Vitamin B1 assists an organic catalyst in cell respiration. This vitamin functions as
A. a polypeptide
B. a coenzyme
C. a substrate
D. an inorganic catalyst
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
B) a coenzyme
- Correct: Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, functions as a coenzyme in cell respiration. Coenzymes are small molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions. In the case of thiamine, it serves as a coenzyme for several enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, particularly in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and the pentose phosphate pathway, which are essential processes in cell respiration. Thiamine helps in the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, ultimately facilitating ATP production.
A) a polypeptide
- Incorrect: Polypeptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, and they serve as the building blocks of proteins. Vitamin B1 is not a polypeptide itself but rather a small organic molecule.
C) a substrate
- Incorrect: Substrates are molecules upon which enzymes act to catalyze biochemical reactions. Vitamin B1 is not a substrate but rather a cofactor (coenzyme) that assists enzymes in catalyzing reactions.
D) an inorganic catalyst
- Incorrect: Inorganic catalysts are typically metallic ions or small inorganic molecules that facilitate chemical reactions but are not part of the reaction products. Vitamin B1 is an organic molecule derived from thiazole and pyrimidine rings and is not classified as an inorganic catalyst.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on Digestive System Practice Exam 1
Question 1:
If no carbohydrate ingestion occurs in the body during a 24-hour period, liver activity provides for the body's needs by
A. emulsification
B. manufacturing more bile
C. converting glycogen into glucose
D. releasing iron
The Correct Answer is C.C) converting glycogen into glucose
- Correct: When no carbohydrate ingestion occurs in the body during a 24-hour period, the liver can provide for the body's glucose needs by converting stored glycogen into glucose through a process known as glycogenolysis. Glycogen is a polysaccharide that serves as a storage form of glucose in the liver and muscles. When blood glucose levels decrease, such as during fasting or low carbohydrate intake, the liver breaks down glycogen into glucose molecules, which are then released into the bloodstream to maintain blood glucose levels and provide energy to cells throughout the body.
A) emulsification
- Incorrect: Emulsification is a process by which bile breaks down large fat globules into smaller droplets to aid in fat digestion in the small intestine. It is not related to the liver's role in glucose metabolism.
B) manufacturing more bile
- Incorrect: The liver produces bile continuously, regardless of carbohydrate ingestion. While the liver's production of bile is important for fat digestion and absorption, it is not directly related to glucose metabolism.
D) releasing iron
- Incorrect: The liver is involved in storing and regulating iron levels in the body, but releasing iron is not directly related to providing for the body's glucose needs in the absence of carbohydrate ingestion.
Question 2:
Hardened deposits of cholesterol that accumulate in the structure that stores bile are known as
A. gallstones
B. ulcers
C. goiters
D. allergies
The Correct Answer is A.A) gallstones
- Correct: Hardened deposits of cholesterol that accumulate in the structure that stores bile, which is the gallbladder, are known as gallstones. Gallstones can also contain other substances, such as bilirubin or calcium salts, in addition to cholesterol. These stones can vary in size and may cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. In severe cases, gallstones may require medical intervention, including surgery, to remove them.
B) ulcers
- Incorrect: Ulcers are sores or lesions that develop in the lining of the digestive tract, commonly in the stomach (gastric ulcers) or the upper part of the small intestine (duodenal ulcers). They are not related to hardened deposits of cholesterol in the gallbladder.
C) goiters
- Incorrect: Goiters are abnormal enlargements of the thyroid gland in the neck. They can be caused by iodine deficiency, thyroid disorders, or other factors, but they are not related to gallstones.
D) allergies
- Incorrect: Allergies are immune responses to specific substances (allergens) that the body perceives as harmful, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, itching, or anaphylaxis. They are not related to hardened deposits of cholesterol in the gallbladder.
Question 3:
Bile is a secretion which aids in the digestion of
A. lipids
B. proteins
C. saccharides
D. starches
The Correct Answer is A.A) lipids
- Correct: Bile is a secretion produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It aids in the digestion of lipids (fats) by emulsifying large fat globules into smaller droplets. This process increases the surface area of fats, allowing digestive enzymes such as lipase to more efficiently break them down into smaller molecules (fatty acids and glycerol) that can be absorbed in the small intestine.
B) proteins
- Incorrect: Bile does not aid in the digestion of proteins. Proteins are broken down by specific digestive enzymes such as pepsin in the stomach and proteases in the small intestine.
C) saccharides
- Incorrect: Bile does not aid in the digestion of saccharides, which are carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are broken down by enzymes such as amylase into simple sugars (monosaccharides) during the process of digestion.
D) starches
- Incorrect: Bile does not aid in the digestion of starches. Starches are complex carbohydrates
Question 4:
Glycogen is best described as a
A. complex carbohydrate that is often stored in red blood cells
B. complete protein necessary for the synthesis of cell membranes
C. polysaccharide that is synthesized and stored within the human liver
D. by-product of sucrose digestion within the pancreas
The Correct Answer is C.C) polysaccharide that is synthesized and stored within the human liver
- Correct: Glycogen is a polysaccharide, which means it is a complex carbohydrate composed of many glucose molecules linked together. It is synthesized and stored primarily in the liver and muscles of humans and other vertebrates. Glycogen serves as a form of energy storage, allowing organisms to store glucose for later use when energy demands are high or when glucose availability is low.
A) complex carbohydrate that is often stored in red blood cells
- Incorrect: While glycogen is a complex carbohydrate, it is not stored in red blood cells. Red blood cells do not contain nuclei or organelles, including glycogen storage structures.
B) complete protein necessary for the synthesis of cell membranes
- Incorrect: Glycogen is not a protein. It is a carbohydrate used for energy storage. Proteins are composed of amino acids and are involved in various cellular functions, including the synthesis of cell membranes, but glycogen does not play a direct role in this process.
D) by-product of sucrose digestion within the pancreas
- Incorrect: Glycogen is not a by-product of sucrose digestion within the pancreas. Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose, and it is broken down into its component sugars by enzymes in the small intestine, not the pancreas. Glycogen is synthesized and stored in the liver and muscles as a form of energy storage.
Question 5:
Vitamin B1 assists an organic catalyst in cell respiration. This vitamin functions as
A. a polypeptide
B. a coenzyme
C. a substrate
D. an inorganic catalyst
The Correct Answer is B.B) a coenzyme
- Correct: Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, functions as a coenzyme in cell respiration. Coenzymes are small molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions. In the case of thiamine, it serves as a coenzyme for several enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, particularly in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and the pentose phosphate pathway, which are essential processes in cell respiration. Thiamine helps in the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, ultimately facilitating ATP production.
A) a polypeptide
- Incorrect: Polypeptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, and they serve as the building blocks of proteins. Vitamin B1 is not a polypeptide itself but rather a small organic molecule.
C) a substrate
- Incorrect: Substrates are molecules upon which enzymes act to catalyze biochemical reactions. Vitamin B1 is not a substrate but rather a cofactor (coenzyme) that assists enzymes in catalyzing reactions.
D) an inorganic catalyst
- Incorrect: Inorganic catalysts are typically metallic ions or small inorganic molecules that facilitate chemical reactions but are not part of the reaction products. Vitamin B1 is an organic molecule derived from thiazole and pyrimidine rings and is not classified as an inorganic catalyst.
Question 6:
Which food would provide the most roughage for the body?
A. baked fresh fish
B. lettuce-and-tomato salad
C. fried chicken breast
D. milkshake
The Correct Answer is B.B) lettuce-and-tomato salad
- Correct: Lettuce-and-tomato salad would provide the most roughage for the body. Roughage, also known as dietary fiber or bulk, refers to the indigestible portion of plant foods that adds bulk to the stool and helps regulate bowel movements. Lettuce and tomatoes are both rich sources of dietary fiber. Lettuce, especially varieties like romaine or leaf lettuce, contains cellulose and other insoluble fibers, while tomatoes contain soluble fibers like pectin. Consuming a salad made of lettuce and tomatoes would provide a significant amount of roughage to the body, promoting digestive health and regular bowel movements.
A) baked fresh fish
- Incorrect: Fish does not contain significant amounts of dietary fiber. While fish is a valuable source of protein and other nutrients, it is not a source of roughage.
C) fried chicken breast
- Incorrect: Fried chicken breast does not contain significant amounts of dietary fiber. Additionally, frying can add unhealthy fats and calories to the chicken breast, further reducing its nutritional value in terms of roughage.
D) milkshake
- Incorrect: Milkshakes are typically made with milk, ice cream, and flavorings, none of which provide dietary fiber. In fact, milkshakes are generally low in fiber and may contain high amounts of sugar and fat, making them poor choices for increasing roughage intake.
Question 7:
Base your answer to the following question on Which statement best expresses the information represented in the graph shown below?
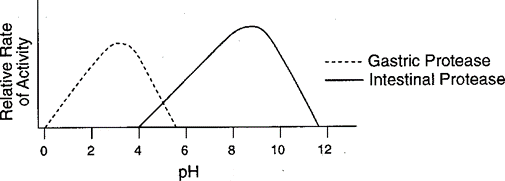
A. The action of enzymes varies with pH.
B. A pH of 7 provides the optimum environment for digestive enzymes.
C. Gastric juice is active at a pH extending from 0 to 12.
D. Acids have a pH greater than 7.
The Correct Answer is A.The action of enzymes vary with pH. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions, and their activity is influenced by various factors including pH.
The pH level affects the ionization state of amino acid residues within the enzyme's active site. This, in turn, can affect the enzyme's ability to bind substrate molecules and catalyze reactions.
Different enzymes have different optimal pH ranges at which they exhibit maximum activity. This optimal pH range is determined by the specific environment in which the enzyme typically functions. For example, pepsin, which is involved in digesting proteins in the stomach, works optimally at an acidic pH around 2, whereas enzymes in the small intestine function optimally at a slightly alkaline pH around 7 to 8.
Extreme deviations from the optimal pH can denature enzymes, causing them to lose their structure and function. Therefore, maintaining the appropriate pH level is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of enzymes in biochemical reactions.
Question 8:
Some vitamins are essential to an organism because they function as
A. coenzymes
B. auxins
C. hormones
D. neurotransmitters
The Correct Answer is A.A) coenzymes
- Correct: Some vitamins function as coenzymes, which are molecules that assist enzymes in their catalytic activity. Coenzymes work together with enzymes to facilitate various biochemical reactions in the body. For example, certain B vitamins (such as thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin) act as coenzymes in energy metabolism, while vitamin K acts as a coenzyme in blood clotting. Without these essential vitamins, many metabolic processes in the body would be impaired, leading to various health problems.
B) auxins
- Incorrect: Auxins are plant hormones that regulate plant growth and development. They are not vitamins and do not function as coenzymes in biochemical reactions in organisms.
C) hormones
- Incorrect: Hormones are signaling molecules that regulate various physiological processes in organisms. While some vitamins may indirectly influence hormone production or function, they do not function primarily as hormones themselves.
D) neurotransmitters
- Incorrect: Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells (neurons) in the nervous system. They are not vitamins and do not function as coenzymes in biochemical reactions in organisms.
Question 9:
The absorptive surface of the small intestine is greater than that of other human digestive organs because of its length and the presence of
A. alveoli
B. neurons
C. villi
D. nephrons
The Correct Answer is C.C) villi
- Correct: The absorptive surface of the small intestine is greatly increased due to the presence of villi. Villi are finger-like projections that line the inner surface of the small intestine. These structures greatly increase the surface area available for absorption. Each villus contains capillaries and lacteals (lymphatic vessels) that absorb nutrients from digested food. The large surface area provided by the villi allows for more efficient absorption of nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
A) alveoli
- Incorrect: Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs during respiration. They are not found in the digestive system and do not contribute to the absorptive surface of the small intestine.
B) neurons
- Incorrect: Neurons are nerve cells that transmit signals throughout the body, including the digestive system. While neurons play a role in regulating digestion and other digestive processes, they do not directly contribute to the absorptive surface of the small intestine.
D) nephrons
- Incorrect: Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. They are not part of the digestive system and do not contribute to the absorptive surface of the small intestine.
Question 10:
Which two organ systems provide materials required for the human body to produce ATP?
A. reproductive and excretory
B. digestive and respiratory
C. respiratory and immune
D. digestive and reproductive
The Correct Answer is B.The digestive system provides materials in the form of nutrients from food, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. These nutrients are broken down during digestion and absorbed into the bloodstream.
The respiratory system provides oxygen, which is necessary for cellular respiration, the process by which ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced in cells. Oxygen is inhaled into the lungs and diffuses into the bloodstream to be transported to cells throughout the body.