What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.
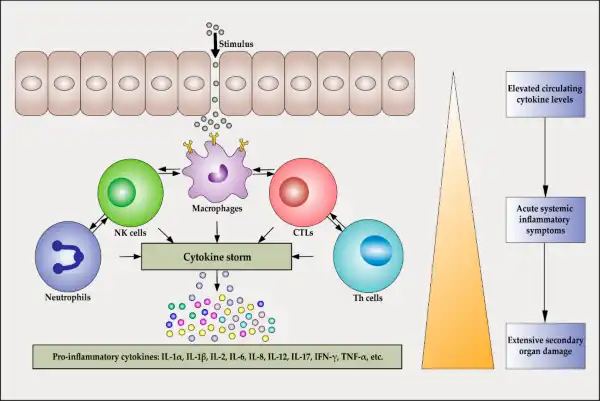
Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
The Correct Answer is A.Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
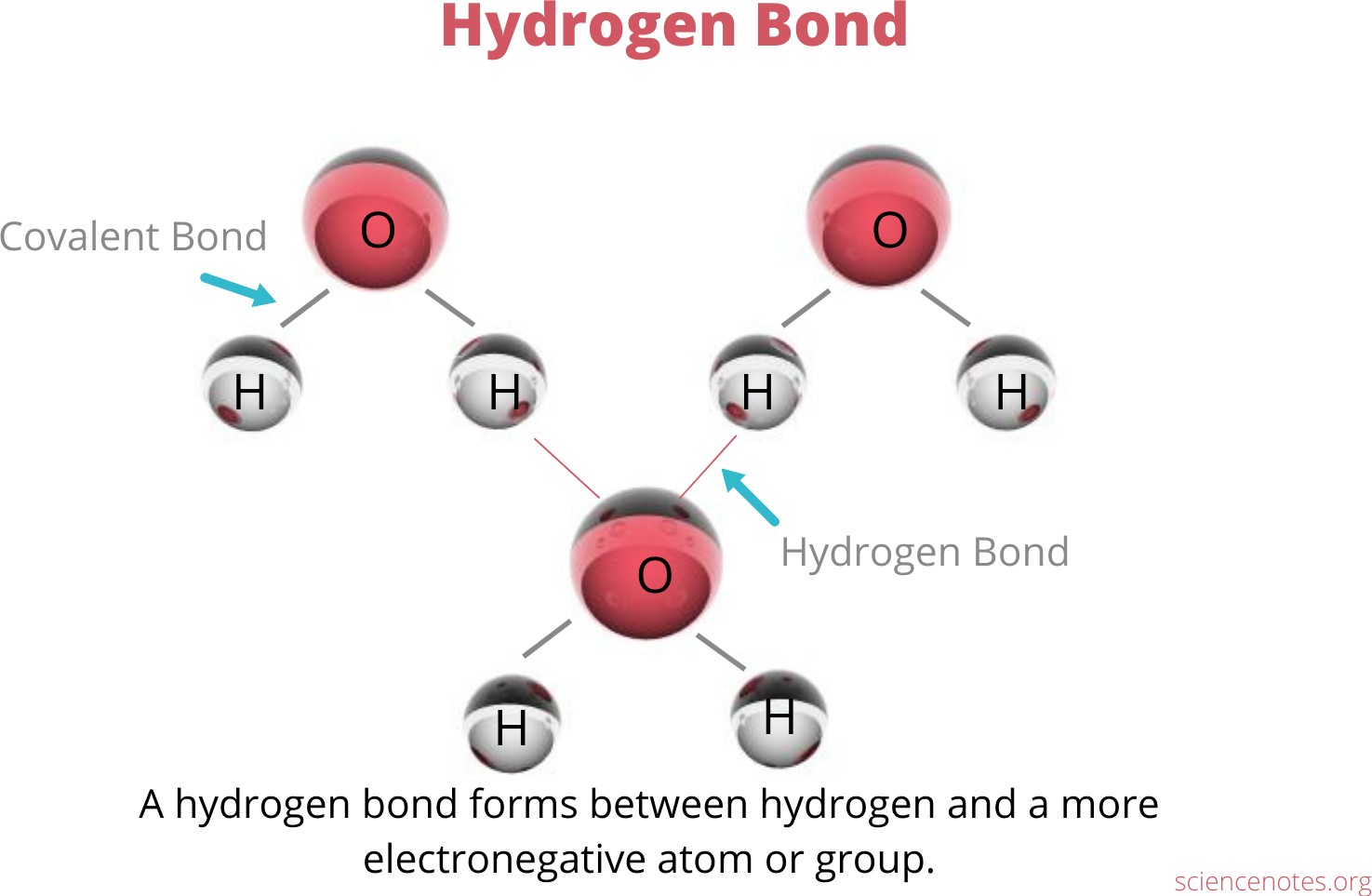 |
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
Question 2:
Which of the following is an example of a storage form of glucose in the human body?
A. Starch
B. Glycogen
C. Fructose
D. Cellulose
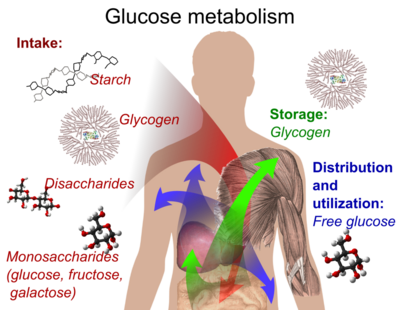
The Correct Answer is B.Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the human body.
It is a polysaccharide that is stored primarily in the liver and muscle tissue and can be broken down into glucose when the body needs energy.
 |
Choice A is incorrect because starch is a storage form of glucose in plants, not in the human body.
Choice C is incorrect because fructose is a simple sugar, not a storage form of glucose.
Choice D is incorrect because cellulose is a structural carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, not a storage form of glucose in the human body.
Question 3:
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
A. Decrease in the concentration of calcium in the glomerulus.
B. Increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
C. Decrease in the concentration of sodium in the blood.
D. Increase in the concentration of magnesium in the blood.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
A patient with chronic kidney disease is at risk for developing an increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood.
The kidneys play a pivotal role in the regulation of electrolyte balance.
With progressive loss of kidney function, derangements in electrolytes inevitably occur and contribute to poor patient outcomes123.
Choice A is incorrect because calcium concentration is not regulated in the glomerulus.
Choice C is incorrect because chronic kidney disease can result in either an increase or decrease in sodium concentration in the blood.
Choice D is incorrect because chronic kidney disease does not necessarily result in an increase in magnesium concentration in the blood.
Question 4:
Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Question 5:
During the menstrual cycle, which structure in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation?
A. Corpus luteum.
B. Fimbriae
C. Follicle
D. Ovarian ligament.
The Correct Answer is A.Corpus luteum.
During the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation.
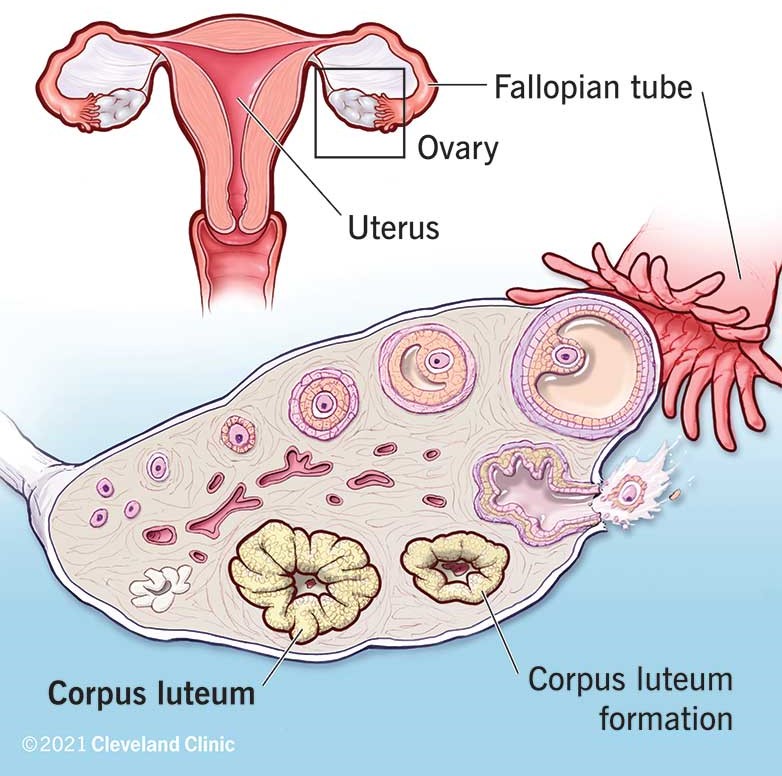
Choice B is incorrect because fimbriae are finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube.
Choice C is incorrect because a follicle is a sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Choice D is incorrect because the ovarian ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the uterus.
Question 6:
What is the function of the neuromuscular junction?
A. To connect muscle fibers to motor neurons
B. To bind acetylcholine to nAChRs
C. To depolarize the muscle cell membrane D.
D. To activate voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane .
The Correct Answer is A.The neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract.
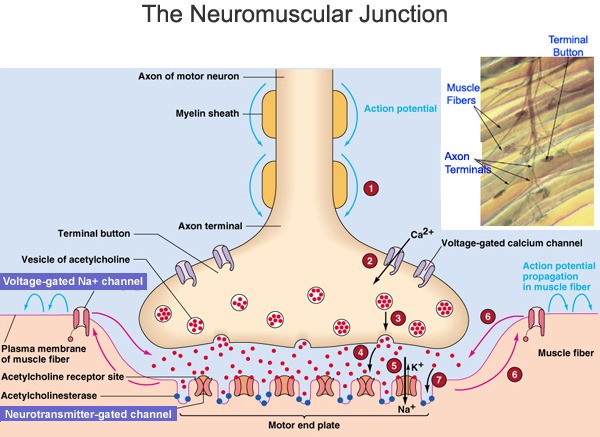
The activation of many muscle fibers together causes muscles to contract, which in turn can produce movement.
Choice B is incorrect because binding acetylcholine to nAChRs is a process that occurs at the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function of the neuromuscular junction itself.
Choice C is incorrect because depolarizing the muscle cell membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
Choice D is incorrect because activating voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
Question 7:
How do neurons communicate with each other?
A. Through electrical signals only
B. Through chemical signals only
C. Through electrical and chemical signals
D. Through mechanical signals only.
The Correct Answer is C.Neurons communicate with each other through both electrical and chemical signals.
The electrical signal, or action potential, runs from the cell body area to the axon terminals, through a thin fiber called axon.
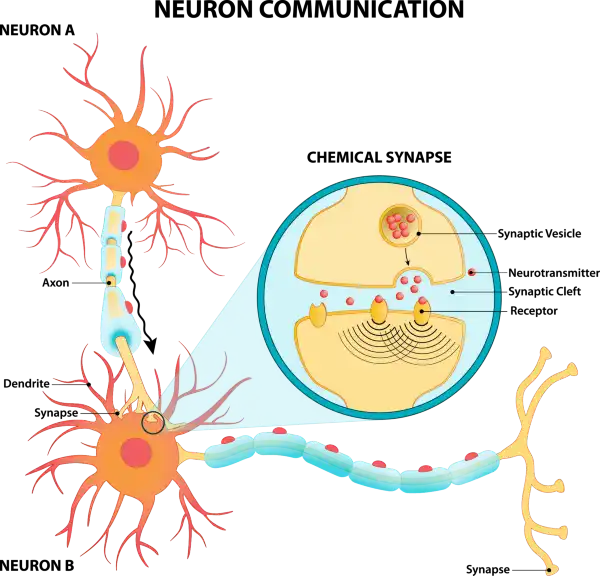
Neurons also communicate with one another at junctions called synapses.
At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell.
Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers.
Choice A is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through electrical signals but also through chemical signals.
Choice B is incorrect because neurons communicate not only through chemical signals but also through electrical signals.
Choice D is incorrect because neurons do not communicate through mechanical signals.
Question 8:
What is the normal flora?
A. A variety of microbial species found in certain areas of the human body.
B. A group of infectious parasites that cause diarrheal diseases.
C. The genetic material of bacteria housed within a true nucleus.
D. The protein coat surrounding the viral genome.
The Correct Answer is A.The normal flora refers to the microbial community that colonizes on the skin and mucus membrane .
Normal flora can be found in many sites of the human body including the skin, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and the digestive tract.
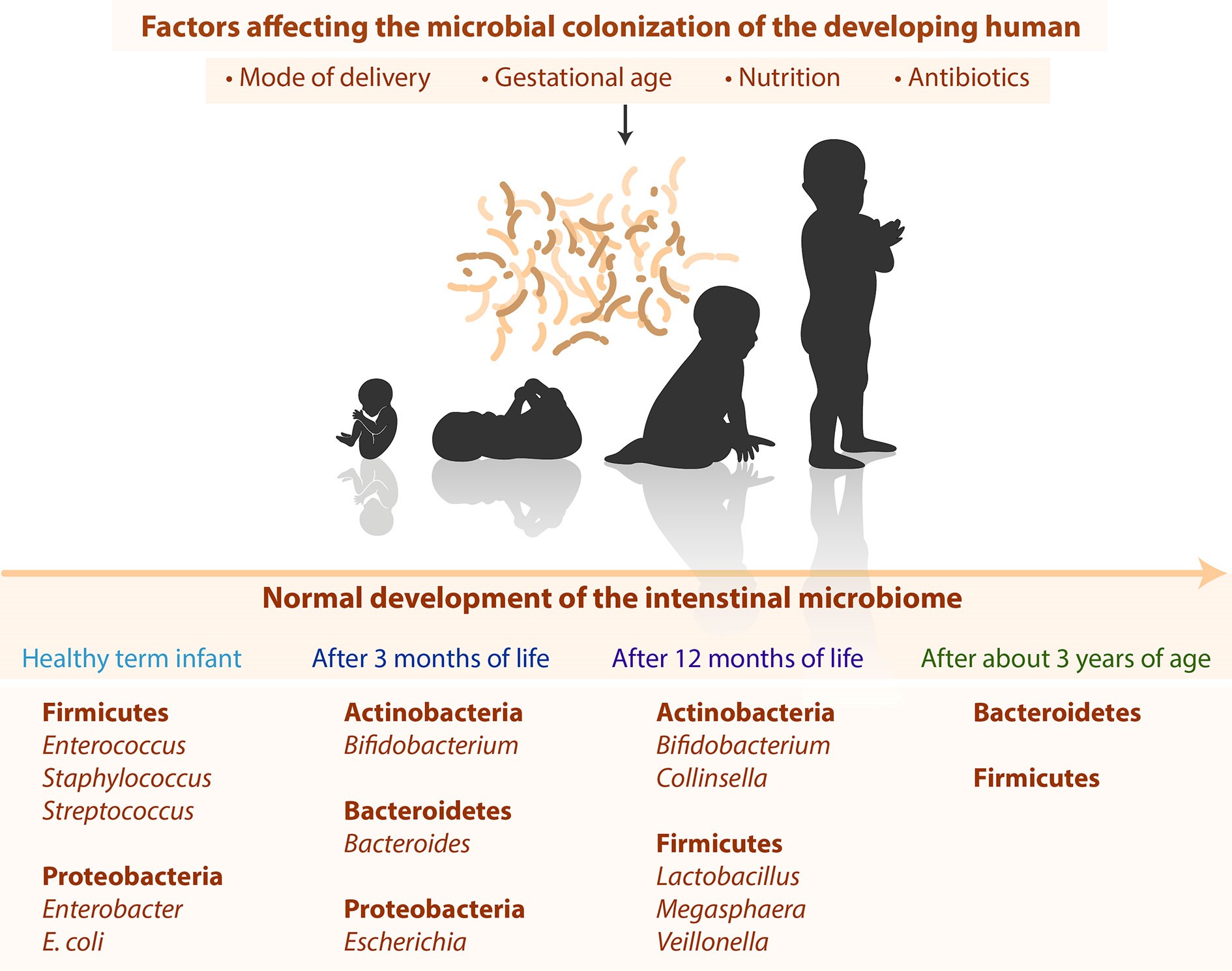
Choice B is incorrect because normal flora does not refer to a group of infectious parasites that cause diarrheal diseases .
Choice C is incorrect because normal flora does not refer to the genetic material of bacteria housed within a true nucleus .
Choice D is incorrect because normal flora does not refer to the protein coat surrounding the viral genome .
Question 9:
What is the purpose of using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) in the laboratory?
A. To separate DNA fragments by size.
B. To amplify specific regions of DNA.
C. To sequence DNA fragments.
D. To analyze protein expression levels.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
To amplify specific regions of DNA.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a laboratory technique used to make many copies of a specific region of DNA.
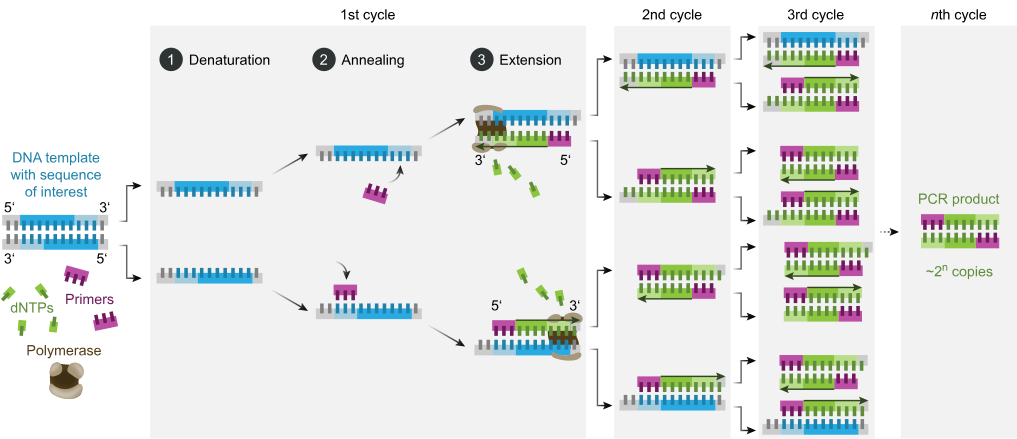 |
The goal of PCR is to make enough of the target DNA region that it can be analyzed or used in some other way.
PCR has many research and practical applications, including DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
Choice A is incorrect because PCR does not separate DNA fragments by size. Choice C is incorrect because PCR does not sequence DNA fragments.
Choice D is incorrect because PCR does not analyze protein expression levels.
Question 10:
What is a primer in DNA sequencing?
A. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
B. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a "starter" for the template.
C. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
D. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a "starter" for the template.
The Correct Answer is C.A primer is a short single-stranded DNA fragment used in certain laboratory techniques, such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
In the PCR method, a pair of primers hybridizes with the sample DNA and defines the region that will be amplified.
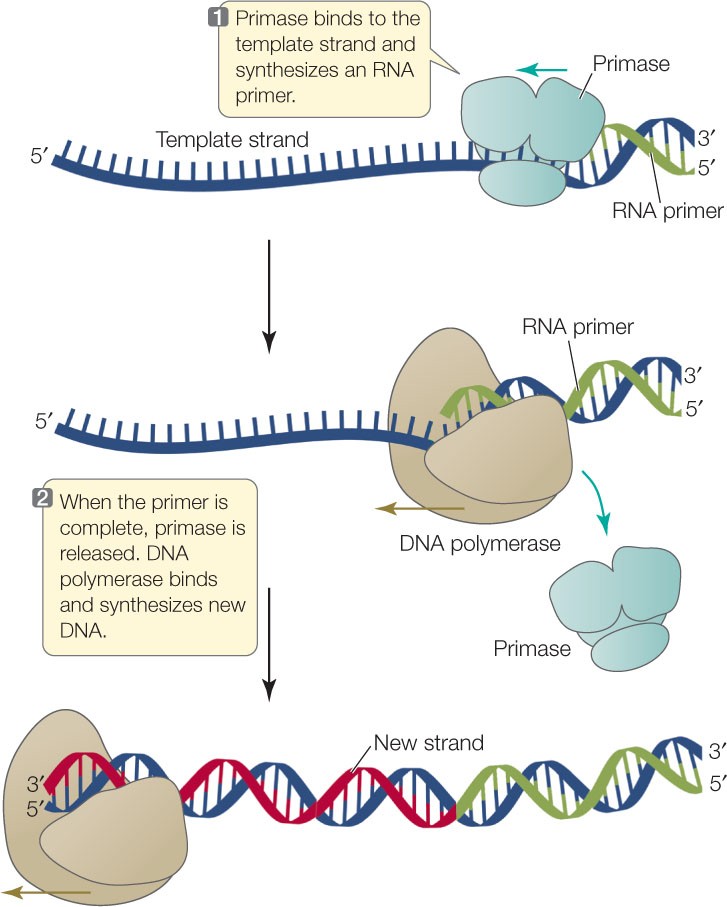
Choice A) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a “starter” for the polymerase is incorrect because primers are single-stranded, not double-stranded.
Choice B) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because it does not make sense for a primer to bind to itself.
Choice D) A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because primers bind to the template DNA, not to the polymerase.
Note: DNA primers are used instead of RNA primers in DNA sequencing and PCR because DNA is more stable, specific, and compatible with the enzymes and processes involved in these techniques.