Which of the following determines the strength of an acidic solution?
A. Litmus paper that turns red
B. Litmus paper that turns blue
C. Measured pH value equal to 7
D. Measured pH value less than 7
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Both litmus paper and a pH scale can be used to indicate whether a solution is acidic. However, a pH scale can also determine the strength of an acid.
Researchers can determine the strength of an acid or a base by measuring the pH of a solution. The pH value describes how acidic or basic a solution is. On pH scale, shown below, if the number is less than 7 the solution is acidic. A pH greater than 7 means the solution is basic. When the pH is exactly 7, the solution is neutral.
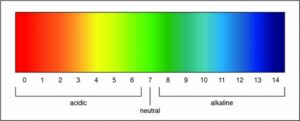
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 2
Question 1:
Fertilization (the fusing of one sperm and an ovum) results in a(n) _____.
A. embryo
B. fetus
C. infant
D. zygote
The Correct Answer is D.Human intercourse consists of the male introducing sperm into the female’s reproductive system. Sperm may then pass through the female’s reproductive system to the Fallopian tubes where one sperm fertilizes an ovum, creating a zygote. The zygote passes out of the Fallopian tube and implants into the uterine wall to begin gestation. Over nine months, the zygote develops and grows into an embryo and then a fetus. An infant is the baby that is born.
Question 2:
An atom has 28 protons, 32 neutrons, and 28 electrons. What is the name of this isotope?
A. Nickel-32
B. Nickel-60
C. Germanium-56
D. Germanium-60
The Correct Answer is B.The number of protons, 28, gives the atomic number, which identifies this atom as nickel. The mass is the number after the dash in the isotope name, which is determined by adding the numbers of protons and neutrons (28 + 32 = 60).
Question 3:
Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
The Correct Answer is D.Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
Question 4:
Which is true regarding the Urinary system?
A. Kidneys makes urine, Kidney help regulate water balance.
B. As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium.
C. Eliminates metabolic wastes., Kidneys makes urine., Kidney help regulate water balance.
D. Kidney help regulate water balance, Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, Eliminates metabolic wastes
The Correct Answer is D.Kidneys makes urine is incorrect. Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase is incorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance is correct. Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is correct. There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes is correct. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
Question 5:
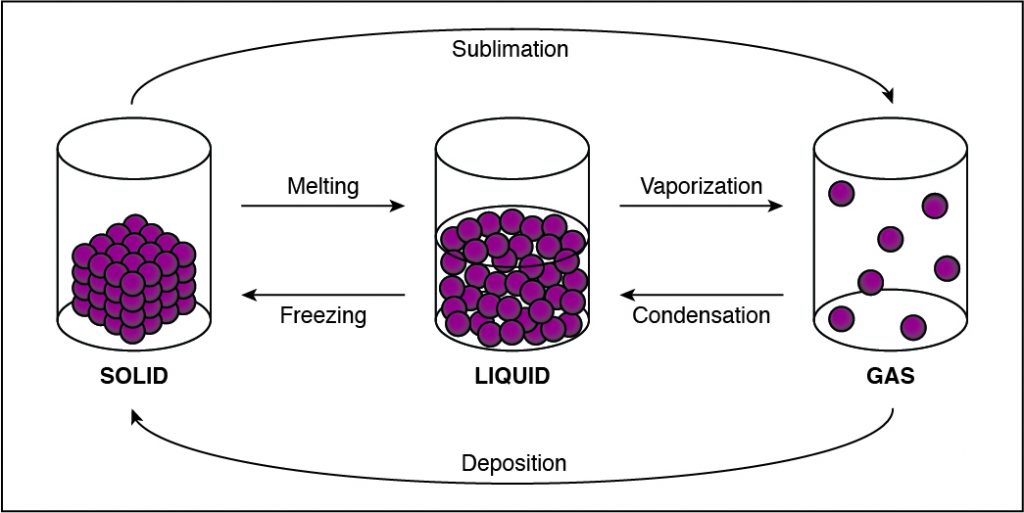
In which state of matter are the intermolecular forces between particles in a substance the strongest?
A. Gas
B. Liquid
C. Plasma
D. Solid
The Correct Answer is D.In solids, particles are usually closer together than in other states of matter because of the strong cohesive forces between the particles.
- Solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas differ from one another in the amount of energy that the particles have and the strength of the cohesive forces that hold the particles together.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Question 6:
During the aging process, not all hormone levels decrease; some actually increase. Which of the following is a hormone that may increase as a person ages?
A. Cortisol
B. Insulin
C. Luteinizing
D. Thyroid
The Correct Answer is C.The aging process affects hormone activity in one of three ways: their secretion can decrease, remain unchanged, or increase.
Hormones that decrease secretion include the following:
- Estrogen (in women)
- Testosterone (in men)
- Growth hormone
- Melatonin
In women, the decline in estrogen levels leads to menopause. In men, testosterone levels usually decrease gradually. Decreased levels of growth hormone may lead to decreased muscle mass and strength. Decreased melatonin levels may play an important role in the loss of normal sleep-wake cycles (circadian rhythms) with aging.
Hormones that usually remain unchanged or slightly decrease include the following:
- Cortisol
- Insulin
- Thyroid hormones
Hormones that may increase secretions levels include the following:
Parathyroid hormone
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine, in the very old
Question 7:
Blood oxygen levels are most likely low when blood _____.
A. leaves the aorta
B. fills the right atrium
C. reaches body tissues
D. flows through arteries
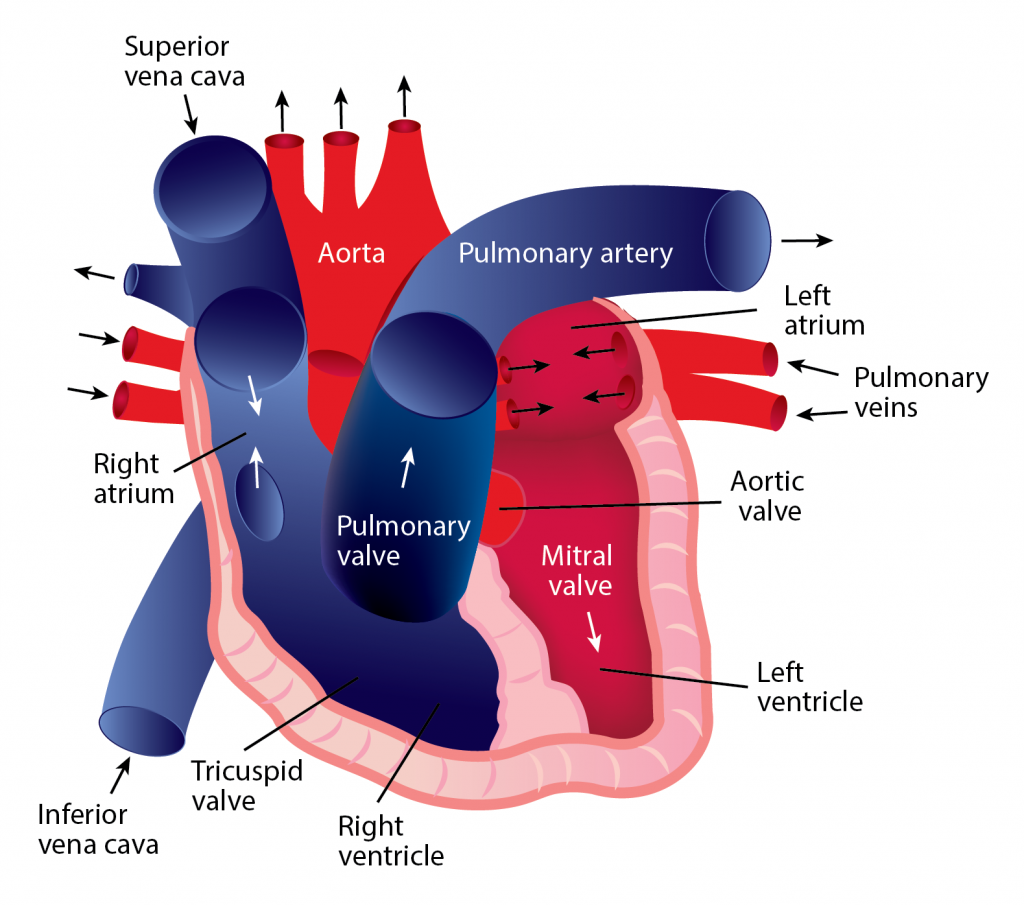
The Correct Answer is B.Blood continually flows in one direction, beginning in the heart and proceeding to the arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. When blood reaches the capillaries, exchanges occur between blood and tissues. After this exchange happens, blood is collected into venules, which feed into veins and eventually flow back to the heart’s atrium. The heart must relax between two heartbeats for blood circulation to begin.
Two types of circulatory processes occur in the body:
Systemic circulation
- The pulmonary vein pushes oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
- As the atrium relaxes, oxygenated blood drains into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. 3. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- Blood travels through the arteries and arterioles before reaching the capillaries that surround the tissues.
Pulmonary circulation
- Two major veins, the Superior Vena Cava and the Inferior Vena Cava, brings deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower half of the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is pooled into the right atrium and then sent into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, which prevents blood from flowing backward.
- The right ventricle contracts, causing the blood to be pushed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Question 8:
A researcher notices a positive correlation between the height of a plant and nutrient concentration over time. Based on this observation, what conclusion does he reach?
A. The height of a plant increases in the absence and presence of the nutrients
B. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant decreases, its height increases.
C. The amount of nutrients available to a plant is independent of how tall the plant gets
D. When the amount of nutrients available to the plant increases, its height also increases.
The Correct Answer is D.Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations. Correlations measure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Question 9:
What is the correct order of the stages of the cell cycle?
A. G1,S,G2,M
B. G2,S,G1,M
C. M,S,G2,G1
D. S,M,G1,G1
The Correct Answer is A.The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
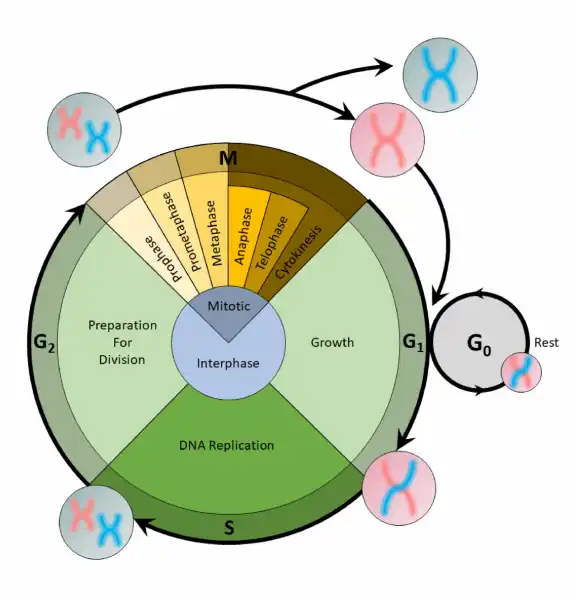
- G1: The first gap phase, during which the cell prepares to copy its DNA
- S: The synthesis phase, during which DNA is copied
- G2 : The second gap phase, during which the cell prepares for cell division
It may appear that little is happening in the cell during the gap phases. Most of the activity occurs at the level of enzymes and macromolecules. The cell produces things like nucleotides for synthesizing new DNA strands, enzymes for copying the DNA, and tubulin proteins for building the mitotic spindle. During the S phase, the DNA in the cell doubles, but few other signs are obvious under the microscope. All the dramatic events that can be seen under a microscope occur during the M phase: the chromosomes move, and the cell splits into two new cells with identical nuclei.
Question 10:
After food has been masticated in the oral cavity, where does it go next?
A. Colon
B. Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Pharynx
The Correct Answer is D.Once the food has been masticated in the oral cavity (mouth), it is then swallowed and travels back into the pharynx down into the esophagus, which leads into the stomach.