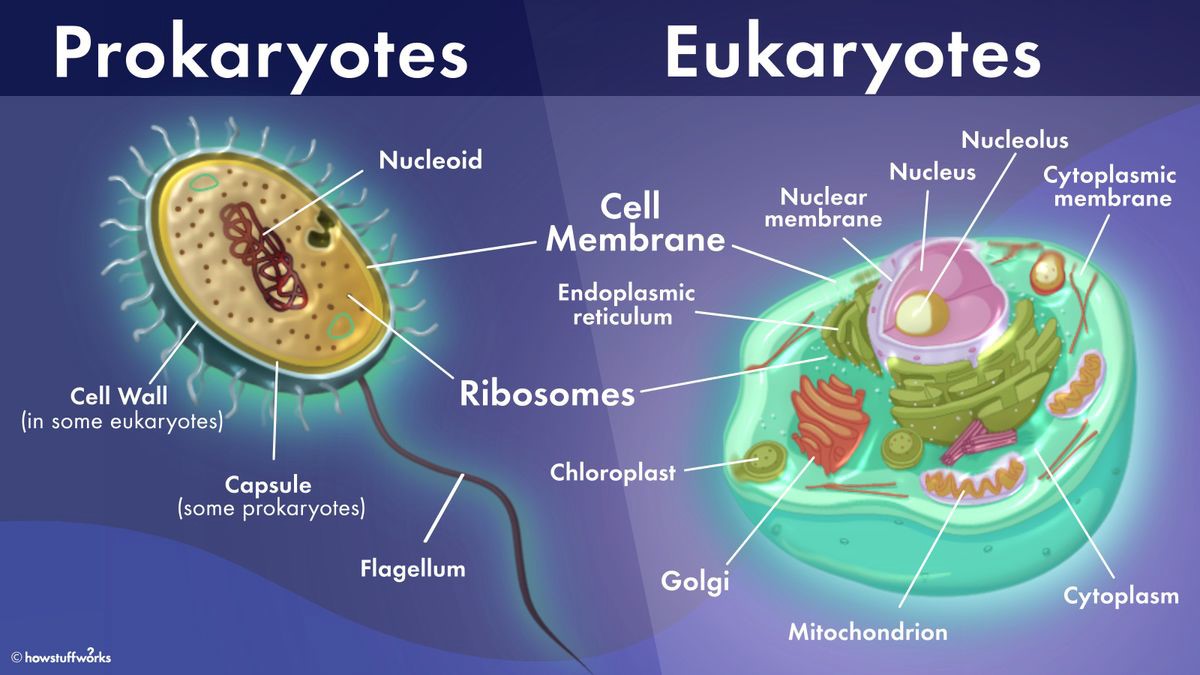
Choice B is incorrect because the Golgi apparatus is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to other parts of the cell or to be secreted outside the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because chloroplasts are not present in prokaryotic cells.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae that are responsible for photosynthesis.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
Question 9:
Which of the following microorganisms lack their own metabolic pathways and can only reproduce inside of a host cell?
A. Bacteria
B. Protozoa
C. Helminths
D. Viruses
The Correct Answer is D.Viruses.
Viruses lack essential machinery needed to reproduce by themselves.
In fact, viruses can only reproduce after infecting a living cell - a process called viral replication.
Once inside a living cell, viruses re-program the cell’s machinery to produce viral proteins and genetic material to make new copies of themselves.
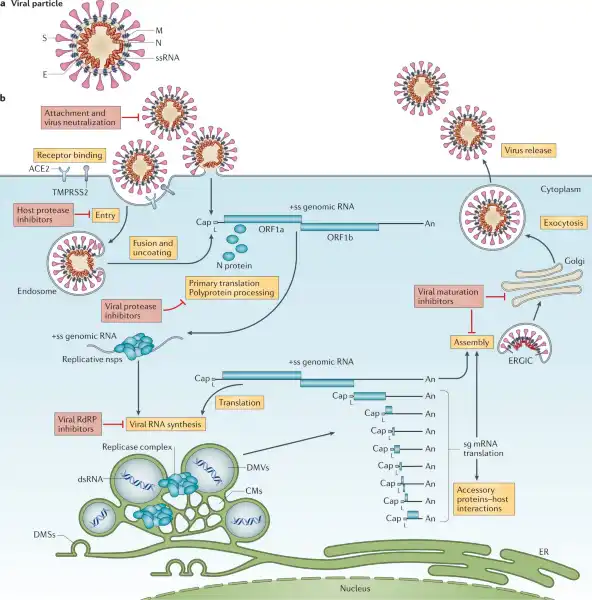
Choice A, Bacteria, is not the correct answer because bacteria have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice B, Protozoa, is also not the correct answer because protozoa are singlecelled eukaryotes that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice C, Helminths, is not the correct answer because helminths are multicellular parasitic worms that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Question 10:
Nitrogen gas is an extremely stable molecule because of which of the following?
A. Ionic bonds
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Resonance bonds
D. Triple covalent bonds
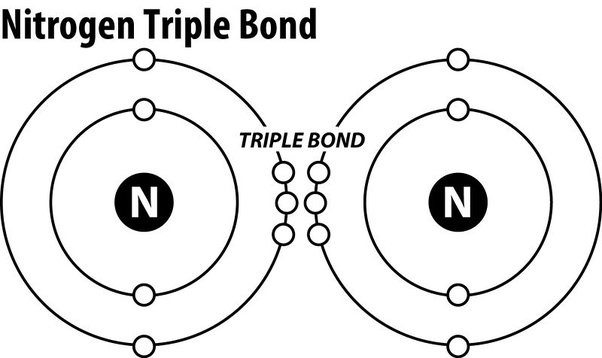
The Correct Answer is D.Triple covalent bonds.
Nitrogen gas (N2) is an extremely stable molecule because it consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together by a triple covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons to form a molecule.
In a triple covalent bond, three pairs of electrons are shared between the two atoms, resulting in a very strong bond that makes the molecule extremely stable.
Choice A.
Ionic bonds is not correct because ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another to form ions, which are then attracted to each other due to their opposite charges.
Nitrogen gas does not contain ions and is not held together by ionic bonds.
Choice B.
Hydrogen bonds is not correct because hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between molecules that contain hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Nitrogen gas does not contain hydrogen atoms and is not held together by hydrogen bonds.
Choice C.
Resonance bonds is not correct because resonance refers to the delocalization of electrons in a molecule where multiple Lewis structures can be drawn to represent the molecule.
Nitrogen gas has a single Lewis structure and does not exhibit resonance.