Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 2
Question 1:
A student notices a pattern of stripes on five tigers. Each of the five tigers has the same stripe pattern. Using his inductive reasoning, what does he logically assume based on this information?
A. The pattern continues to change over time.
B. Natural adaptations cause this pattern to occur
C. Each offspring will have the same stripe pattern
D. Ancestors of the tigers have different stripe patterns
The Correct Answer is C.Inductive reasoning involves making specific observations and using them to make broad statements. The student observes that all of the tigers have the same stripe pattern. He can use this observation to make the broad statement that all the tigers’ offspring will have the same stripe pattern.
Inductive reasoning involves drawing a general conclusion from specific observations. This form of reasoning is referred to as the “from the bottom up” approach. Information gathered from specific observations can be used to make a general conclusion about the topic under investigation. In other words, conclusions are based on observed patterns in data.
Question 2:
Which of the following determines the strength of an acidic solution?
A. Litmus paper that turns red
B. Litmus paper that turns blue
C. Measured pH value equal to 7
D. Measured pH value less than 7
The Correct Answer is D.Both litmus paper and a pH scale can be used to indicate whether a solution is acidic. However, a pH scale can also determine the strength of an acid.
Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
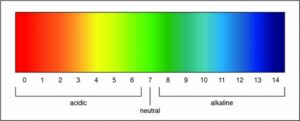
Question 3:
What raw inorganic material would an autotroph most likely use to create chemical energy for growth?
A. carbon dioxide
B. minerals in soil
C. decaying matter
D. sugar molecules
The Correct Answer is B.Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophs are organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Question 4:
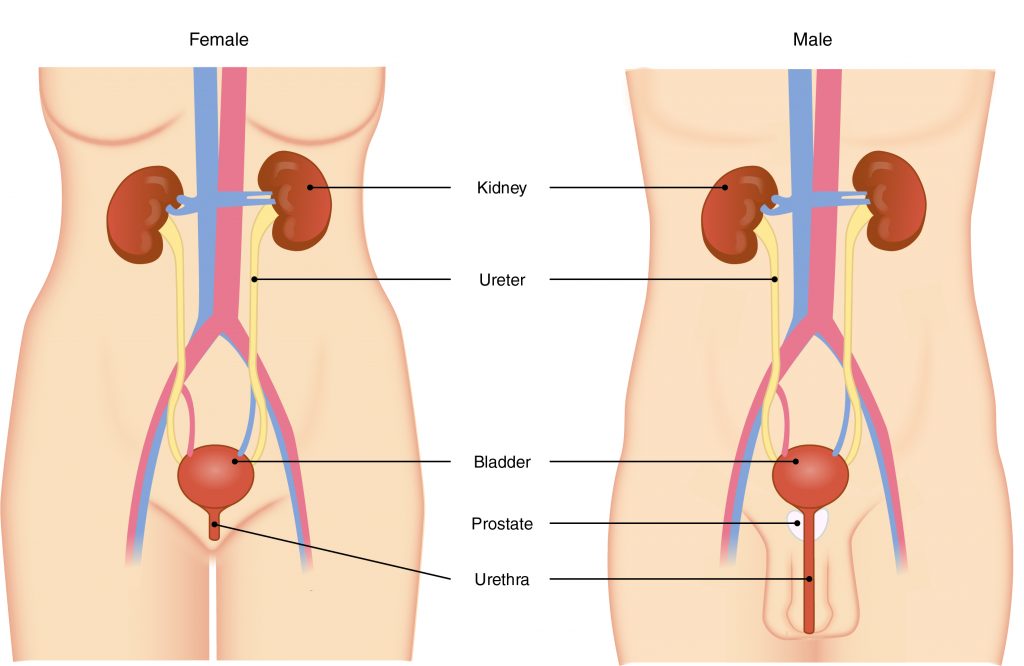
What is the final structure through which urine must travel to empty out of the body?
A. Bladder
B. Kidney
C. Ureter
D. Urethra
The Correct Answer is D.The primary organ of the urinary system is the kidney. Blood from the heart flows through the kidneys via the renal artery. As blood drains from the kidney, it exits through a series of veins, the most prominent of which is the renal vein. When urine is produced, it does not drain through the tubes through which blood flows. Rather, urine flows through two ureters before emptying into the urinary bladder.
The following steps outline how the urinary system works:
- Kidney filters and excretes wastes from blood, producing urine.
- Urine flows down the ureters.
- Urine empties into the bladder and is temporarily stored.
- Bladder, when filled, empties urine out of the body via the urethra.
Question 5:
Fertilization (the fusing of one sperm and an ovum) results in a(n) _____.
A. embryo
B. fetus
C. infant
D. zygote
The Correct Answer is D.Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating a zygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Question 6:
The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines
A. the primary structure of a codon
B. the primary structure of a protein
C. the primary structure of a nucleotide
D. the primary structure of a nucleic acid.
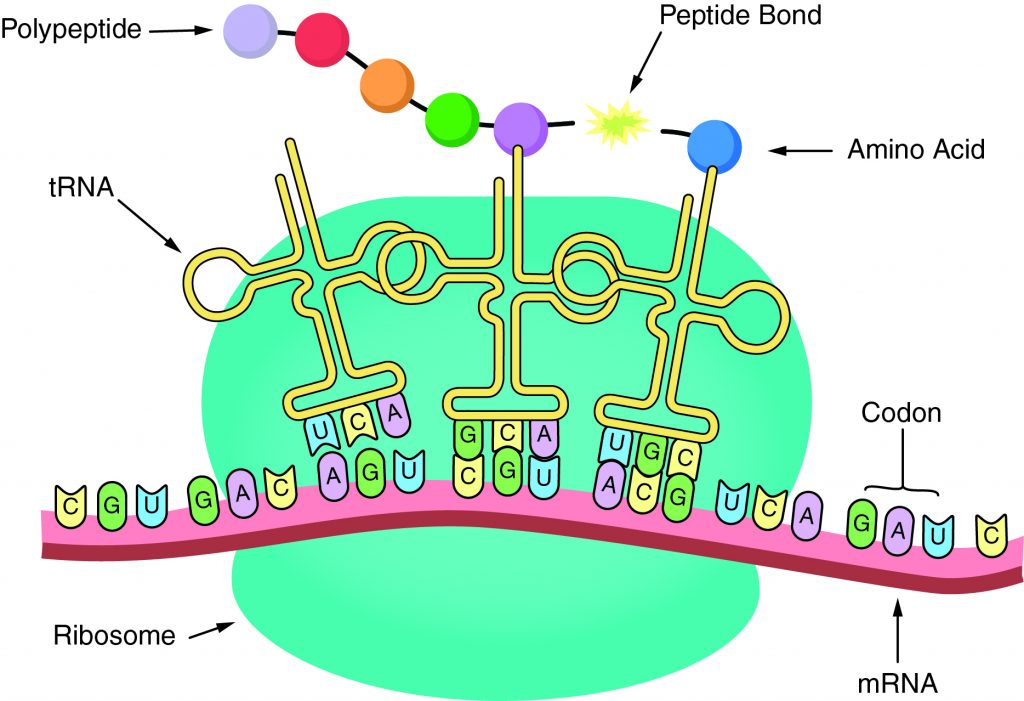
The Correct Answer is B.The sequence of amino acids in a gene determines the primary structure of a protein. The components necessary for translation are located in the cytoplasm. Translation is the making of proteins by mRNA binding to a ribosome with the start codon that initiates the production of amino acids. A peptide bond forms and connects the amino acids together. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s structure, which determines its function.
Question 7:
An intracellular chemical signal can be produced in the cell membrane. Once it is produced, where does it go?
A. To a different cell
B. To another part of the same cell
C. To a region right outside the cell
D. To an area with a high ion concentration
The Correct Answer is B.There are two major types of receptor molecules that respond to an intercellular chemical signal:
- Intracellular receptors: These receptors are located in either the cytoplasm or the nucleus of the cell. Signals diffuse across the cell membrane and bind to the receptor sites on intracellular receptors, of the same cell.
- Membrane-bound receptors: These receptors extend across the cell membrane, with their receptor sites on the outer surface of the cell membrane. They respond to intercellular chemical signals that are large, water-soluble molecules that do not diffuse across the cell membrane.
Question 8:
A researcher notices a positive correlation between the height of a plant and nutrient concentration over time. Based on this observation, what conclusion does he reach?
A. The height of a plant increases in the absence and presence of the nutrients
B. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant decreases, its height increases.
C. The amount of nutrients available to a plant is independent of how tall the plant gets
D. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant increases, its height also increases.
The Correct Answer is D.Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations. Correlations measure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Question 9:
Which of the following is a component of a chromosome?
A. Centromere
B. Gamete
C. Homologue
D. Ribose
The Correct Answer is A.The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
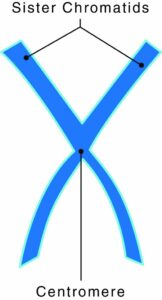
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
Question 10:
What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
The Correct Answer is B.A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.