What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 2
Question 1:
A researcher notices a positive correlation between the height of a plant and nutrient concentration over time. Based on this observation, what conclusion does he reach?
A. The height of a plant increases in the absence and presence of the nutrients
B. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant decreases, its height increases.
C. The amount of nutrients available to a plant is independent of how tall the plant gets
D. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant increases, its height also increases.
The Correct Answer is D.Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations. Correlations measure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Question 2:
Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
The Correct Answer is D.Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
Question 3:
What solution has a pH of 7?
A. Aniline
B. Pyridine
C. Pure water
D. Sodium hydroxide
The Correct Answer is C.A pH of 7 is a neutral solution, which is how pure water is classified. Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
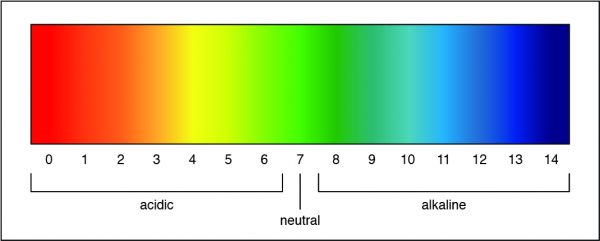
Question 4:
What type of bond forms between nitrogen and oxygen, and why?
A. Ionic, because electrons are shared
B. Covalent, because electrons are shared
C. Ionic, because electrons are transferred
D. Covalent, because electrons are transferred
The Correct Answer is B.Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, which means they will share electrons in a covalent bond. For example, two oxygen atoms form a double bond, in which two pairs of electrons (four electrons total) are shared. Similarly, two nitrogen atoms form a molecule with a triple bond, in which three pairs of electrons (six electrons total) are shared.
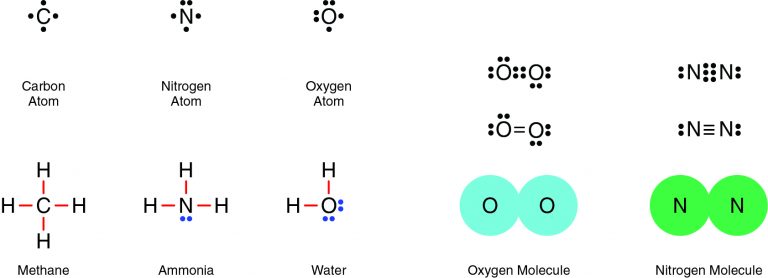
Question 5:
Which of the following are included in the male reproductive system?
A. the penis and epididymis
B. the vas deferens and uterus
C. the penis and Fallopian tubes
D. the penis, scrotum, and cervix
The Correct Answer is A.The main male reproductive organs are the penis and the testicles, which are located external to the body. The penis is composed of a long shaft and a bulbous end called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually surrounded by an extension of skin called the foreskin.
The testes (analogous to the female ovaries), or testicles, are retained in a pouch of skin called the scrotum, which descends from the base of the penis. The scrotum contains nerves and blood vessels needed to support the testicles’ functions. Each testicle (or testis) produces sperm (analogous to the female ova), which are passed into a series of coiled tubules called the epididymis. The epididymis stores and nurtures sperm until they are passed into the vas deferens, a tubule that is about 30 centimeters long, extending from the testicle into the pelvis and ending at the ejaculatory duct.
The epididymis and vas deferens are supported by several accessory glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper glands) that produce fluid components of semen and support the sperm cells.
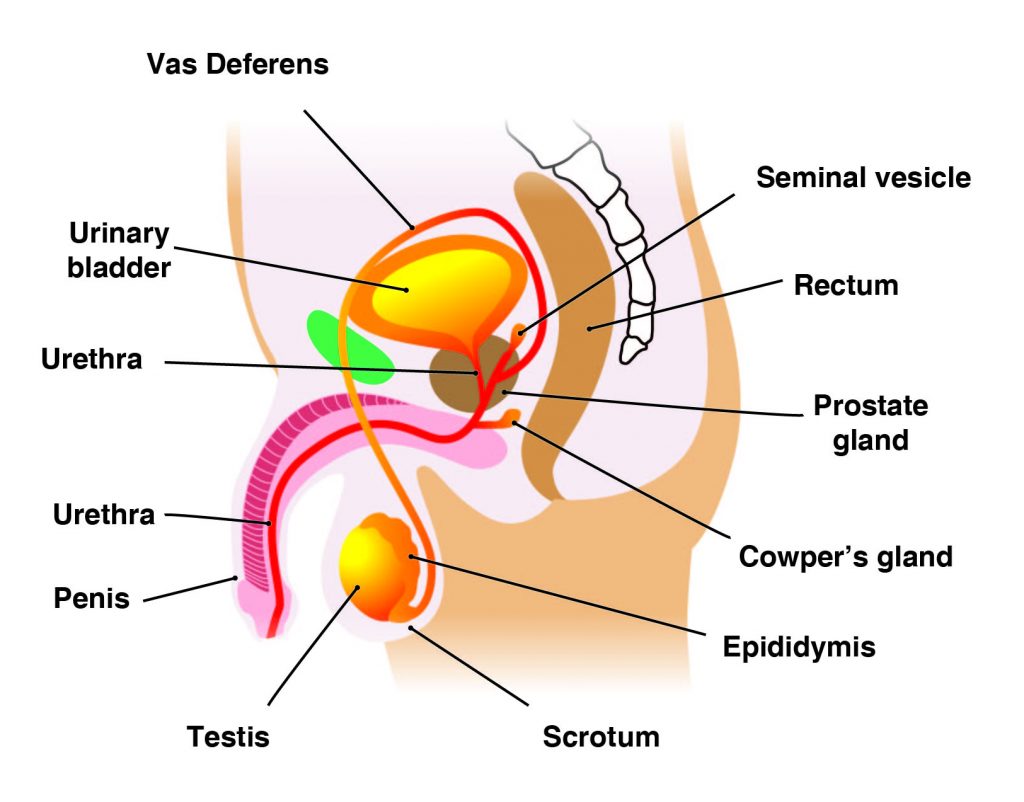
Question 6:
What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
The Correct Answer is D.The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
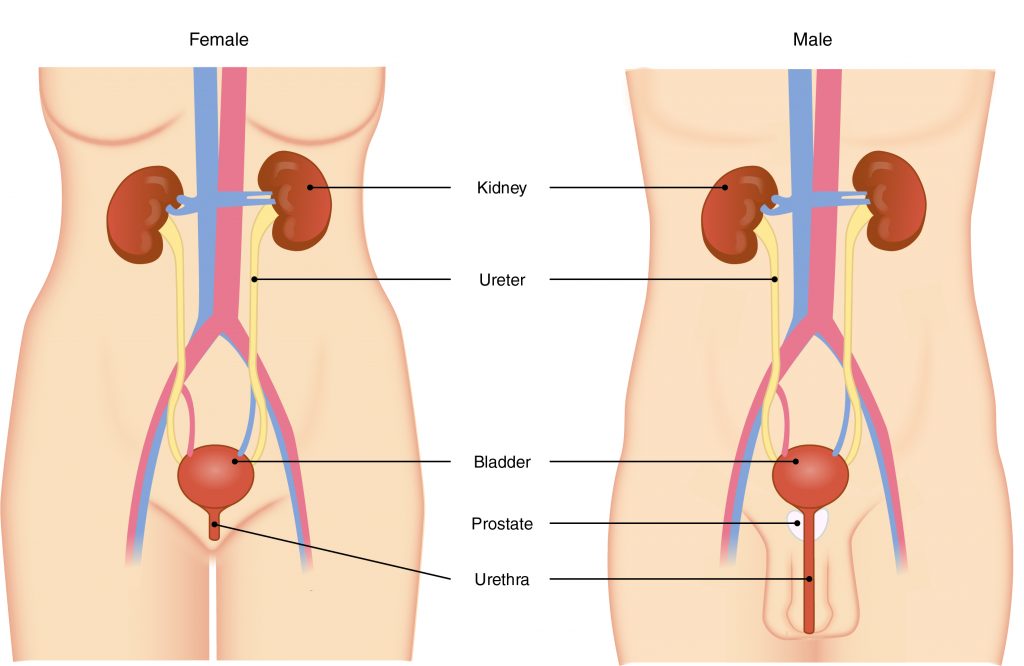
Question 7: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
The Correct Answer is A. Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.Question 8:
Which choice best describes homeostasis?
A. A functional system of the body
B. Blood flow to every cell in the body
C. A relatively constant environment within the body
D. Neural pathways that have integrated into the body
The Correct Answer is C.Homeostasis is the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body. Each cell of the body is surrounded by a small amount of fluid, and the normal functions of each cell depend on the maintenance of its fluid environment within a narrow range of conditions, including temperature, volume, and chemical content. These conditions are known as variables. For example, body temperature is a variable that can increase in a hot environment or decrease in a cold environment.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms in the human body: negative and positive.
- Negative Feedback: Most systems of the body are regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, which maintain homeostasis. Negative means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted. The maintenance of normal blood pressure is a negative-feedback mechanism. Normal blood pressure is important because it is responsible for moving blood from the heart to tissues.
- Positive Feedback: Positive-feedback mechanisms are not homeostatic and are rare in healthy individuals. Positive means that when a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response of the system is to make the deviation even greater. Positive feedback therefore usually creates a cycle leading away from homeostasis and, in some cases, results in death. Inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of positive feedback.
Question 9:
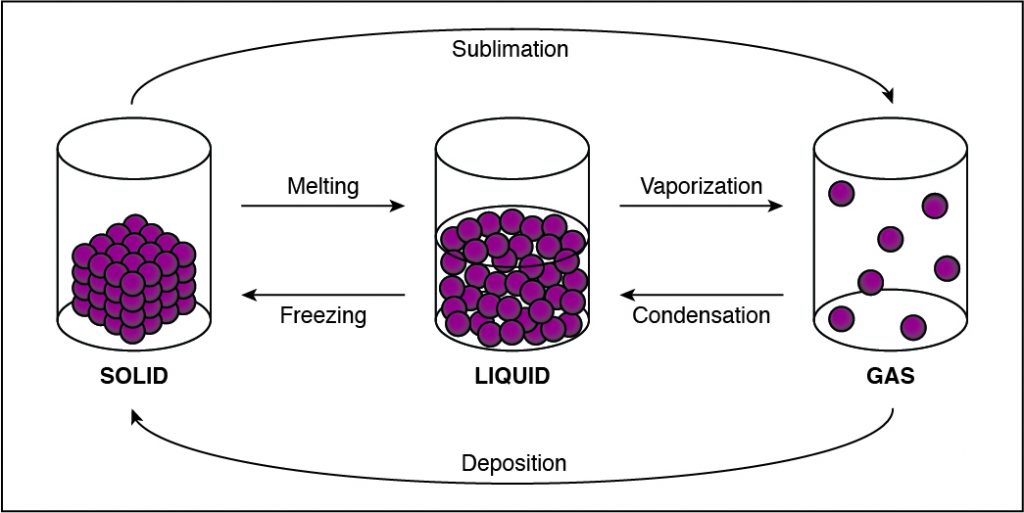
In which state of matter are the intermolecular forces between particles in a substance the strongest?
A. Gas
B. Liquid
C. Plasma
D. Solid
The Correct Answer is D.In solids, particles are usually closer together than in other states of matter because of the strong cohesive forces between the particles.
- Solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas differ from one another in the amount of energy that the particles have and the strength of the cohesive forces that hold the particles together.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Question 10:
When would a cell most likely contain the most nucleotides?
A. S
B. G1
C. M
D. G2
The Correct Answer is B.A cell copies its DNA during the S phase, and nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Thus, the step preceding the S phase, the G1 phase, is the phase of the cell cycle when the cell would contain the most nucleotides.
For a cell to divide into more cells, it must grow, copy its DNA, and produce new daughter cells. The cell cycle regulates cellular division. This process can either prevent a cell from dividing or trigger it to start dividing.
The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
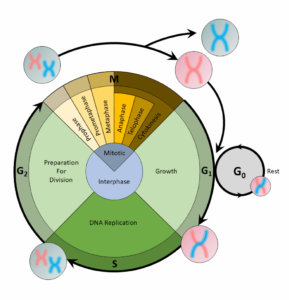
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.