Which of the following is a component of a chromosome?
A. Centromere
B. Gamete
C. Homologue
D. Ribose
The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
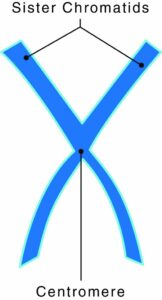
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.