What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
Question 2:
Why is water sometimes called the "universal solvent"?.
A. Because water dissolves all solutes equally well.
B. Because water is a nonpolar solvent.
C. Because water is good at dissolving ions and polar molecules.
D. Because water is poor at dissolving nonpolar molecules.
The Correct Answer is C.Water is sometimes called the “universal solvent” because it dissolves more substances than any other liquid.
This is due to its polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds, which allows it to dissolve ions and polar molecules.
Choice A) Because water dissolves all solutes equally well is incorrect because water does not dissolve all solutes equally well.
Choice B) Because water is a nonpolar solvent is incorrect because water is a polar solvent.
Choice D) Because water is poor at dissolving nonpolar molecules is incorrect because it does not explain why water is called the “universal solvent”.
Question 3:
Which of the following is a consequence of increased viscosity of a fluid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. The fluid will have a lower density.
C. The fluid will have a higher flow rate.
D. The fluid will have a higher pressure.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
Question 4:
Which of the following hormones is responsible for regulating the body's metabolism and energy levels?
A. Estrogen
B. Progestin
C. Thyroxine
D. Androgen
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is choice C. Thyroxine.
Thyroxine (T4) is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that controls your body’s metabolism, the process in which your body transforms the food you eat into energy.
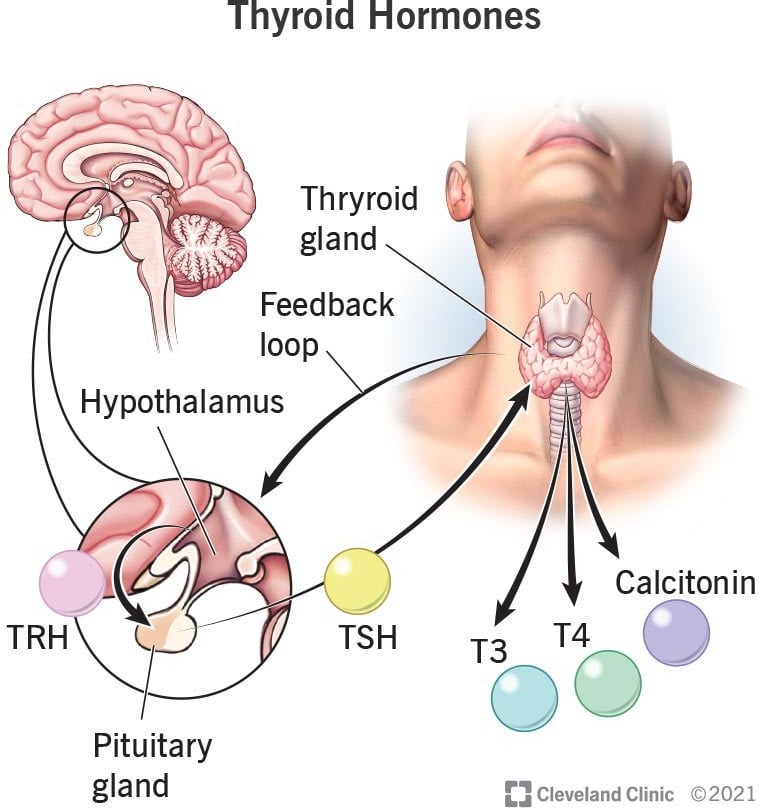
Choice A, Estrogen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Choice B, Progestin, is not the correct answer because it is a synthetic form of progesterone used in hormonal birth control and hormone replacement therapy.
Choice D, Androgen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Question 5:
A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder.
The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
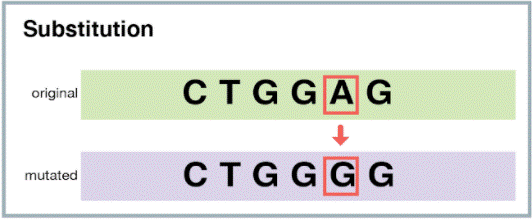 |
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
Question 6:
What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
The Correct Answer is C.Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Question 7:
What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
The Correct Answer is A.Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
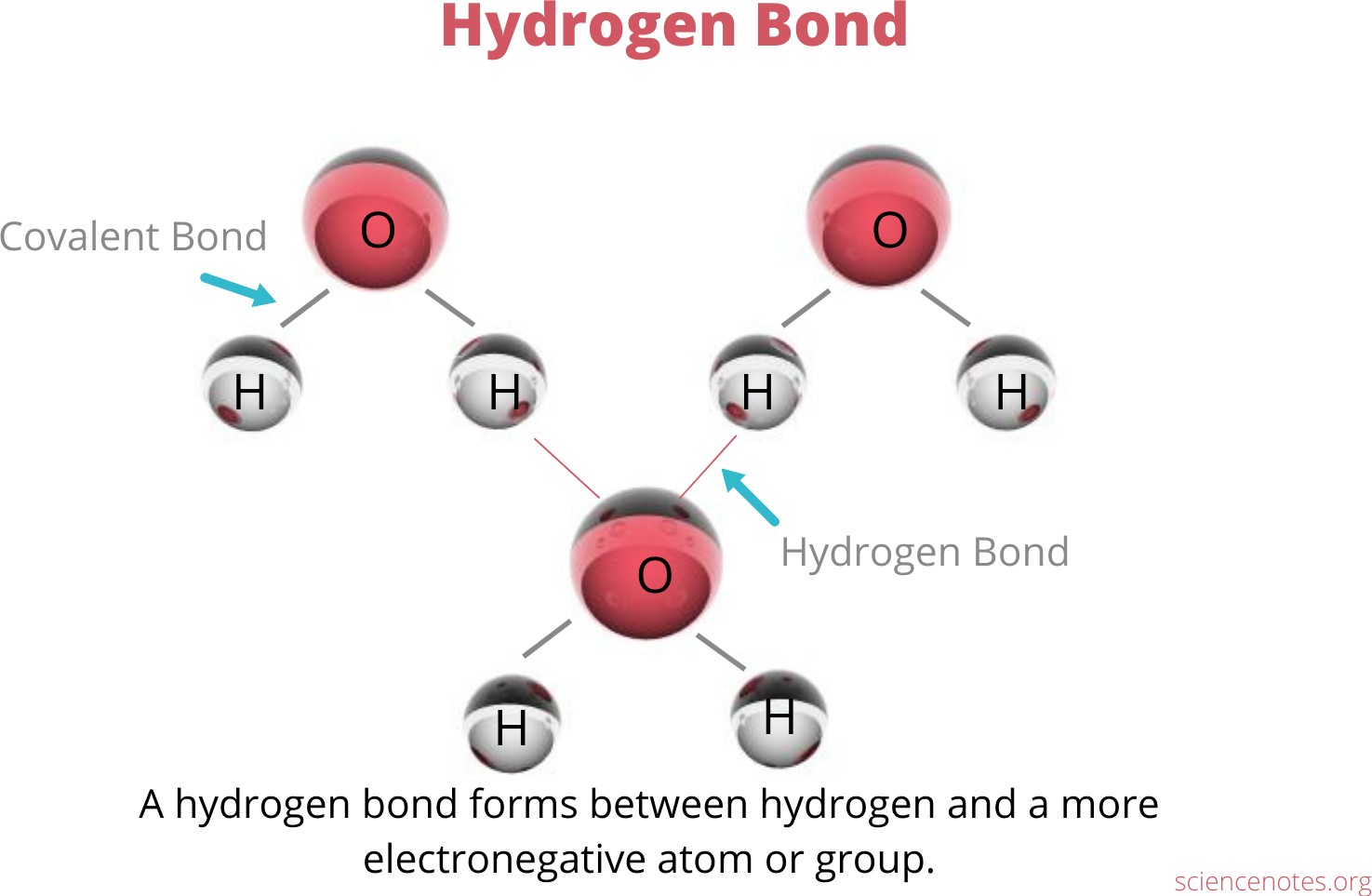 |
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
Question 8:
Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
The Correct Answer is C.Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
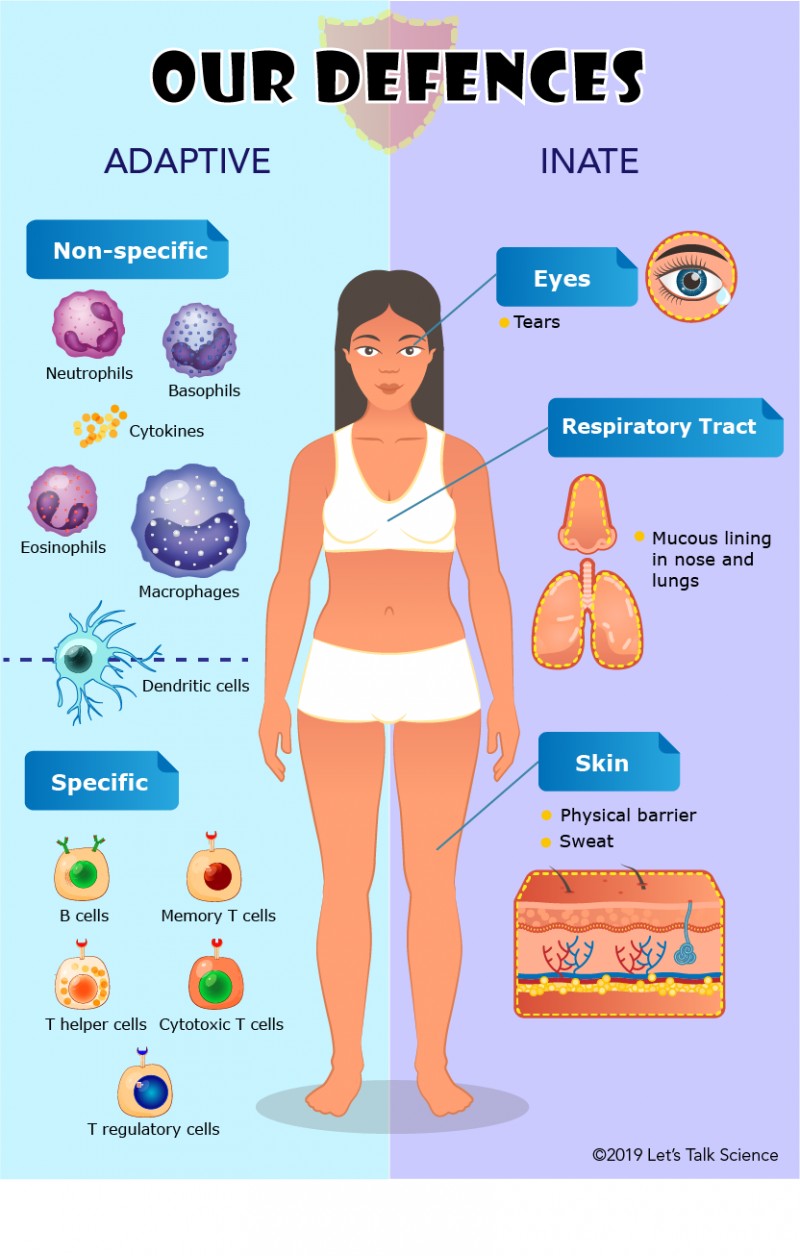
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Question 9:
Which factor is primarily responsible for the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis?
A. Hydrostatic pressure of the solution.
B. Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
C. Temperature of the solution.
D. Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules .
The Correct Answer is B.Concentration of solute particles in the solution.
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
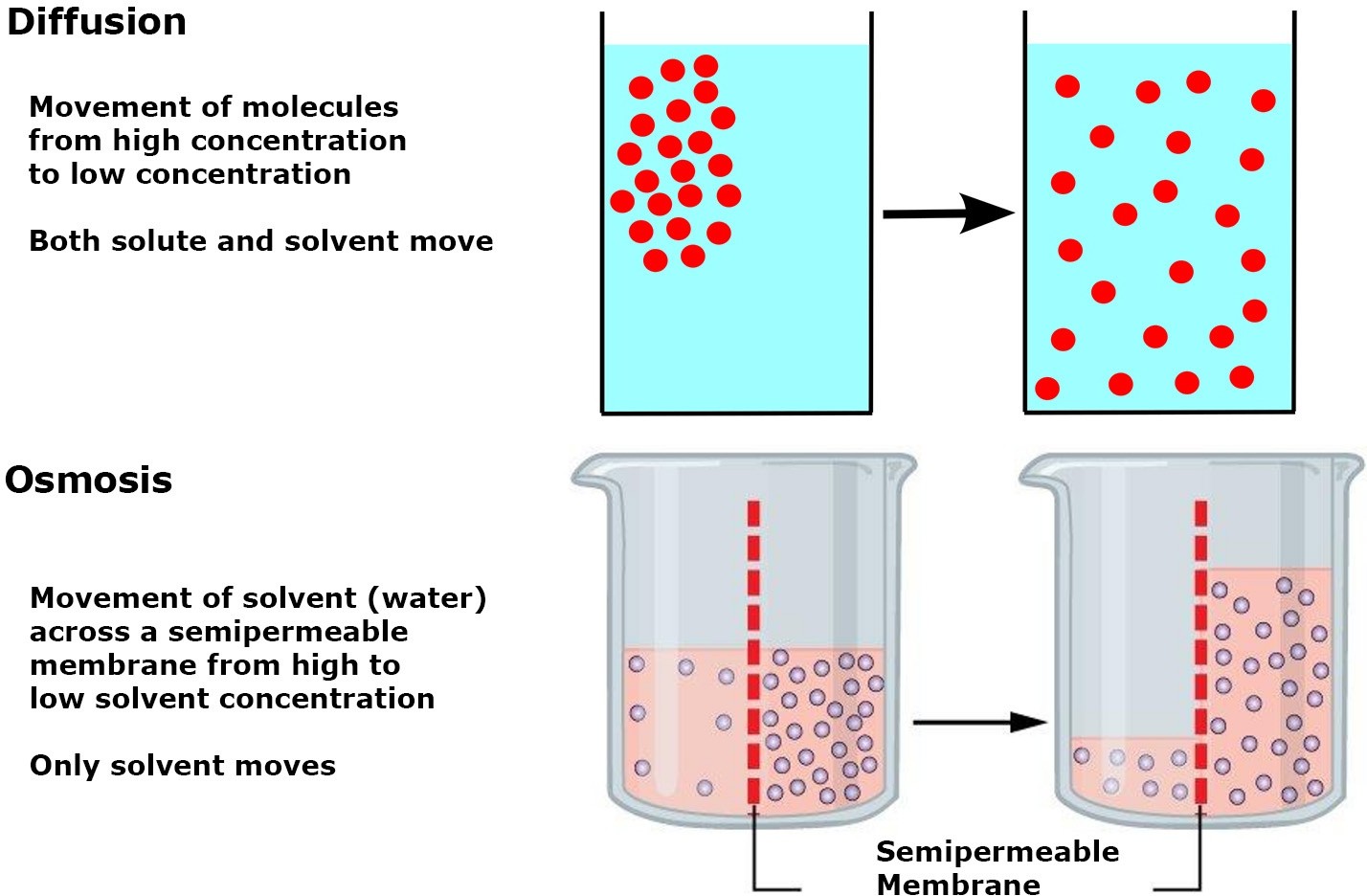
The concentration of solute particles in the solution is the primary factor that determines the movement of water across cell membranes in osmosis.
Hydrostatic pressure (choice A) can affect the movement of water across cell membranes but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Temperature (choice C) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Kinetic energy of liquid water molecules (choice D) can affect the rate of osmosis but is not the primary factor responsible for osmosis.
Question 10:
What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
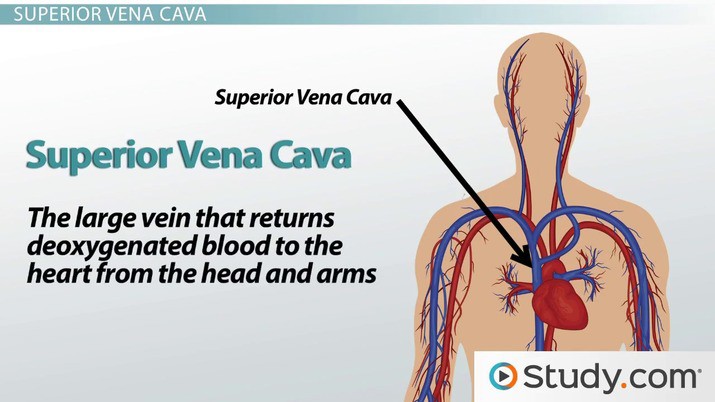
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.