In which state of matter do the particles of iron have the lowest amount of cohesion?
A. Solid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
B. Liquid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
C. Gaseous iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
D. The particles have the same amount of cohesion in all states of matter.
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 2
Question 1:
What organelle is only associated with plant cells?
A. Cell wall
B. Ribosome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Golgi apparatus
The Correct Answer is A.Only plant cells have cell walls, which help protect the cell and provide structural support. The cell wall also enforces the overall structural integrity of the plant cell, and it is found outside the cell membrane. The next organelle is a chloroplast. It is found in the cytoplasm of only plant cells. Chloroplasts are photosynthetic compounds used to make food for plant cells by harnessing energy from the sun. These organelles play a role in photosynthesis.
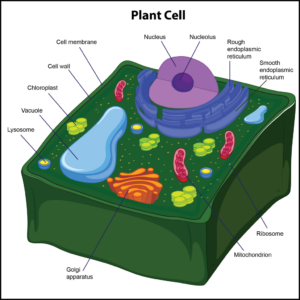
Question 2:
Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
The Correct Answer is A.The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
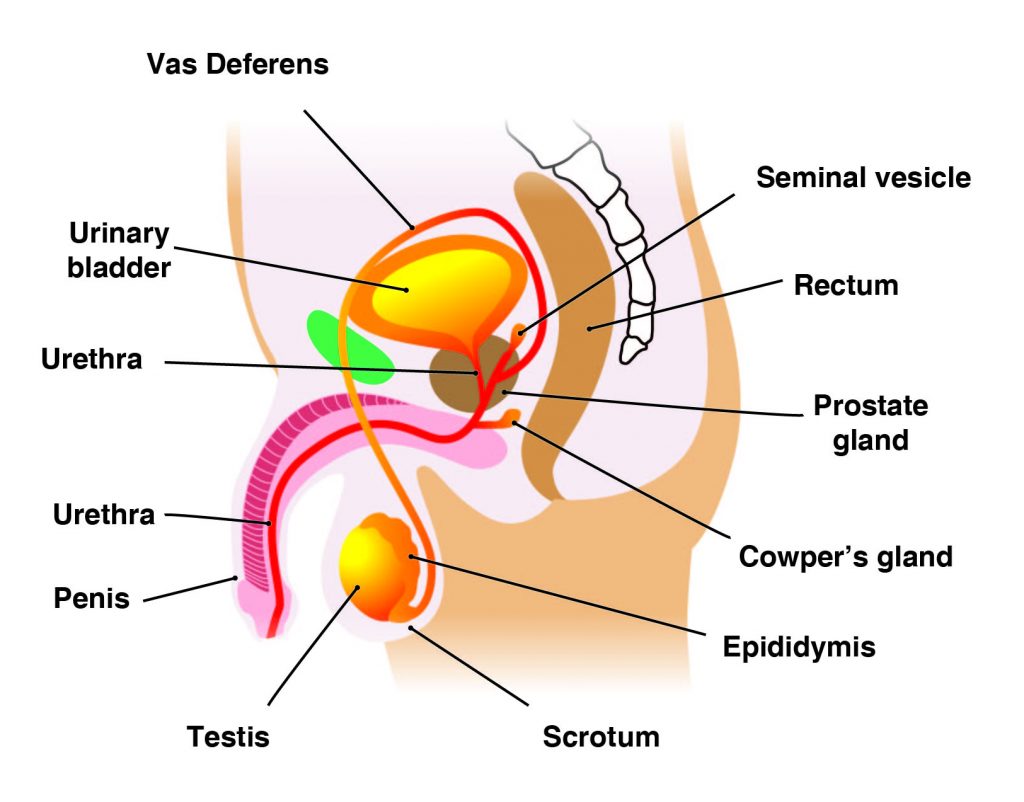
Question 3:
Which part of the digestive system comes before the stomach?
A. mouth
B. esophagus
C. ileum
D. colon
The Correct Answer is B.Oral Cavity is the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestine is about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colon is about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
Question 4:
Fertilization (the fusing of one sperm and an ovum) results in a(n) _____.
A. embryo
B. fetus
C. infant
D. zygote
The Correct Answer is D.Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating a zygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Question 5:
Where is skeletal muscle found?
A. Inside the heart
B. Attached to bone
C. Lining the walls of the bladder
D. Within the gastrointestinal tract
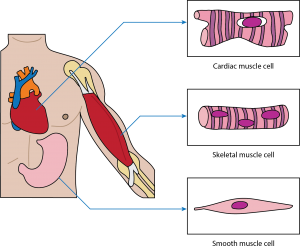
The Correct Answer is B.Skeletal muscle: This muscle cell is striated, long, and cylindrical. There are many nuclei in a skeletal muscle cell. Attached to bones in the body, skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily, meaning that it is under conscious control.
Smooth muscle: This muscle consists of nonstriated muscle cells that are spindle-shaped. Like cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contain one nucleus. This muscle type is found in the walls of internal organs like the bladder and stomach. Smooth muscle contraction is involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle: This muscle consists of muscle cells that are striated, short, and branched. These cells contain one nucleus, are branched, and are rectangular. Cardiac muscle contraction is an involuntary process, which is why it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. This muscle is found in the walls of the heart.
Question 6:
In which state of matter do the particles of iron have the lowest amount of cohesion?
A. Solid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
B. Liquid iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
C. Gaseous iron particles have the lowest amount of cohesion
D. The particles have the same amount of cohesion in all states of matter.
The Correct Answer is C.The particles in a sample of gas are farther apart than in solids or liquids and therefore have the lowest amount of cohesion.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Question 7:
Blood oxygen levels are most likely low when blood _____.
A. leaves the aorta
B. fills the right atrium
C. reaches body tissues
D. flows through arteries
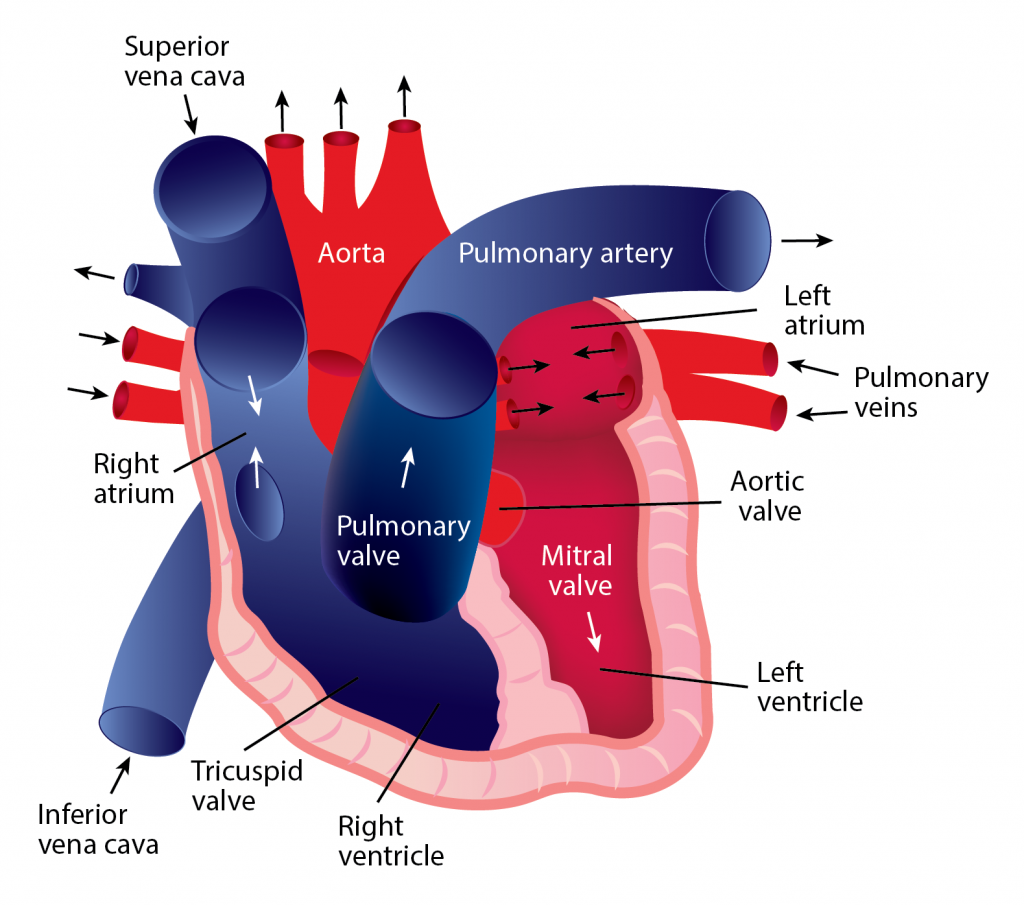
The Correct Answer is B.Blood continually flows in one direction, beginning in the heart and proceeding to the arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. When blood reaches the capillaries, exchanges occur between blood and tissues. After this exchange happens, blood is collected into venules, which feed into veins and eventually flow back to the heart’s atrium. The heart must relax between two heartbeats for blood circulation to begin.
Two types of circulatory processes occur in the body:
Systemic circulation
- The pulmonary vein pushes oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
- As the atrium relaxes, oxygenated blood drains into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. 3. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- Blood travels through the arteries and arterioles before reaching the capillaries that surround the tissues.
Pulmonary circulation
- Two major veins, the Superior Vena Cava and the Inferior Vena Cava, brings deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower half of the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is pooled into the right atrium and then sent into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, which prevents blood from flowing backward.
- The right ventricle contracts, causing the blood to be pushed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Question 8:
Which is classified as a type of acid-base reaction that produces a salt?
A. Combination
B. Decomposition
C. Hydrolysis
D. Neutralization
The Correct Answer is D.A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes, neutralization reactions also occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as an ionic compound that includes any cation except H+ and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
Question 9:
A spoonful of sugar is added to a hot cup of tea. All the sugar dissolves. How can the resulting solution be described?
A. Saturated and homogeneous
B. Saturated and heterogeneous
C. Unsaturated and homogeneous
D. Unsaturated and heterogeneous
The Correct Answer is C.Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- A mixture is when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- A homogeneous mixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. A heterogeneous mixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. An unsaturated solution has the ability to dissolve more solute and a saturated solution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
Question 10:
What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
The Correct Answer is D.The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.