What is the name of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the human body?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Estrogen
D. Testosterone
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
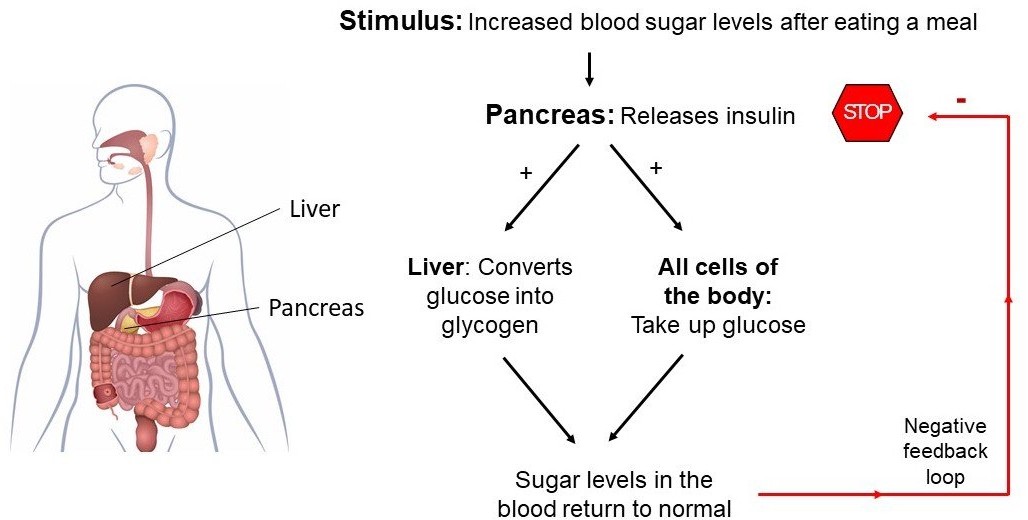
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. After a person eats a meal, the levels of glucose in the blood rise, which stimulates the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts on various cells in the body, particularly those in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue, to promote the uptake, use, and storage of glucose.
Insulin helps to lower the levels of glucose in the blood by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells, stimulating the liver and muscle cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen, and inhibiting the production and release of glucose by the liver. This process is known as glucose homeostasis, and it helps to keep the levels of glucose in the blood within a normal range.
Deficiencies or abnormalities in insulin production or function can lead to a range of metabolic disorders, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 3
Question 1:
Which of the following is a chemical property of a substance?
A. Density
B. Melting point
C. Boiling point
D. Reactivity with acid
The Correct Answer is D.Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance.
Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance. Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
Question 2:
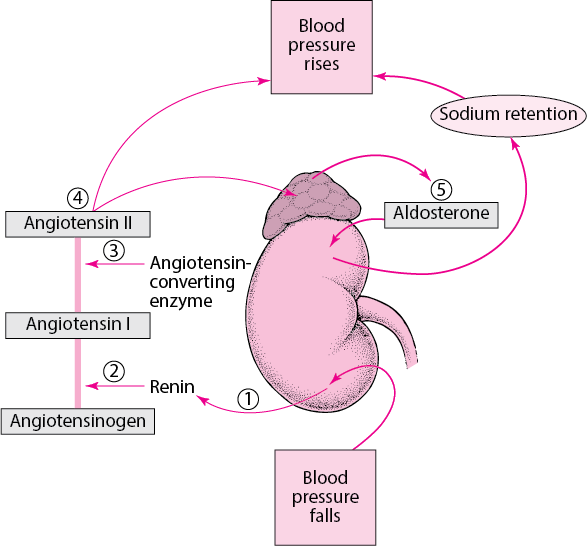
Which of the following substances is excreted by the kidneys to regulate blood pressure?
A. renin
B. erythropoietin
C. calcitriol
D. urobilinogen
The Correct Answer is A.Renin is an enzyme that is produced by the kidneys and it acts to elevate blood pressure. When blood pressure falls, the kidneys secrete renin into the bloodstream ³.
 |
Question 3:
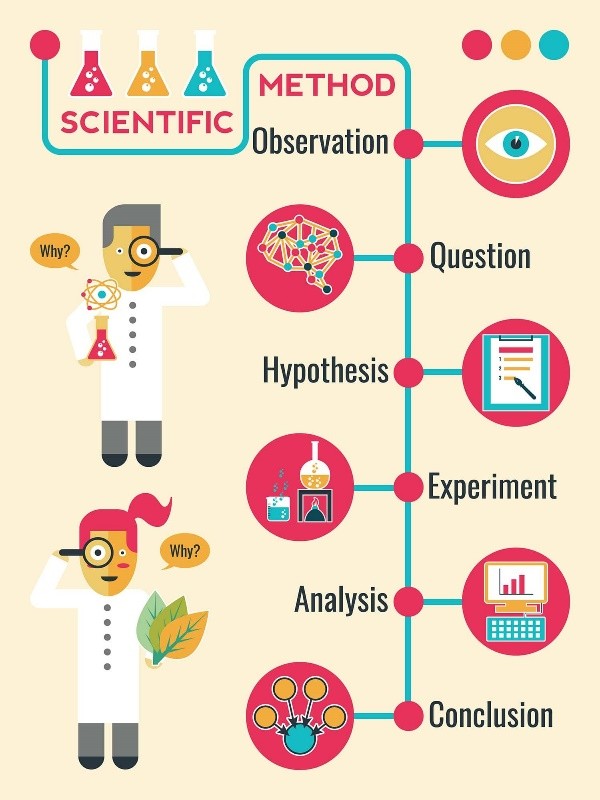
What are the steps involved in the scientific method?
A. Observation, hypothesis, prediction, experimentation, analysis, conclusion.
B. Hypothesis, observation, prediction, experimentation, analysis, conclusion.
C. Prediction, observation, experimentation, analysis, conclusion, hypothesis.
D. Observation, data collection, analysis, experimentation, hypothesis, conclusion.
The Correct Answer is A.The scientific method is a systematic approach used to answer questions or test hypotheses about the natural world. The steps involved in the scientific method are:
- Observation: This is the first step in the scientific method. It involves observing a phenomenon or a problem and gathering information about it.
- Hypothesis: After making an observation, a scientist forms a hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the phenomenon or problem.
- Prediction: Based on the hypothesis, the scientist makes a prediction about what will happen in an experiment or what they will observe.
- Experimentation: The scientist designs and conducts an experiment to test the hypothesis and prediction.
- Analysis: The data collected from the experiment are analyzed to determine if they support or refute the hypothesis.
- Conclusion: Based on the analysis of the data, the scientist draws a conclusion about whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted.
Option b) is incorrect because it starts with hypothesis before observation. Option c) is incorrect because prediction comes before experimentation. Option d) is incorrect because hypothesis comes after observation and data collection.
 |
Question 4:
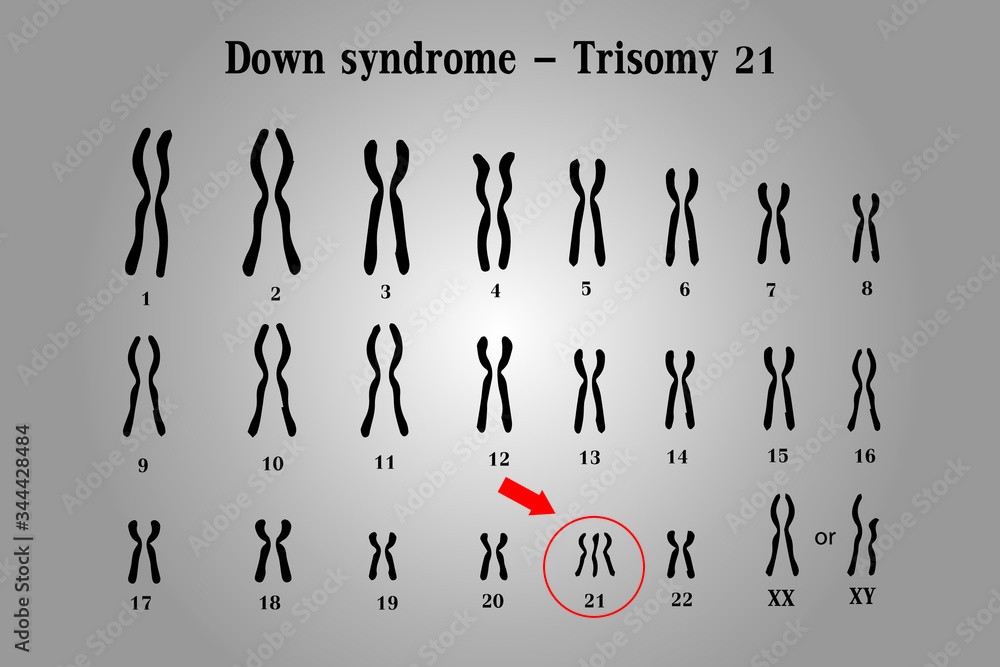
What is the name of the genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Klinefelter syndrome
C. Down syndrome
D. Huntington's disease
The Correct Answer is C.Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is also known as trisomy 21, because affected individuals have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two.
The extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome occurs due to a random error in cell division, which leads to the production of an abnormal gamete (egg or sperm) with an extra copy of the chromosome. When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, and develops into a fetus with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is characterized by a range of physical and intellectual symptoms, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, heart defects, and increased risk of certain medical conditions such as leukemia and Alzheimer's disease. However, the severity and expression of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
 |
Question 5:
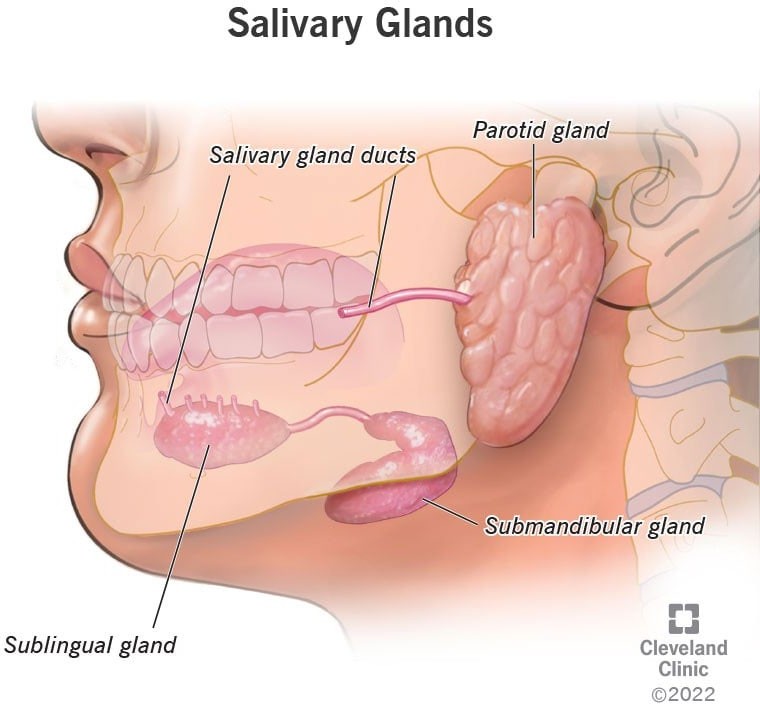
What are the three types of salivary glands and where are they located in the mouth?
A. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the cheeks, tongue, and roof of the mouth, respectively.
B. Sublingual, submandibular, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
C. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the roof of the mouth, cheeks, and under the jawbone, respectively.
D. Sublingual, parotid, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
The Correct Answer is C.The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands.
- Parotid glands are located just in front of your ears.
- Sublingual glands are located below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth.
- Submandibular glands are located below your jaw.
 |
Question 6:
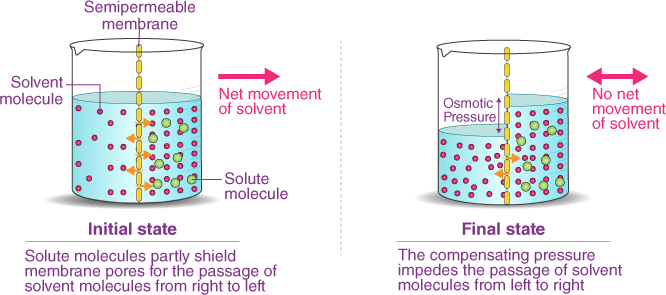
Which of the following describes the process of osmosis?
A. Movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
B. Movement of substances against a concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
C. Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
D. Movement of substances into a cell by engulfing them with the plasma membrane.
The Correct Answer is C.Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
 |
Question 7:
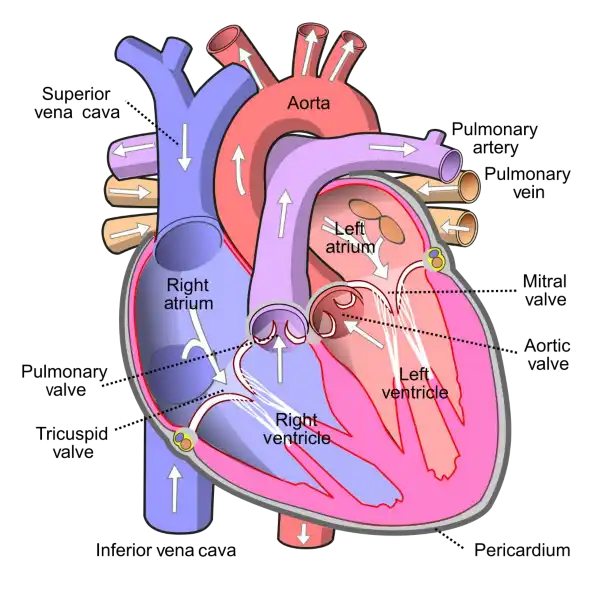
What is the name of the valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle in the heart?
A. Aortic valve
B. Mitral valve
C. Tricuspid valve
D. Pulmonary valve
The Correct Answer is B.The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
 |
Question 8:
During embryonic development, which of the following germ layers forms the nervous system?
A. Ectoderm
B. Endoderm
C. Mesoderm
D. Exoderm
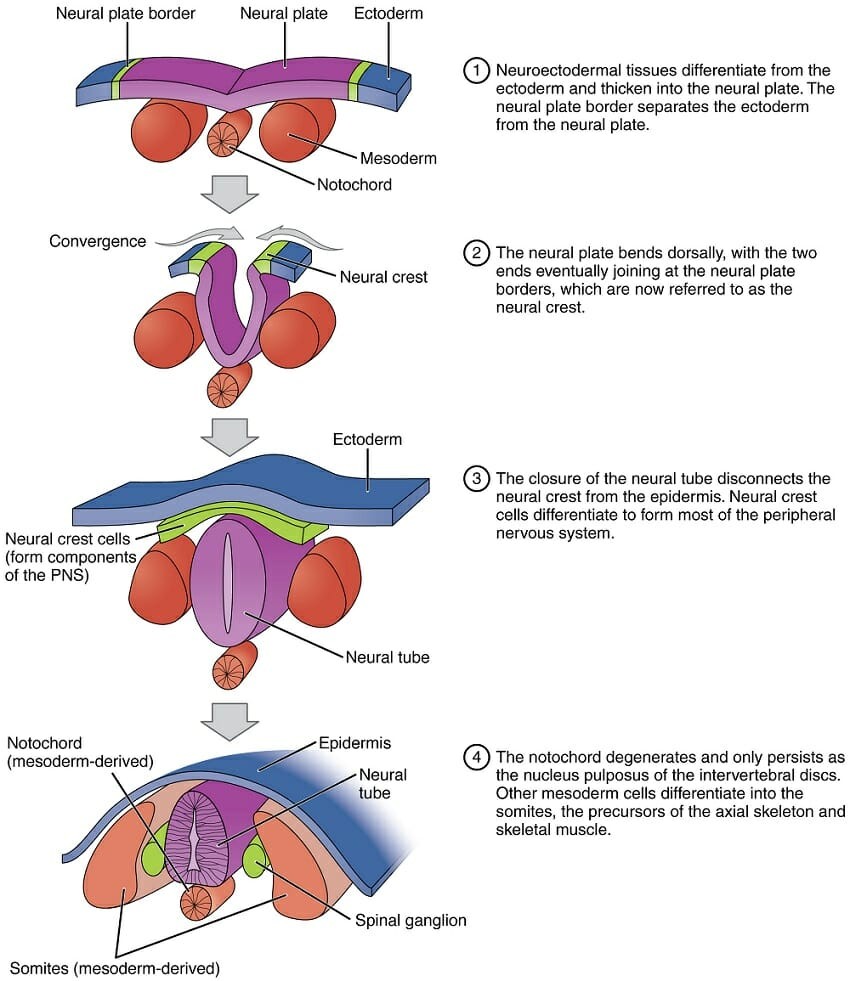
The Correct Answer is A.The three germ layers that form during embryonic development are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The ectoderm is the outermost layer, and it gives rise to the skin, hair, nails, and nervous system. The nervous system develops from a specialized region of the ectoderm called the neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube. The neural tube ultimately gives rise to the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system, as well as the peripheral nervous system. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts, while the mesoderm gives rise to the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, and several other organs. The exoderm is not a germ layer and does not exist during embryonic development.
Question 9:
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
A. Calcium binds to tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
B. Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to initiate the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
C. Calcium activates the motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction.
D. Calcium is required for the relaxation of muscles after contraction.
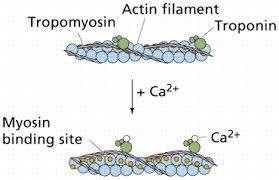
The Correct Answer is B.Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
Question 10:
Which of the following describes the function of ligaments?
A. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to bone
B. Ligaments attach two bones
C. Ligaments attach bones to tendons
D. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to tendons
The Correct Answer is B.Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, preventing excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.