Which of the following describes the process of osmosis?
A. Movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
B. Movement of substances against a concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
C. Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
D. Movement of substances into a cell by engulfing them with the plasma membrane.
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Selectively permeable membranes allow only certain molecules to pass through, while preventing the passage of others.
In osmosis, the movement of water molecules is driven by the concentration gradient of solutes, which cannot pass through the membrane. If one side of the membrane has a higher concentration of solutes than the other, water molecules will move from the side with the lower concentration of solutes to the side with the higher concentration of solutes, in an atempt to dilute the solutes and equalize the concentration on both sides.
Osmosis is important in many biological processes, including the uptake of water by plant roots, the regulation of water balance in animal cells, and the preservation of food by adding salt or sugar to create a hypertonic environment that inhibits bacterial growth.
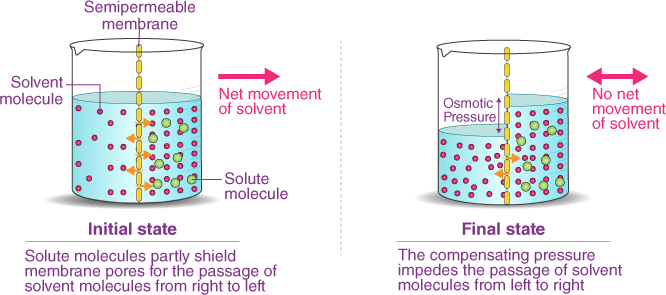 |
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 3
Question 1:
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
A. Calcium binds to tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin.
B. Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to initiate the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
C. Calcium activates the motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction.
D. Calcium is required for the relaxation of muscles after contraction.
The Correct Answer is B.Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
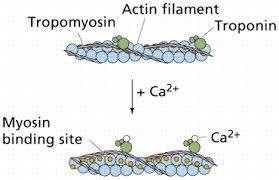
Question 2:
Which of the following is a function of the respiratory system?
A. Transport of nutrients to the body
B. Pumping of blood to the lungs
C. Exchange of gases between the body and the environment
D. Digestion of food in the stomach
The Correct Answer is C.One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
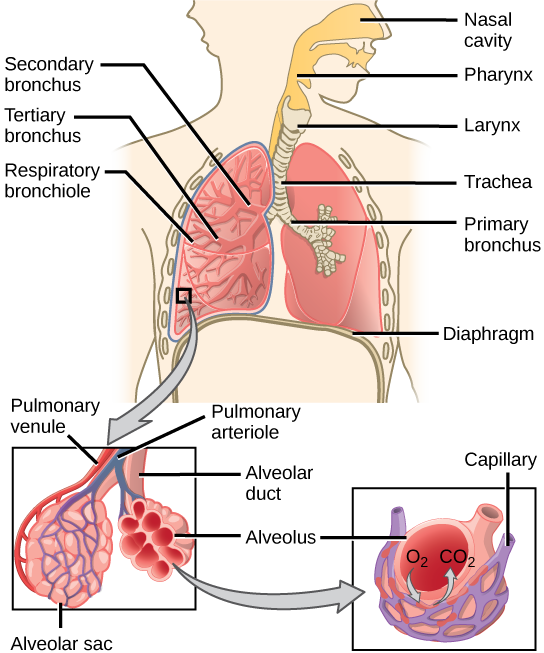 |
Question 3:
Which of the following describes the function of ligaments?
A. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to bone
B. Ligaments attach two bones
C. Ligaments attach bones to tendons
D. Ligaments attach skeletal muscles to tendons
The Correct Answer is B.Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, preventing excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.
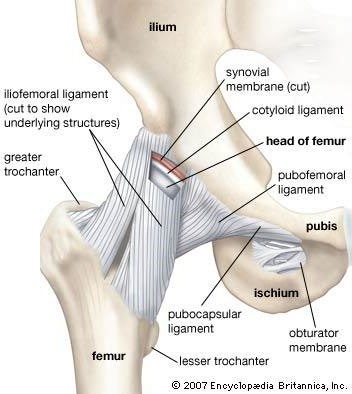
Question 4:
Which of the following units is used to indicate length?
A. kg
B. L
C. s
D. m
The Correct Answer is D.The unit used to indicate length is the meter (m). It is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
Question 5:
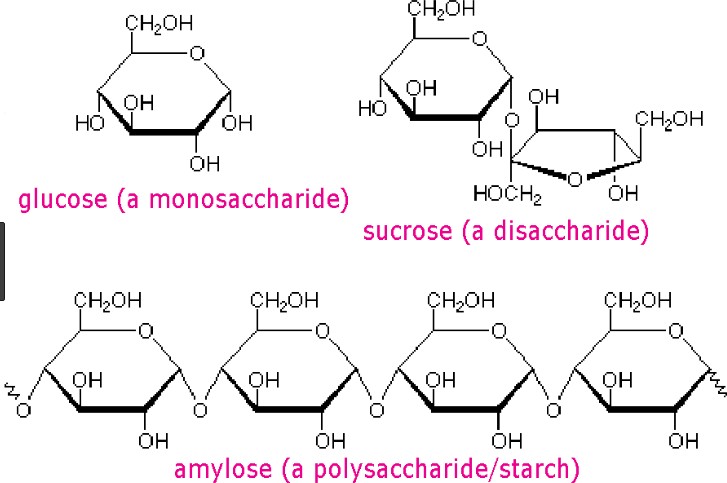
What is the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide?
A. Monosaccharides are composed of two sugar molecules while disaccharides are composed of a single sugar molecule.
B. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars while disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars.
C. Monosaccharides are only found in plants while disaccharides are only found in animals.
D. Monosaccharides are used for energy storage while disaccharides are used for structural purposes.
The Correct Answer is B.Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
Question 6:
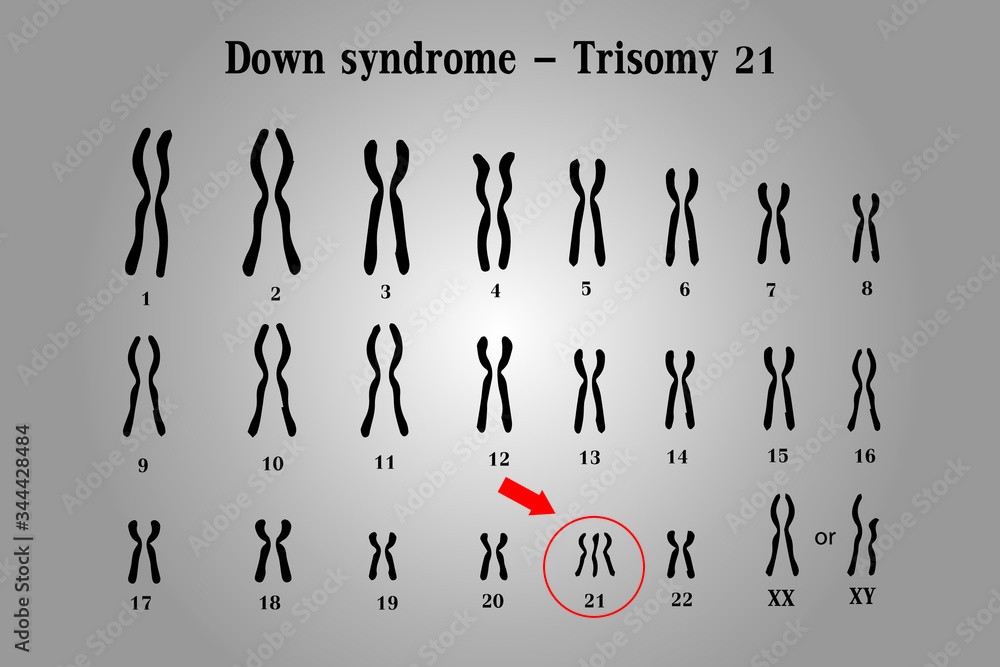
What is the name of the genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Klinefelter syndrome
C. Down syndrome
D. Huntington's disease
The Correct Answer is C.Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is also known as trisomy 21, because affected individuals have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two.
The extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome occurs due to a random error in cell division, which leads to the production of an abnormal gamete (egg or sperm) with an extra copy of the chromosome. When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, and develops into a fetus with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is characterized by a range of physical and intellectual symptoms, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, heart defects, and increased risk of certain medical conditions such as leukemia and Alzheimer's disease. However, the severity and expression of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
 |
Question 7:
A researcher collects data on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month. This data would be most useful to analyze which of the following:
A. traffic paterns during rush hour
B. pedestrian movement during the day
C. air pollution levels in the area
D. noise levels in the area
The Correct Answer is A.The data collected by the researcher on the number of cars passing through a busy intersection at different times of the day for a month would be most useful to analyze traffic paterns during rush hour.
Question 8:
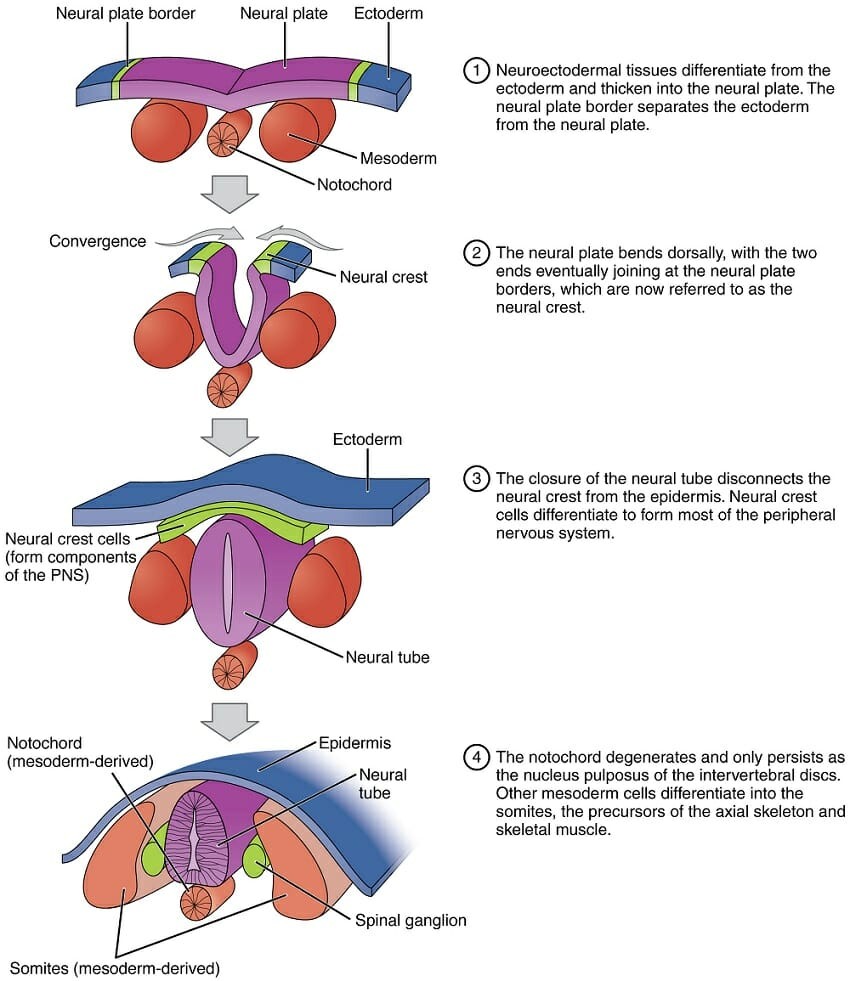
During embryonic development, which of the following germ layers forms the nervous system?
A. Ectoderm
B. Endoderm
C. Mesoderm
D. Exoderm
The Correct Answer is A.The three germ layers that form during embryonic development are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The ectoderm is the outermost layer, and it gives rise to the skin, hair, nails, and nervous system. The nervous system develops from a specialized region of the ectoderm called the neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube. The neural tube ultimately gives rise to the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system, as well as the peripheral nervous system. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts, while the mesoderm gives rise to the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, and several other organs. The exoderm is not a germ layer and does not exist during embryonic development.
Question 9:
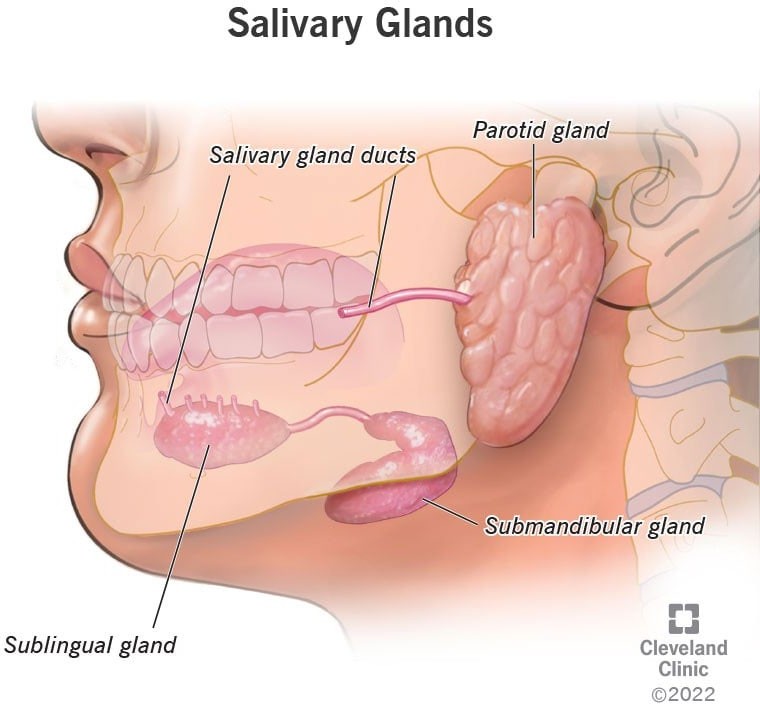
What are the three types of salivary glands and where are they located in the mouth?
A. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the cheeks, tongue, and roof of the mouth, respectively.
B. Sublingual, submandibular, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
C. Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands located in the roof of the mouth, cheeks, and under the jawbone, respectively.
D. Sublingual, parotid, and buccal glands located in the tongue, cheeks, and lips, respectively.
The Correct Answer is C.The three major pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, sublingual glands, and submandibular glands.
- Parotid glands are located just in front of your ears.
- Sublingual glands are located below either side of your tongue, under the floor of your mouth.
- Submandibular glands are located below your jaw.
 |
Question 10:
Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
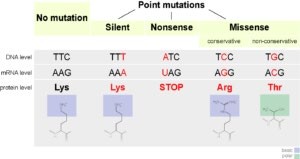
The Correct Answer is C.A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
 |