Which of the following describes the function of ligaments?
A. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to bone
B. Ligaments attach two bones
C. Ligaments attach bones to tendons
D. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to tendons
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, preventing excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.
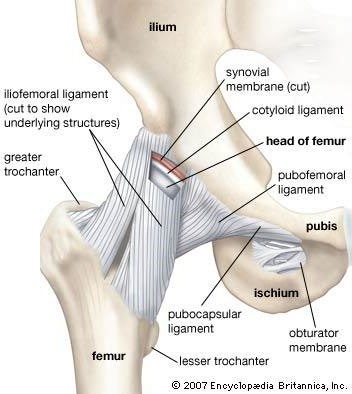
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 3
Question 1:
What is the difference between a solid and a liquid?
A. Solids have a definite shape and volume while liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape.
B. Solids have no definite shape or volume while liquids have a definite volume and take the shape of their container.
C. Solids and liquids have the same physical properties.
D. Solids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container while liquids have a definite shape and volume.
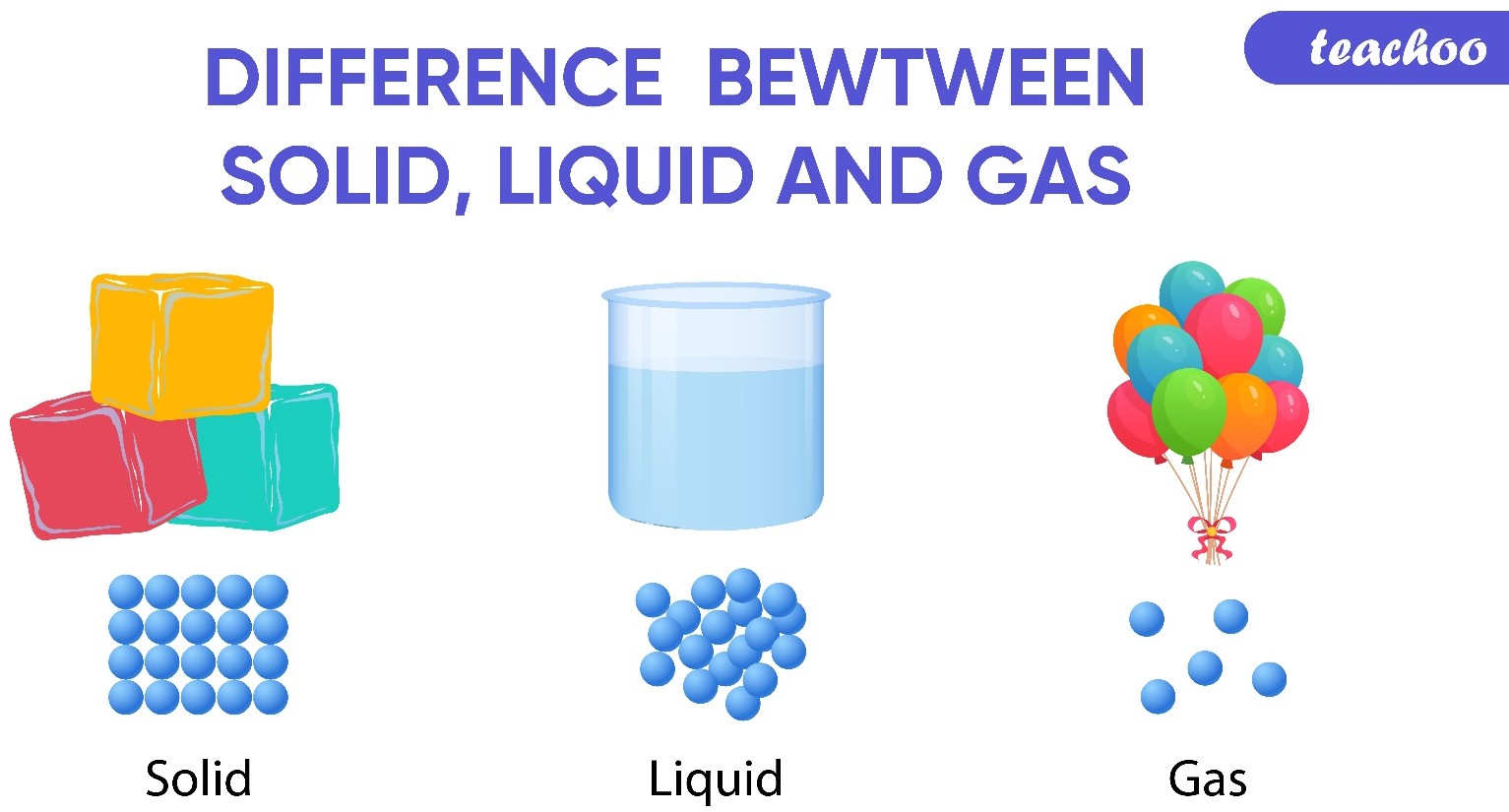
The Correct Answer is A.The main difference between a solid and a liquid is their physical state and the way their particles are arranged. In a solid, the particles are tightly packed together and have a fixed position, which gives the solid a definite shape and volume. Solids are also characterized by their high density, low compressibility, and high thermal conductivity.
In contrast, the particles in a liquid are more loosely packed and can move around each other, which allows the liquid to take the shape of its container. Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape, which means they can be poured or spilled. Liquids also have a lower density than solids, are more compressible than solids, and have lower thermal conductivity than solids.
Option b) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid. Option c) is incorrect because solids and liquids have different physical properties. Option d) is incorrect because it describes the properties of a gas, not a liquid or a solid.
 |
Question 2:
What is the name of the dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing?
A. Diaphragm
B. Trachea
C. Bronchus
D. Alveoli
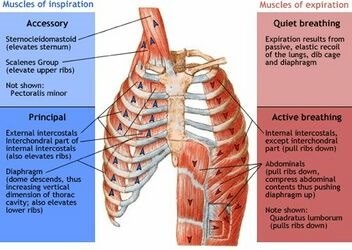
The Correct Answer is A.The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
 |
Question 3:
Which of the following units is used to indicate length?
A. kg
B. L
C. s
D. m
The Correct Answer is D.The unit used to indicate length is the meter (m). It is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
Question 4:
What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
A. A physical change involves the rearrangement of atoms and molecules while a chemical change involves the formation of new substances with different chemical properties.
B. A physical change involves the change of one state of mater to another while a chemical change involves the change of one substance into another.
C. A physical change involves the breaking of chemical bonds while a chemical change involves the breaking of intermolecular forces.
D. A physical change involves the release of energy while a chemical change involves the absorption of energy.
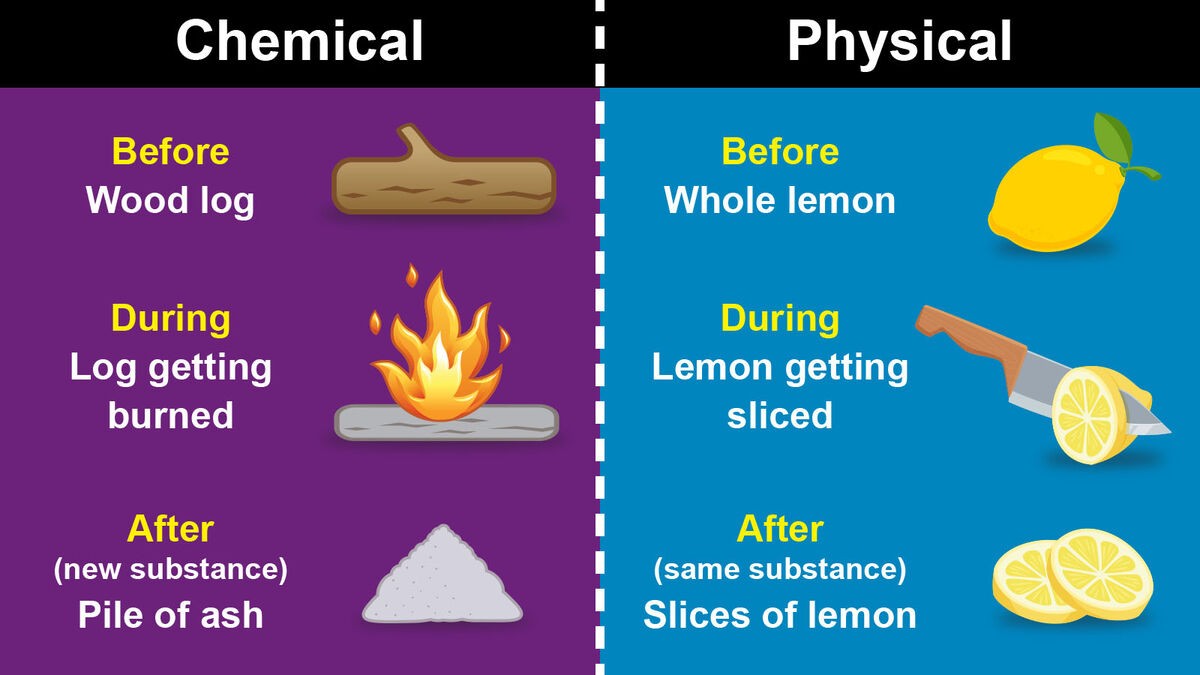
The Correct Answer is A.A physical change is a change that affects the physical properties of a substance, but does not change its chemical identity. Physical changes include changes in state, such as melting or boiling, changes in shape or size, and changes in phase, such as the dissolution of a solid in a liquid. In a physical change, the atoms and molecules of the substance are rearranged, but no new substances are formed.
A chemical change, on the other hand, is a change that results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties. Chemical changes involve the breaking of chemical bonds between atoms and the formation of new bonds to create new compounds. Chemical changes are usually accompanied by a change in color, the formation of a gas or a solid, or the release or absorption of energy.
Overall, the main difference between a physical change and a chemical change is that a physical change only affects the physical properties of a substance while a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties.
 |
Question 5:
What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
A. To produce energy for the cell
B. To store genetic information
C. To transport molecules within the cell
D. To synthesize proteins in the cell
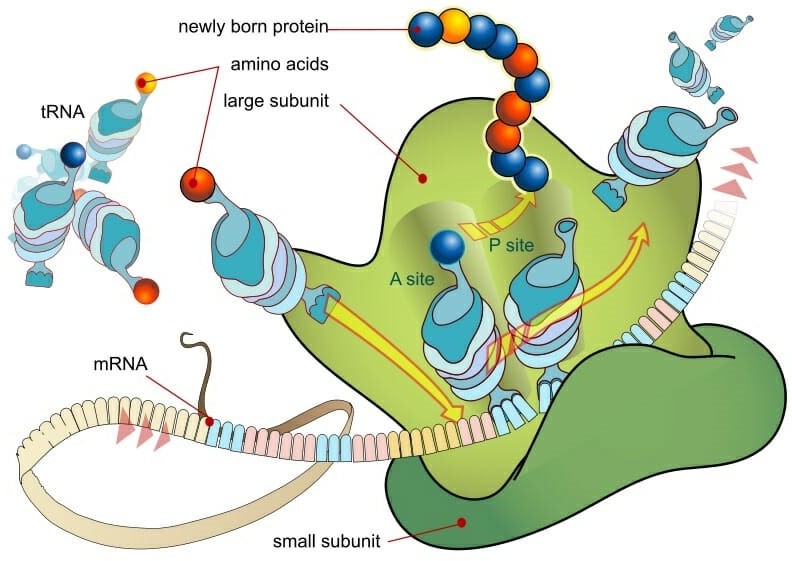
The Correct Answer is D.Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
Question 6:
What is the name of the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels in the human body?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Estrogen
D. Testosterone
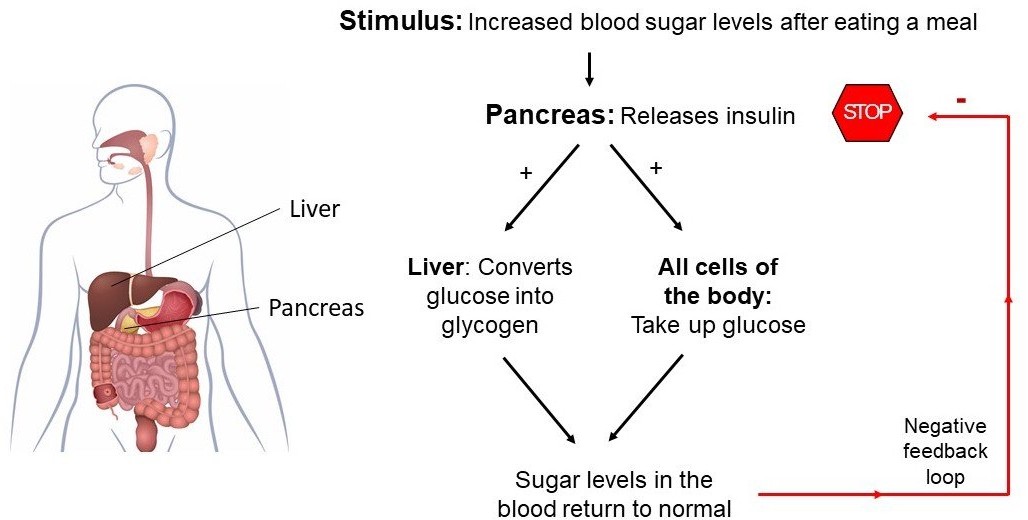
The Correct Answer is A.Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. After a person eats a meal, the levels of glucose in the blood rise, which stimulates the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts on various cells in the body, particularly those in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue, to promote the uptake, use, and storage of glucose.
Insulin helps to lower the levels of glucose in the blood by increasing the uptake of glucose by cells, stimulating the liver and muscle cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen, and inhibiting the production and release of glucose by the liver. This process is known as glucose homeostasis, and it helps to keep the levels of glucose in the blood within a normal range.
Deficiencies or abnormalities in insulin production or function can lead to a range of metabolic disorders, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
Question 7:
What is the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions?
A. Isotonic contractions produce no movement while isometric contractions produce movement.
B. Isotonic contractions produce movement while isometric contractions produce no movement.
C. Isotonic contractions generate tension in the muscle while isometric contractions involve shortening of the muscle fibers.
D. Isotonic contractions involve contraction of individual muscle fibers while isometric contractions involve the entire muscle.
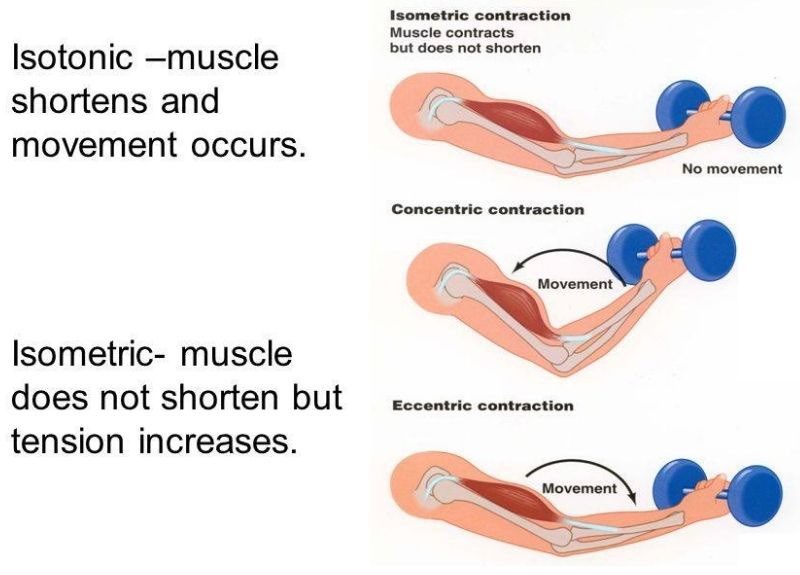
The Correct Answer is B.Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
 |
Question 8:
What are the five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards?
A. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
B. Thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
C. Lumbar, thoracic, cervical, coccygeal, sacral
D. Sacral, lumbar, cervical, thoracic, coccygeal
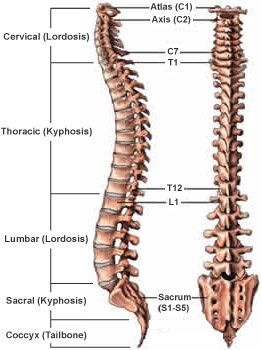
The Correct Answer is A.The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
- Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
- Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
- Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
- Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |
Question 9:
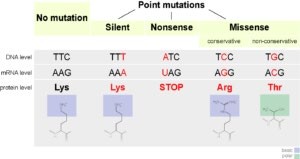
Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
The Correct Answer is C.A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
 |
Question 10:
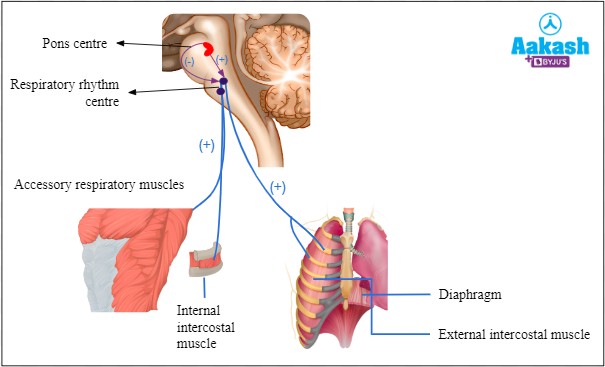
Which part of the respiratory system is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth?
A. Bronchi
B. Alveoli
C. Diaphragm
D. Trachea
The Correct Answer is C.Diaphragm is responsible for regulating breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the
bottom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
 |