What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
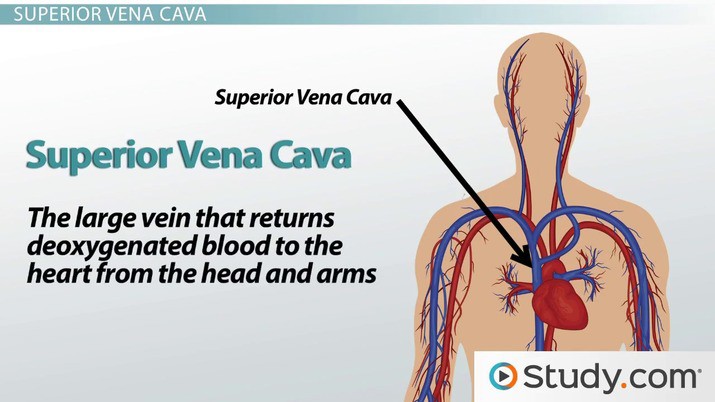
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
The Correct Answer is C.Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
Question 2:
What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
The Correct Answer is C.Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Question 3:
How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
Question 4:
A nurse is reviewing the results of a patient’s DNA sequencing test, which was performed to diagnose a genetic disorder.
The nurse notices that the patient has a mutation in one of the bases of the DNA. Which of the following is the correct term for this type of mutation?
A. Deletion
B. Insertion
C. Substitution
D. Inversion
The Correct Answer is C.The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
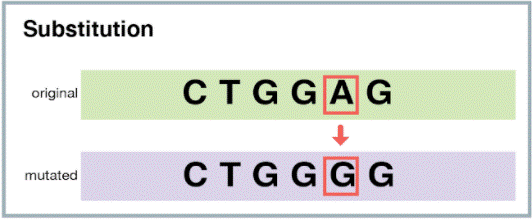 |
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
Question 5:
A nurse is conducting a research study to compare the effects of two different pain medications on postoperative patients.
The nurse randomly assigns the patients to either receive medication A or medication B. Which of the following is the best way to ensure that the study is valid and reliable?
A. Use a large sample size and a standardized procedure for administering the medications.
B. Use a placebo group and a double-blind technique for giving the medications.
C. Use a matched-pairs design and a crossover technique for switching the medications.
D. Use a convenience sample and a pretest-posttest design for measuring the pain levels.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
Using a placebo group and a double-blind technique for giving the medications is the best way to ensure that the study is valid and reliable.
A placebo group helps control for the placebo effect, which can influence the results of a study.
A double-blind technique means that neither the patients nor the researchers know which medication is being given, reducing bias.
Choice A is not the best answer because while a large sample size and standardized procedure can increase reliability, they do not address validity.
Choice C is not the best answer because a matched-pairs design and crossover technique are useful for reducing variability but do not address validity.
Choice D is not the best answer because a convenience sample may not be representative and a pretest-posttest design does not control for extraneous variables.
Question 6:
Which organ in the human body is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells?
A. Spleen
B. Kidneys
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The spleen is an organ in the human body that is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells.
Choice B is incorrect because the kidneys are responsible for filtering waste from the blood and regulating electrolyte balance.
Choice C is incorrect because the pancreas produces hormones and enzymes that aid in digestion.
Choice D is incorrect because the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism.
Question 7:
What is the name of the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion?
A. Ionization
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Isotopic decay
The Correct Answer is A.Ionization is the process in which an atom loses or gains electrons to form an ion.
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Choice B is not the best answer because oxidation refers to the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule.
Choice C is not the best answer because reduction refers to the gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
Choice D is not the best answer because isotopic decay refers to the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
Question 8:
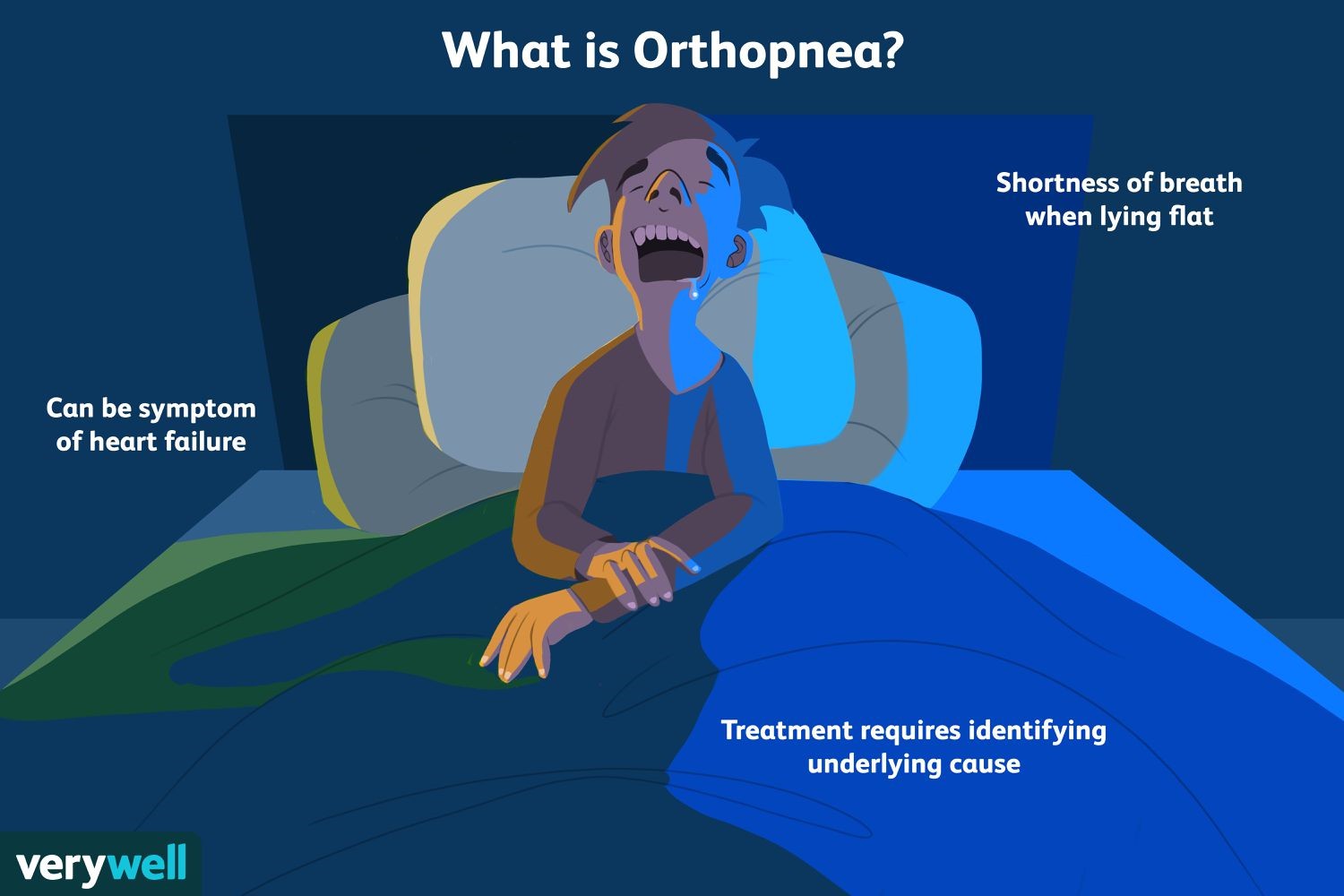
Which of the following refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand?
A. Orthopnea
B. Hypoxia
C. Tachypnea
D. Bradypnea
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Orthopnea.
Orthopnea refers to a condition in which a patient experiences difficulty breathing while lying down, but their breathing improves when they sit up or stand.
 |
Choice B, Hypoxia, is not the correct answer because it refers to a condition in which there is a lack of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Choice C, Tachypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to rapid breathing.
Choice D, Bradypnea, is not the correct answer because it refers to abnormally slow breathing.
Question 9:
A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis.
What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
The Correct Answer is C.Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
Question 10:
Which of the following structures in the nephron is responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients?
A. Distal tubule
B. Proximal tubule
C. Glomerulus
D. Loop of Henle
The Correct Answer is B.Proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is responsible for reabsorbing all the nutrients and most of the water.
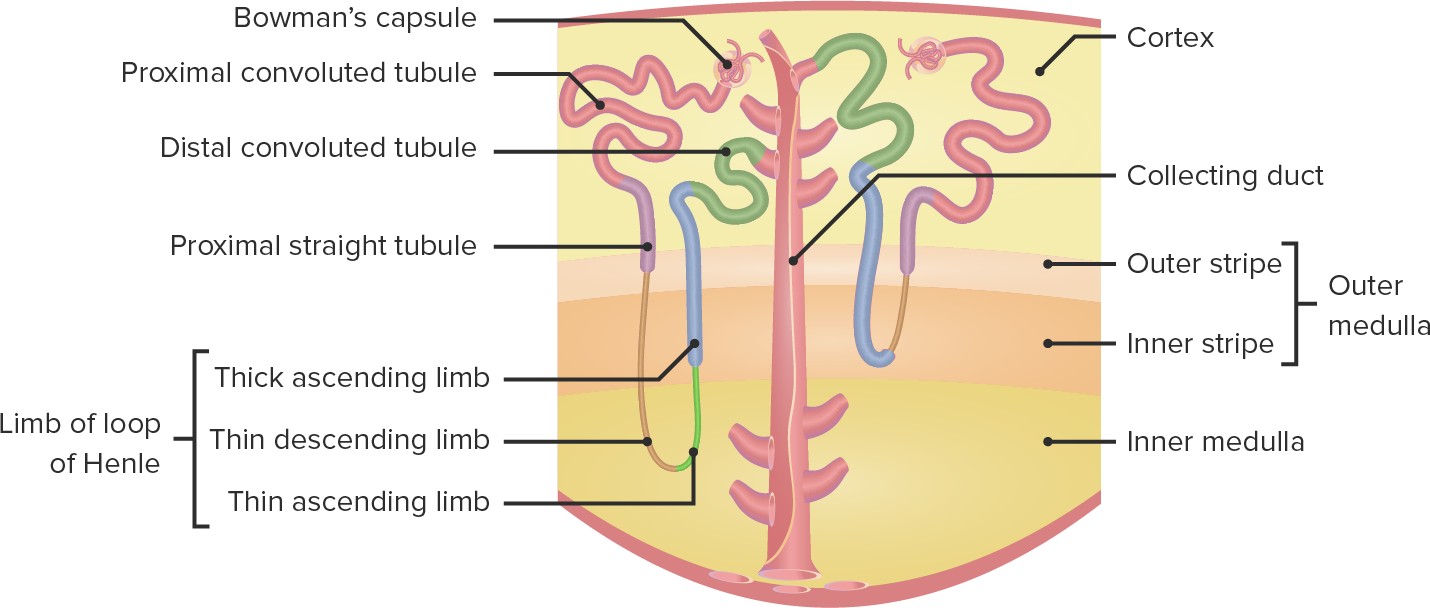 |
Choice A is incorrect because the distal tubule is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.
Choice C is incorrect because the glomerulus is responsible for filtering fluid and solutes out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate.
Choice D is incorrect because the Loop of Henle is not primarily responsible for reabsorbing ions, water and nutrients.