What are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA?
A. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
B. Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine.
C. Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine.
D. Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine.
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
These are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA1.
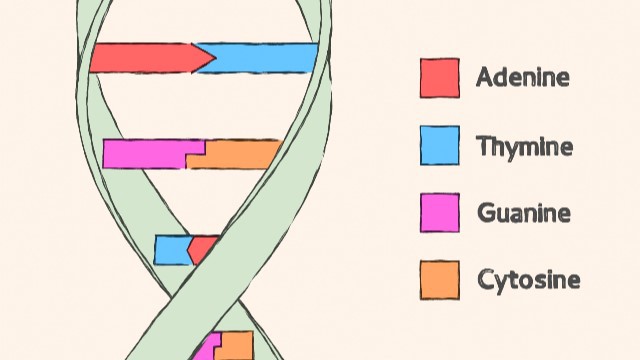
Choice B) Adenine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanine is incorrect because Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice C) Adenosine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine and Guanosine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Choice D) Adenosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Guanosine is incorrect because Adenosine, Thymidine and Cytidine are not nucleotide bases found in DNA.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
A patient with a history of heart failure is prescribed a medication that increases urine output to reduce fluid buildup.
Which of the following statements best describes the mechanism of action of the prescribed medication?
A. Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
B. Blocks beta receptors.
C. Increases sodium and water reabsorption.
D. Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The Correct Answer is D.The correct answer is choice D - Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The medication prescribed to the patient is a diuretic, which removes water and electrolytes from the body by increasing urination 1.
This helps reduce fluid buildup in the body.
Choice A, Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice B, Blocks beta receptors, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice C, Increases sodium and water reabsorption, is not the correct answer because it would have the opposite effect of reducing fluid buildup.
Question 2:
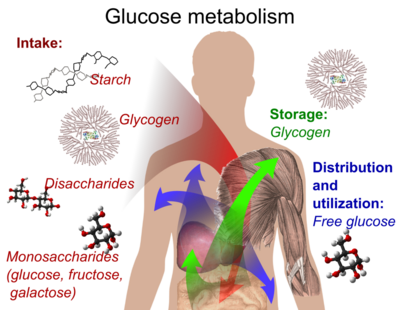
Which of the following is an example of a storage form of glucose in the human body?
A. Starch
B. Glycogen
C. Fructose
D. Cellulose
The Correct Answer is B.Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the human body.
It is a polysaccharide that is stored primarily in the liver and muscle tissue and can be broken down into glucose when the body needs energy.
 |
Choice A is incorrect because starch is a storage form of glucose in plants, not in the human body.
Choice C is incorrect because fructose is a simple sugar, not a storage form of glucose.
Choice D is incorrect because cellulose is a structural carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, not a storage form of glucose in the human body.
Question 3:
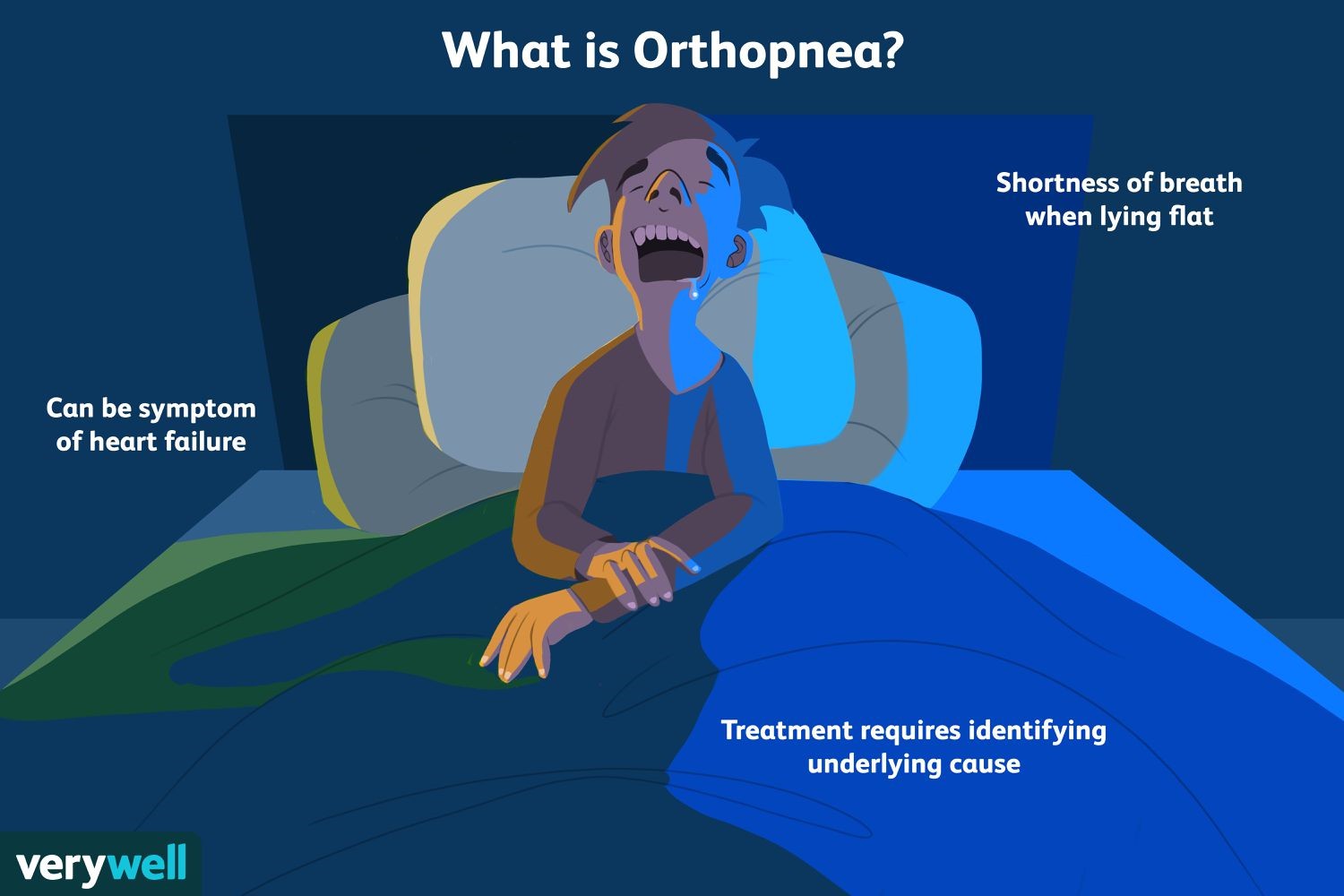
Which of the following refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand?
A. Orthopnea
B. Hypoxia
C. Tachypnea
D. Bradypnea
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Orthopnea.
Orthopnea refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand.
 |
Choice B, Hypoxia, is not the correct answer because it refers to a condition in which there is a lack of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Choice C, Tachypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to rapid breathing.
Choice D, Bradypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to abnormally slow breathing.
Question 4:
Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Question 5:
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
A. Decrease in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus.
B. Increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
C. Decrease in the concentration of sodium in the blood.
D. Increase in the concentration of magnesium in the blood.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing an increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
The kidneys play a pivotal role in the regulation of electrolyte balance.
With progressive loss of kidney function, derangements in electrolytes inevitably occur and contribute to poor patient outcomes123.
Choice A is incorrect because calcium concentration is not regulated in the glomerulus.
Choice C is incorrect because chronic kidney disease can result in either an increase or decrease in sodium concentration in the blood.
Choice D is incorrect because chronic kidney disease does not necessarily result in an increase in magnesium concentration in the blood.
Question 6:
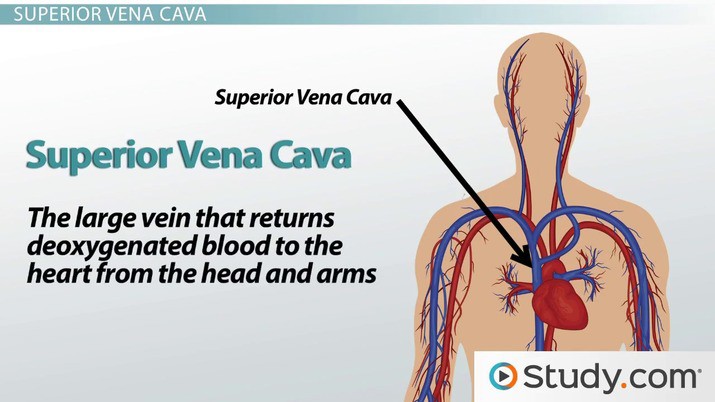
What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
Question 7:
Which organ in the human body is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells?
A. Spleen
B. Kidneys
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The spleen is an organ in the human body that is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells.
Choice B is incorrect because the kidneys are responsible for filtering waste from the blood and regulating electrolyte balance.
Choice C is incorrect because the pancreas produces hormones and enzymes that aid in digestion.
Choice D is incorrect because the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
Question 8:
How do neurons communicate with each other?
A. Through electrical signals only
B. Through chemical signals only
C. Through electrical and chemical signals
D. Through mechanical signals only.
The Correct Answer is C.Neurons communicate with each other through both electrical and chemical signals.
The electrical signal, or action potential, runs from the cell body area to the axon terminals, through a thin fiber called axon.
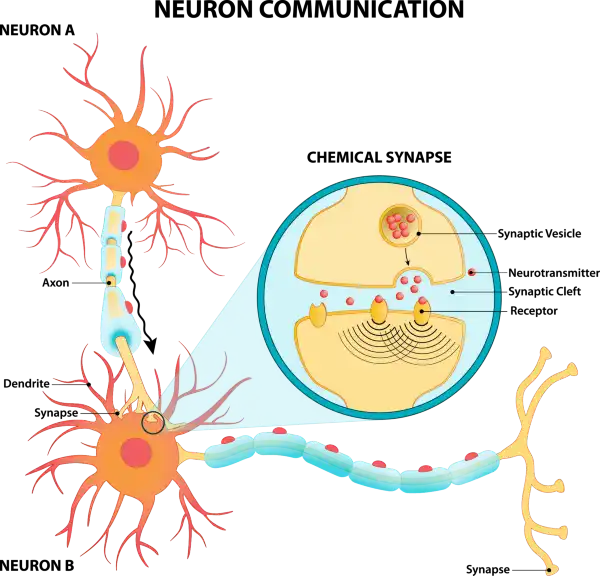
Neurons also communicate with one another at junctions called synapses.
At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell.
Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers.
Choice A is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through electrical signals but also through chemical signals.
Choice B is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through chemical signals but also through electrical signals.
Choice D is incorrect because neurons do not communicate through mechanical signals.
Question 9:
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been declared brain dead and is awaiting organ donation.
Which of the following interventions is most important to preserve the viability of the organs?
A. Administering antibiotics to prevent infection.
B. Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
C. Providing emotional support to the family members.
D. Applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
Early identification and management of potential organ donors must take into consideration specific pathophysiologic changes for medical optimization 1.
The VIPPS (ventilation, infusion and pumping, pharmacological treatment, and specificities) strategy is a mnemonic method that brings together key aspects of the restoration of oxygen delivery to tissues during hemodynamic instability plus organ optimization strategies.
Choice A is incorrect because administering antibiotics to prevent infection is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Choice C is incorrect because providing emotional support to family members, while important, is not an intervention that directly affects organ viability.
Choice D is incorrect because applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Question 10:
Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.