What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
A. To produce energy for the cell
B. To store genetic information
C. To transport molecules within the cell
D. To synthesize proteins in the cell
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
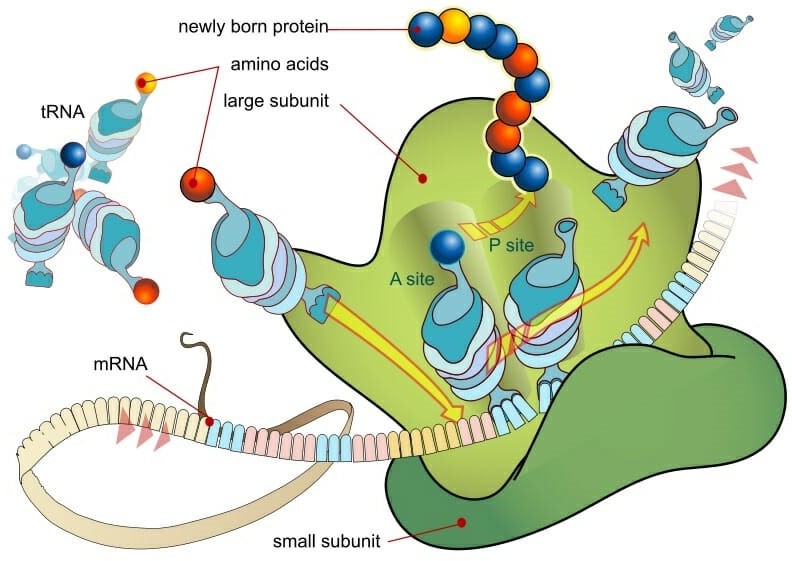
Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 3
Question 1:
What are the three types of salivary glands and where are they located in the mouth?
A. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the cheeks, tongue, and roof of the mouth, respectively.
B. Sublingual, submandibular, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
C. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the roof of the mouth, cheeks, and under the jawbone, respectively.
D. Sublingual, parotid, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
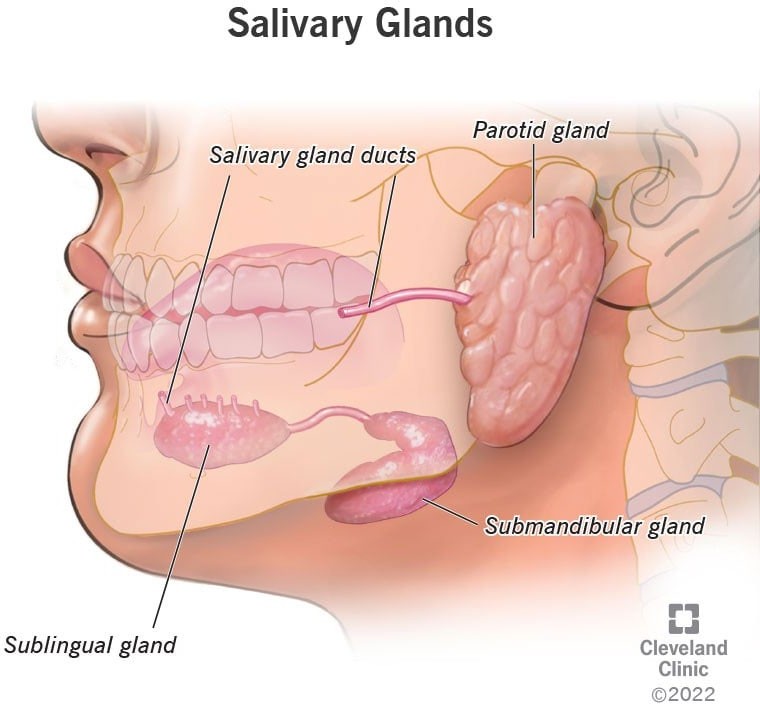
The Correct Answer is C.The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands.
- Parotid glands are located just in front of your ears.
- Sublingual glands are located below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth.
- Submandibular glands are located below your jaw.
 |
Question 2:
What is the name of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the human body?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Estrogen
D. Testosterone
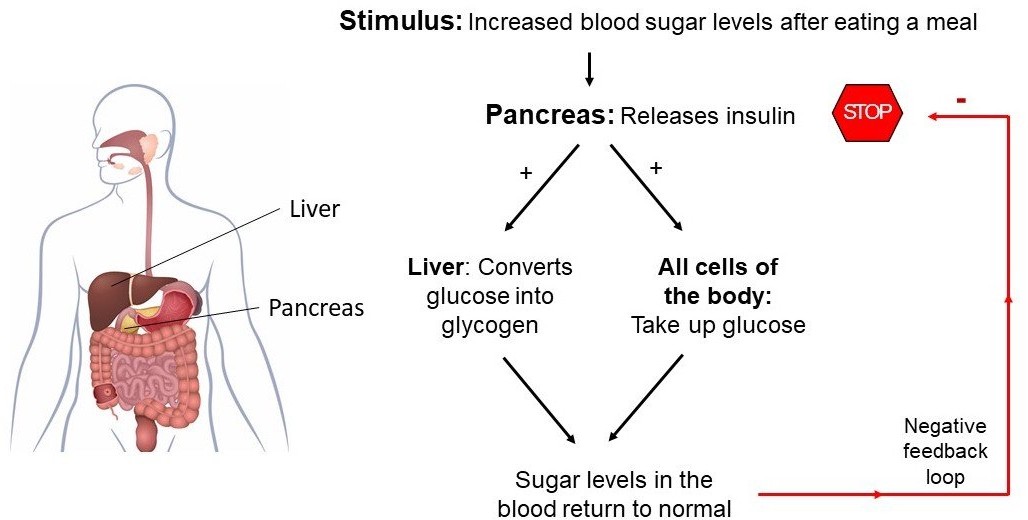
The Correct Answer is A.Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. After a person eats a meal, the levels of glucose in the blood rise, which stimulates the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts on various cells in the body, particularly those in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue, to promote the uptake, use, and storage of glucose.
Insulin helps to lower the levels of glucose in the blood by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells, stimulating the liver and muscle cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen, and inhibiting the production and release of glucose by the liver. This process is known as glucose homeostasis, and it helps to keep the levels of glucose in the blood within a normal range.
Deficiencies or abnormalities in insulin production or function can lead to a range of metabolic disorders, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
Question 3:
Which of the following statements is true regarding vaccines?
A. Vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against
B. Vaccines work by providing passive immunity to the individual
C. Vaccines work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of the pathogen
D. Vaccines only provide protection against bacterial infections
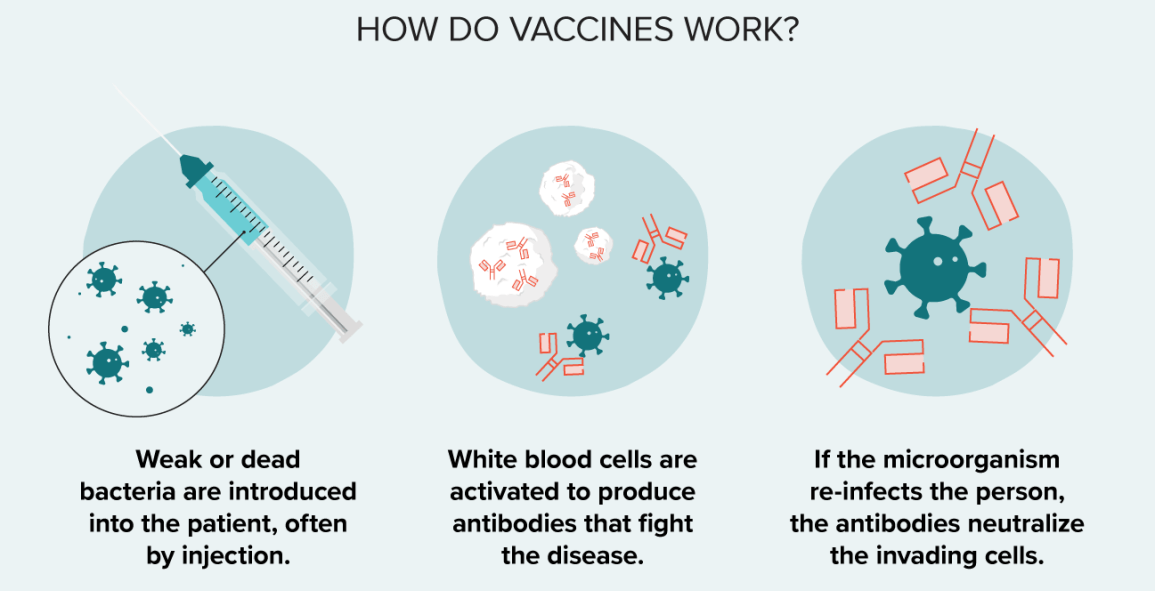
The Correct Answer is C.Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
Question 4:
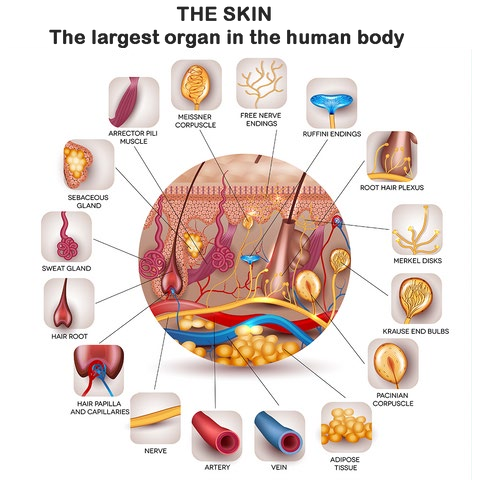
What is the largest organ in the human body by surface area?
A. Brain
B. Heart
C. Liver
D. Skin
The Correct Answer is D.The largest organ in the human body by surface area is the skin. It covers the entire external surface of the body and has an average surface area of about 20 square feet in adults.
 |
Question 5:
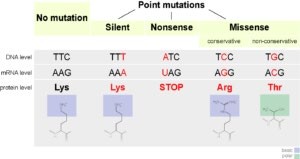
Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
The Correct Answer is C.A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
 |
Question 6:
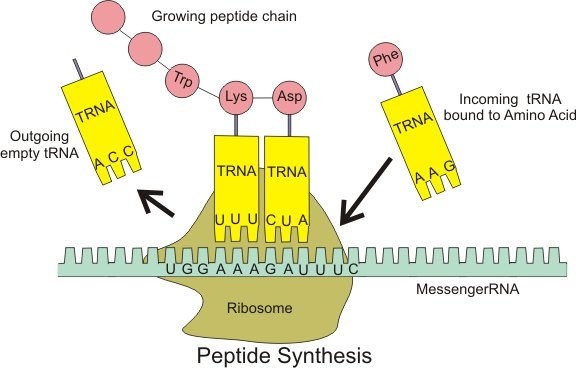
Which of the following types of RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis?
A. Messenger RNA
B. Ribosomal RNA
C. Transfer RNA
D. Small nuclear RNA
The Correct Answer is C.Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific sequence of three nucleotides called an anticodon, which pairs with a complementary codon in the messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence. Each tRNA also carries a specific amino acid that corresponds to the codon it recognizes, allowing the ribosome to link the amino acids together in the correct order to form a protein.
In contrast, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome itself, where it helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is involved in splicing of pre-mRNA molecules during post-transcriptional processing.
 |
Question 7:
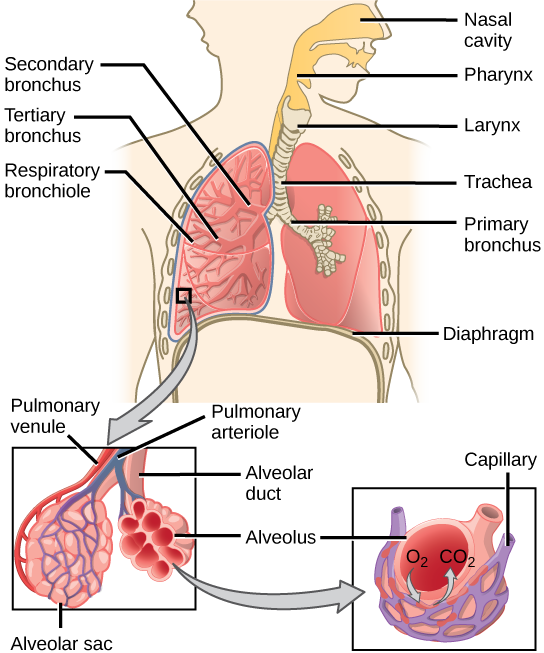
Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
A. Transport of nutrients to the body
B. Pumping of blood to the lungs
C. Exchange of gases between the body and the environment
D. Digestion of food in the stomach
The Correct Answer is C.One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
 |
Question 8:
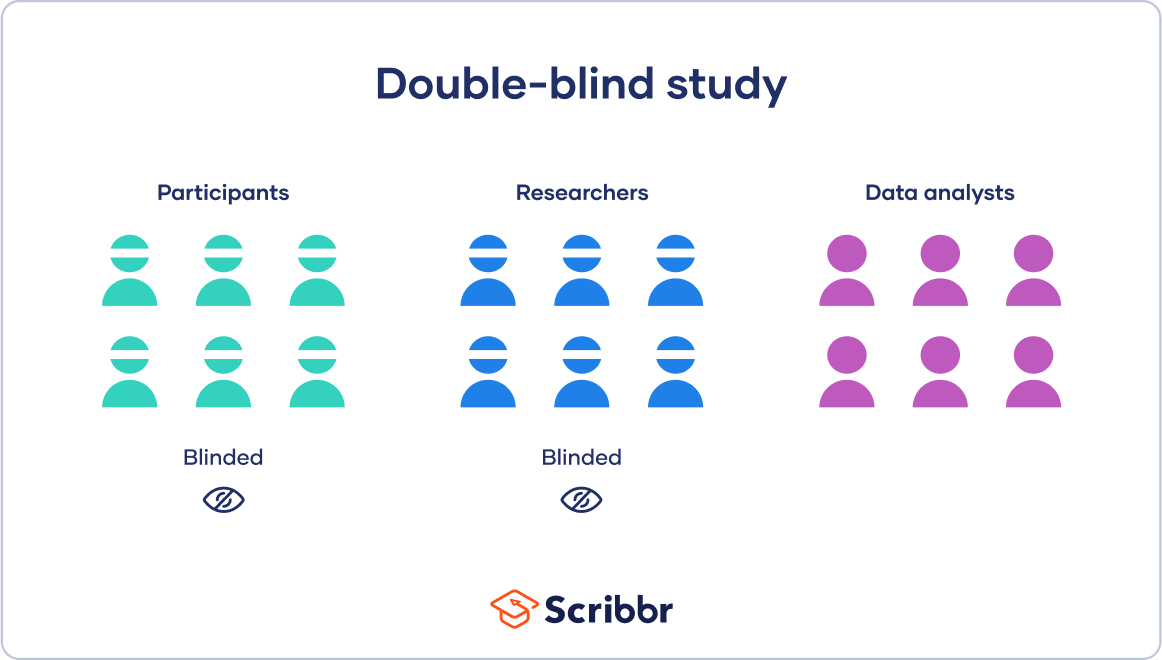
Which of the following is an example of a double-blind study?
A. Participants are randomly assigned to a treatment group or a control group
B. Participants and researchers both know which group participants are assigned to
C. Participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but researchers do
D. Both participants and researchers do not know which group participants are assigned to
The Correct Answer is D.A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to. Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind. Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to. Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Question 9:
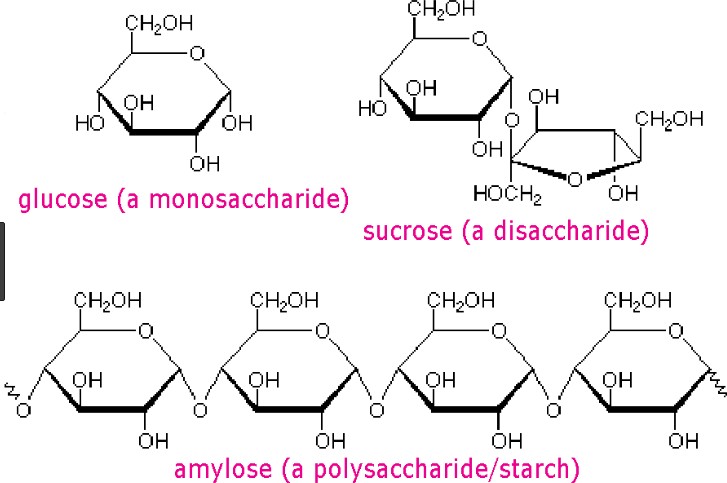
What is the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide?
A. Monosaccharides are composed of two sugar molecules while disaccharides are composed of a single sugar molecule.
B. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars while disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars.
C. Monosaccharides are only found in plants while disaccharides are only found in animals.
D. Monosaccharides are used for energy storage while disaccharides are used for structural purposes.
The Correct Answer is B.Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
Question 10:
What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
A. To produce energy for the cell
B. To store genetic information
C. To transport molecules within the cell
D. To synthesize proteins in the cell
The Correct Answer is D.Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
