What is the name of the dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing?
A. Diaphragm
B. Trachea
C. Bronchus
D. Alveoli
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
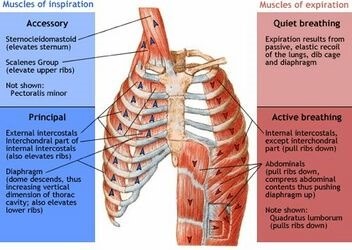
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 1
Question 1:
Which of the following types of RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis?
A. Messenger RNA
B. Ribosomal RNA
C. Transfer RNA
D. Small nuclear RNA
The Correct Answer is C.Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific sequence of three nucleotides called an anticodon, which pairs with a complementary codon in the messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence. Each tRNA also carries a specific amino acid that corresponds to the codon it recognizes, allowing the ribosome to link the amino acids together in the correct order to form a protein.
In contrast, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome itself, where it helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is involved in splicing of pre-mRNA molecules during post-transcriptional processing.
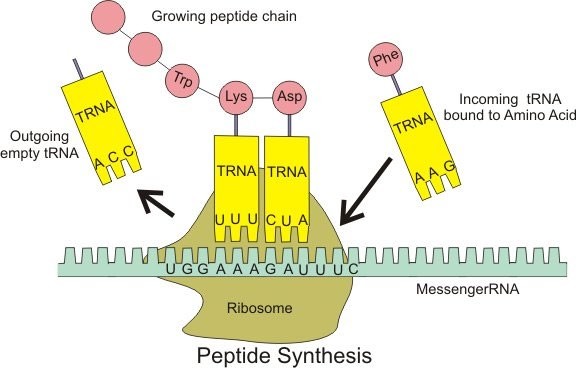 |
Question 2:
Which of the following is NOT one of the four primary tissue types found in the human body?
A. Epithelial
B. Nervous
C. Connective
D. Exocrine glandular
The Correct Answer is D.Exocrine glandular is not one of the four primary ssue types found in the human body. The four primary ssue types are epithelial, nervous, connective, and muscle.
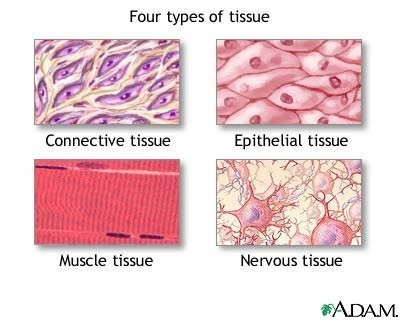
Question 3:
What is the role of the epididymis in sperm maturation?
A. The epididymis produces sperm cells.
B. The epididymis stores and protects sperm cells until ejaculation.
C. The epididymis is responsible for the transport of sperm cells from the testes to the urethra.
D. The epididymis provides nourishment to sperm cells.
The Correct Answer is B.The epididymis is a coiled tube located at the back of each testicle where the sperm mature and are stored until ejaculation. Sperm are produced in the testes and then transported to the epididymis where they undergo maturation and become motile. The epididymis provides a protective environment for the sperm, allowing them to mature and become more resilient to external stressors. During ejaculation, the sperm are transported from the epididymis to the vas deferens and then to the urethra for ejaculation.
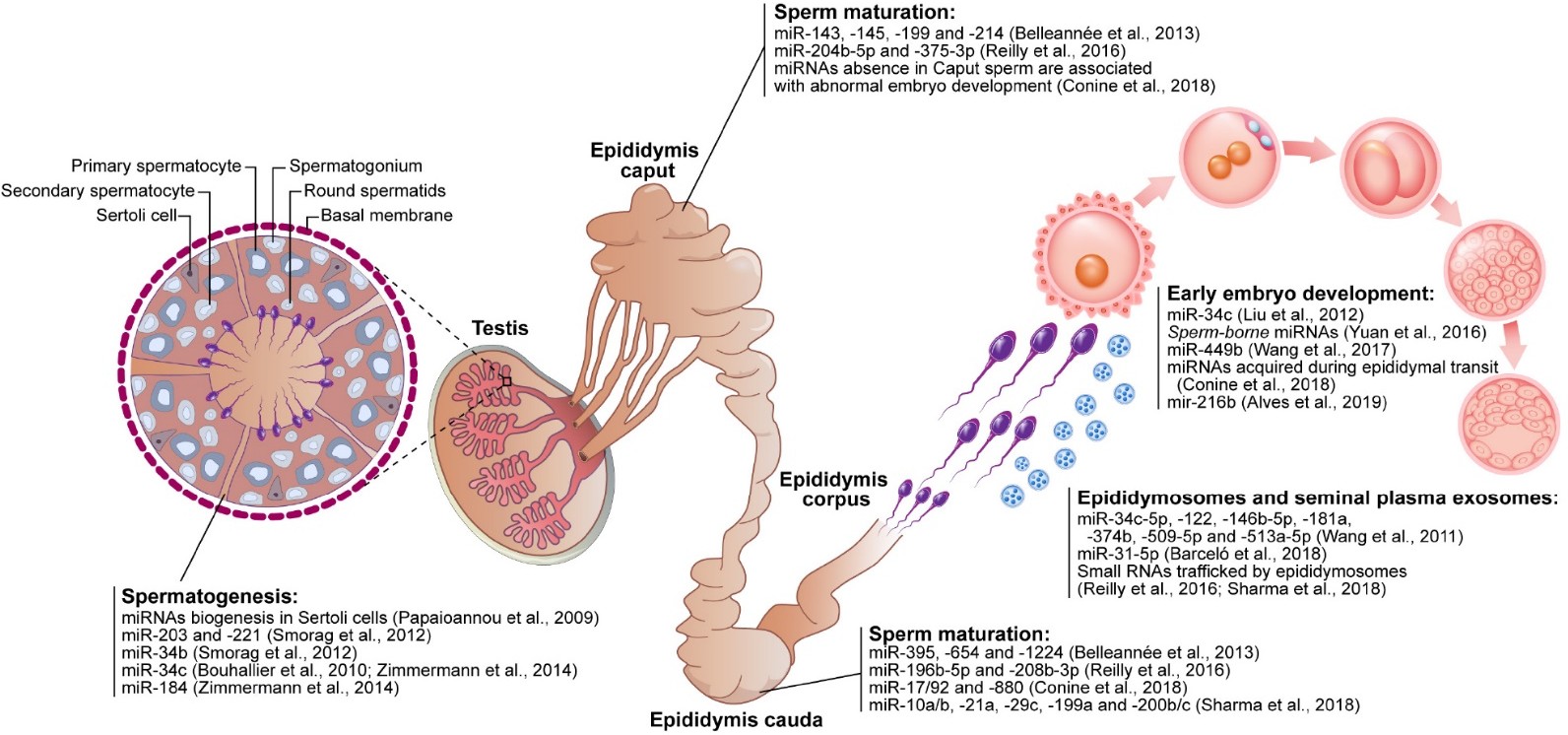 |
Question 4:
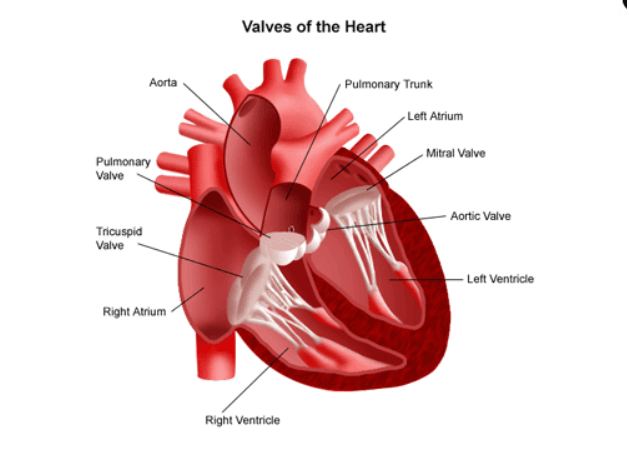
What is the name of the valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle in the heart?
A. Aortic valve
B. Mitral valve
C. Tricuspid valve
D. Pulmonary valve
The Correct Answer is B.The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
Question 5:
Which of the following is a chemical property of a substance?
A. Density
B. Melting point
C. Boiling point
D. Reactivity with acid
The Correct Answer is D.Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance. Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance.
Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
Question 6:
A researcher collects data on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month. This data would be most useful to analyze which of the following:
A. traffic patterns during rush hour
B. pedestrian movement during the day
C. air pollution levels in the area
D. noise levels in the area
The Correct Answer is A.The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic patterns during rush hour.
Question 7:
Which of the following is a characteristic of innate immunity?
A. It is highly specific to particular pathogens.
B. It is acquired over time through exposure to pathogens.
C. It provides immediate, non-specific protection.
D. It involves the production of antibodies.
The Correct Answer is C.Innate immunity is a fundamental aspect of the body's defense mechanism that operates from birth. It offers immediate protection against a wide range of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, without requiring prior exposure to these invaders.
This defense system is non-specific, meaning it doesn't target a particular pathogen but rather provides a generalized response to various threats. Innate immunity includes physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, as well as cellular components such as phagocytes and natural killer cells. These elements work together to detect and neutralize potential threats swiftly, preventing infections from taking hold in the body.
Question 8:
What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
A. Elbow joint
B. Hip joint
C. Knee joint
D. Shoulder joint
The Correct Answer is D.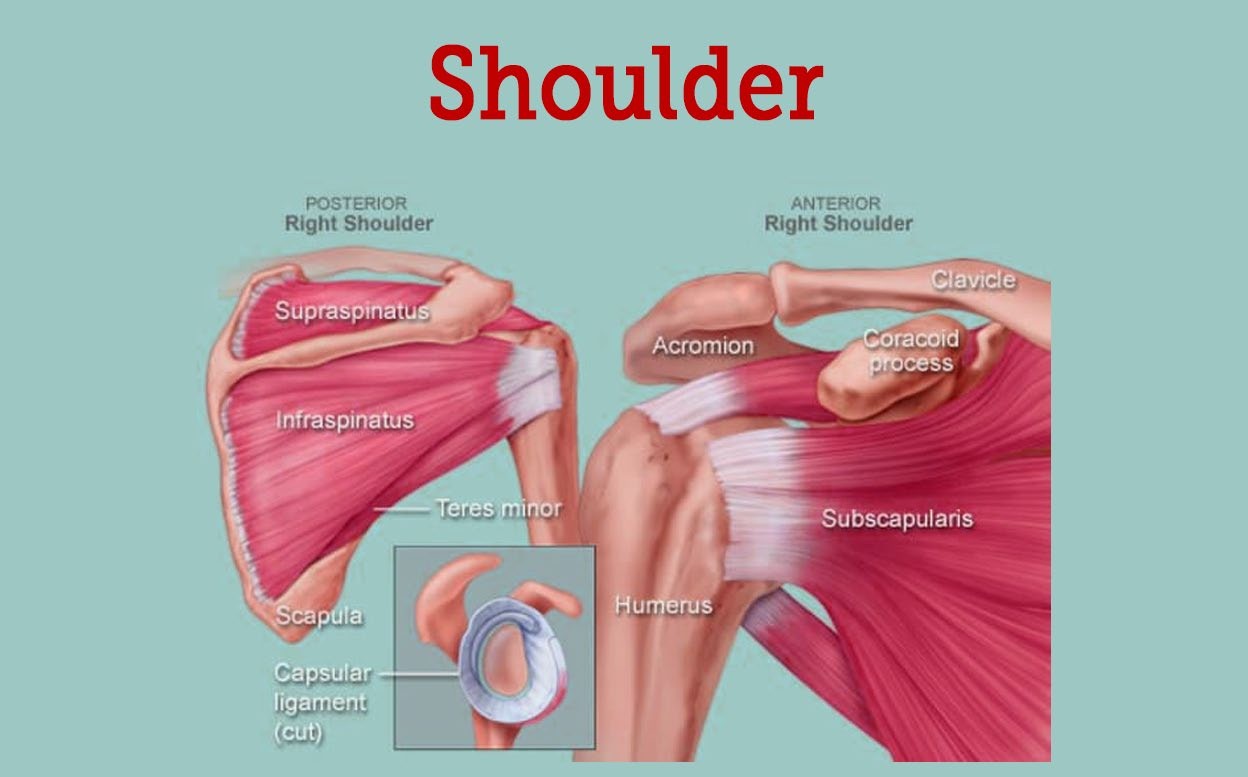 |
Question 9:
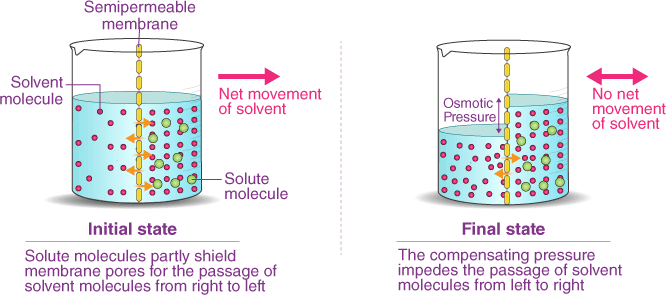
Which of the following describes the process of osmosis?
A. Movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
B. Movement of substances against a concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
C. Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
D. Movement of substances into a cell by engulfing them with the plasma membrane.
The Correct Answer is C.Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes
than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
 |
Question 10:
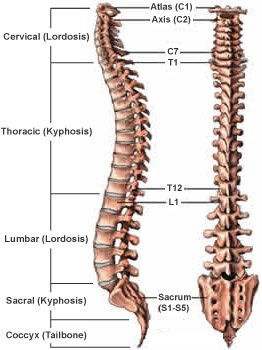
What are the five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards?
A. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
B. Thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
C. Lumbar, thoracic, cervical, coccygeal, sacral
D. Sacral, lumbar, cervical, thoracic, coccygeal
The Correct Answer is A.The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
2. Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
3. Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
4. Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
5. Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |