To separate genomic DNA fragments by size, which of these laboratory methods is most useful?
A. Titration
B. Electrophoresis
C. Filtration
D. Spectrophotometry
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Electrophoresis is the most useful laboratory method for separating genomic DNA fragments by size.
Electrophoresis is a technique that uses an electric field to separate charged molecules, such as DNA fragments, based on their size and charge.
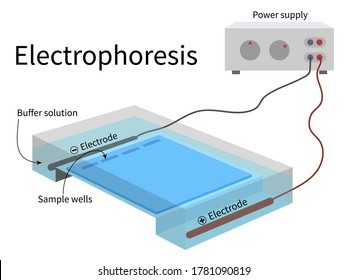
Choice A is not correct because titration is a laboratory method used to determine the concentration of a solution.
Choice C is not correct because filtration is a laboratory method used to separate solids from liquids.
Choice D is not correct because spectrophotometry is a laboratory method used to measure the absorbance of light by a solution.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 2
Question 1:
Which of the following processes causes most of the carbon dioxide from the blood to move into the alveoli?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Diffusion down a concentration gradient.
C. Passive transport using carrier proteins.
D. Active transport using energy.
The Correct Answer is B.Diffusion down a concentration gradient causes most of the carbon dioxide from the blood to move into the alveoli.
The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration and is carried by the blood to the lungs to be exhaled.
In the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood (where its concentration is high) into the alveoli (where its concentration is lower) down its concentration gradient.
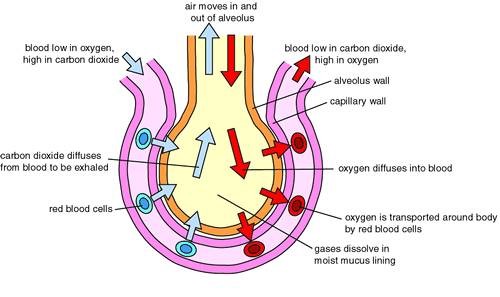
Choice A is incorrect because carbon dioxide is not converted to carbon monoxide in the body.
Choice C is incorrect because passive transport using carrier proteins is not the primary mechanism by which carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
Choice D is incorrect because active transport using energy is not involved in the movement of carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli.
Question 2:
Which of the following substances protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation?
A. Melanin
B. Perspiration
C. Sebum
D. Keratin
The Correct Answer is A.Melanin.
Melanin is a pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in the skin.
It protects the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation by absorbing and dissipating over 99.9% of absorbed UV radiation.
This helps to prevent DNA damage and other adverse effects of UV radiation on the skin.
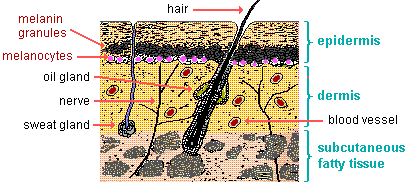
Choice B.
Perspiration is not correct because it is a fluid produced by sweat glands in the skin that helps to regulate body temperature, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
Choice C.
Sebum is not correct because it is an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands in the skin that helps to lubricate and protect the skin, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
Choice D.
Keratin is not correct because it is a fibrous protein that provides strength and durability to the skin, hair and nails, but it does not protect the skin from UV radiation.
Question 3:
In a phase diagram, which of the following is the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously?
A. Triple point
B. Critical temperature
C. Critical point
D. Absolute zero
The Correct Answer is A.Triple point.
In a phase diagram, the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously is the triple point.
The triple point is a unique point on a phase diagram where the three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) can coexist in equilibrium.
At the triple point, the temperature and pressure of the substance are fixed.
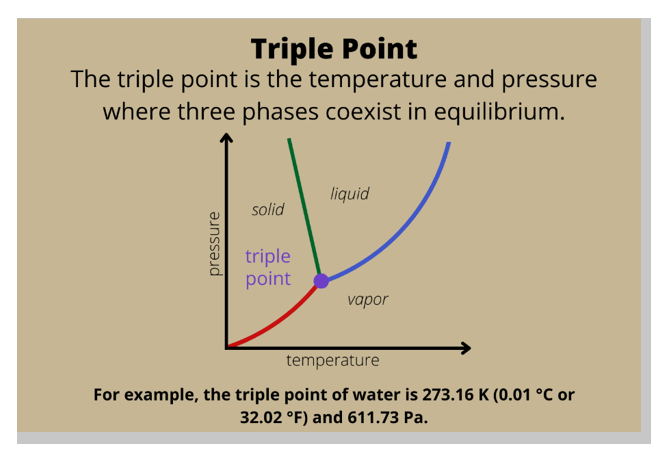
Option B, critical temperature, is the temperature at which a gas cannot be liquefied, regardless of the pressure applied.
It is a characteristic property of a substance and is typically higher than the boiling point of the liquid at standard pressure.
Option C, critical point, is the point on a phase diagram where the liquid and gas phases of a substance become indistinguishable.
At the critical point, the distinction between the liquid and gas phases disappears, and the substance becomes a supercritical fluid.
Option D, absolute zero, is the theoretical temperature at which all matter has zero thermal energy.
At absolute zero, all substances are in their solid state, but it is not relevant to a phase diagram, as it is a temperature where no transitions between states occur.
In summary, the term used for a substance held at a temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance exist simultaneously in a phase diagram is the triple point, whereas the other options provided are not relevant or are characteristic properties of substances in different contexts.
Question 4:
Which of the following summarizes a change that takes place as a solid turns to a liquid?
A. Particles become less ordered.
B. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
C. Particles move closer together
D. Intermolecular forces between particles become stronger.
The Correct Answer is A.As a solid turns to a liquid, the particles become less ordered and more free to move around.
Choice B is not correct because particles have an increase in mobility as a solid turns to a liquid.
Choice C is not correct because particles move further apart as a solid turns to a liquid.
Choice D is not correct because intermolecular forces between particles become weaker as a solid turns to a liquid.
Question 5:
Nitrogen gas is an extremely stable molecule because of which of the following?
A. Ionic bonds
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Resonance bonds
D. Triple covalent bonds
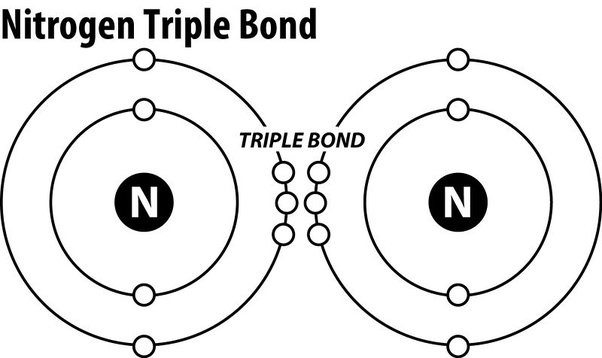
The Correct Answer is D.Triple covalent bonds.
Nitrogen gas (N2) is an extremely stable molecule because it consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together by a triple covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons to form a molecule.
In a triple covalent bond, three pairs of electrons are shared between the two atoms, resulting in a very strong bond that makes the molecule extremely stable.
Choice A.
Ionic bonds is not correct because ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another to form ions, which are then attracted to each other due to their opposite charges.
Nitrogen gas does not contain ions and is not held together by ionic bonds.
Choice B.
Hydrogen bonds is not correct because hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between molecules that contain hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Nitrogen gas does not contain hydrogen atoms and is not held together by hydrogen bonds.
Choice C.
Resonance bonds is not correct because resonance refers to the delocalization of electrons in a molecule where multiple Lewis structures can be drawn to represent the molecule.
Nitrogen gas has a single Lewis structure and does not exhibit resonance.
Question 6:
Which of the following best describes the result of using a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
A. The reaction is completed in a shorter amount of time
B. A more desirable product is often formed
C. A greater amount of heat energy is released by the reaction
D. The yield of product is increased
The Correct Answer is A.A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
As a result, the reaction is completed in a shorter amount of time.
Choice B is not correct because using a catalyst does not necessarily result in the formation of a more desirable product.
Choice C is not correct because using a catalyst does not necessarily result in the release of a greater amount of heat energy by the reaction.
Choice D is not correct because using a catalyst does not necessarily increase the yield of product.
Question 7:
Which of the following is the function of a totipotent cell?
A. Fights infectious diseases.
B. Aids in the maturation of sex cells.
C. Carries electrical impulses.
D. Develops into any kind of cell.
The Correct Answer is D.A totipotent cell can self-renew by dividing and develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo and into extra-embryonic tissues such as the placenta.
A fertilized egg is a totipotent stem cell and as such can develop into any specialized cell found in the organism.
Choice A is not correct because totipotent cells do not fight infectious diseases.
Choice B is not correct because totipotent cells do not aid in the maturation of sex cells.
Choice C is not correct because totipotent cells do not carry electrical impulses.
Question 8:
Which of the following substances is excreted by sweat glands in response to the breakdown of proteins and the formation of ammonia?
A. Urea
B. Sebum
C. Water
D. Lysozymes
The Correct Answer is A.Urea is a substance that is excreted by sweat glands in response to the breakdown of proteins and the formation of ammonia.
When proteins are broken down, they produce ammonia, which is a highly toxic compound for the body.
Ammonia is then converted into urea and released out of the body through sweat glands.
Choice B.
Sebum is not correct because it is an oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands to lubricate and protect the skin, but it is not related to the breakdown of proteins or the formation of ammonia.
Choice C.
Water is not correct because while it is a component of sweat, it is not specifically related to the breakdown of proteins or the formation of ammonia.
Choice D.
Lysozymes are not correct because they are enzymes found in tears, saliva and other body fluids that have antibacterial properties, but they are not related to the breakdown of proteins or the formation of ammonia.
Question 9:
Which of the following types of cells produce and release antibodies?
A. Natural killer cells
B. Cytotoxic T-cells
C. Plasma B cells
D. Helper T-cells
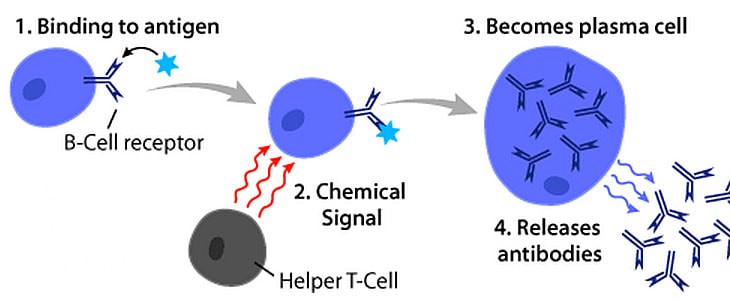
The Correct Answer is C.Plasma B cells.
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells).
When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone.
The mature B cells, called plasma cells, secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
Choice A, Natural killer cells, is not the correct answer because natural killer cells are a type of white blood cell that play a major role in the host-rejection of both tumors and virally infected cells.
Choice B, Cytotoxic T-cells, is not the correct answer because cytotoxic T-cells are a type of white blood cell that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected (particularly with viruses), or cells that are damaged in other ways.
Choice D, Helper T-cells, is not the correct answer because helper T-cells are a type of white blood cell that play an important role in the immune system by helping other white blood cells fight infections.
Question 10:
Which of the following microorganisms lack their own metabolic pathways and can only reproduce inside of a host cell?
A. Bacteria
B. Protozoa
C. Helminths
D. Viruses
The Correct Answer is D.Viruses.
Viruses lack essential machinery needed to reproduce by themselves.
In fact, viruses can only reproduce after infecting a living cell - a process called viral replication.
Once inside a living cell, viruses re-program the cell’s machinery to produce viral proteins and genetic material to make new copies of themselves.
Choice A, Bacteria, is not the correct answer because bacteria have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice B, Protozoa, is also not the correct answer because protozoa are singlecelled eukaryotes that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.
Choice C, Helminths, is not the correct answer because helminths are multicellular parasitic worms that have their own metabolic pathways and can reproduce outside of a host cell.