Which of the following is an example of a double-blind study?
A. participants are randomly assigned to a treatment group or a control group
B. participants and researchers both know which group participants are assigned to
C. participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but researchers do
D. Both participants and researchers do not know which group participants are assigned to
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to.
Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind.
Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to.
Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
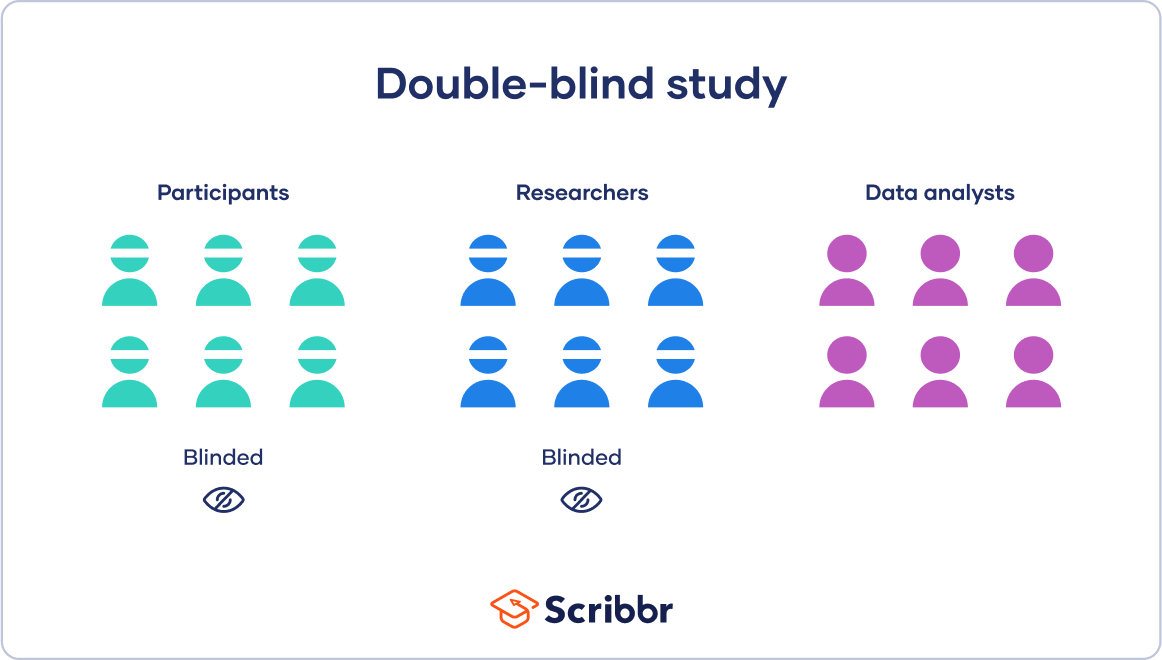
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 1
Question 1:
Which of the following is an example of a double-blind study?
A. participants are randomly assigned to a treatment group or a control group
B. participants and researchers both know which group participants are assigned to
C. participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but researchers do
D. Both participants and researchers do not know which group participants are assigned to
The Correct Answer is D.A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to.
Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind.
Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to.
Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.

Question 2:
Which of the following is a chemical property of a substance?
A. Density
B. Melting point
C. Boiling point
D. Reactivity with acid
The Correct Answer is D.Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance. Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance.
Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
Question 3:
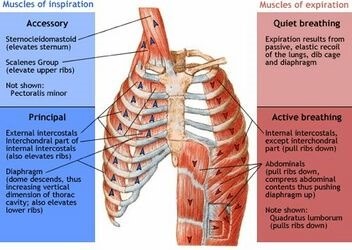
What is the name of the dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing?
A. Diaphragm
B. Trachea
C. Bronchus
D. Alveoli
The Correct Answer is A.The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
Question 4:
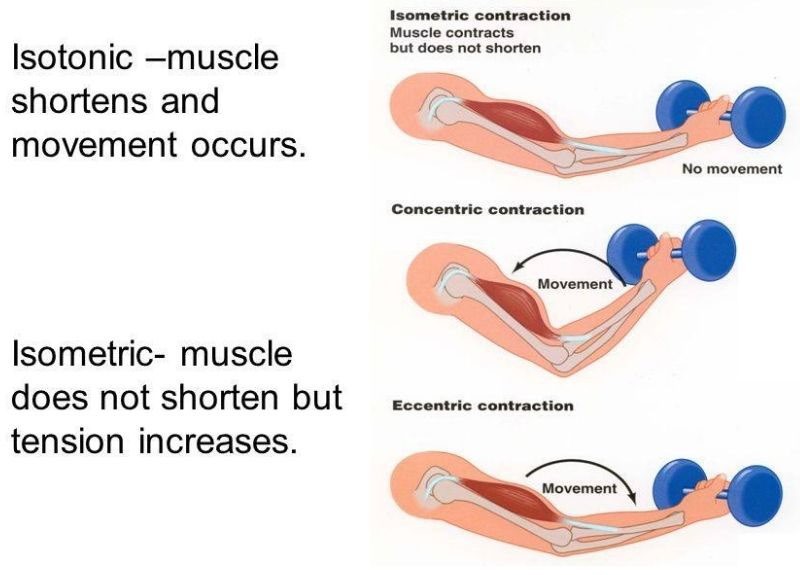
What is the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions?
A. Isotonic contractions produce no movement while isometric contractions produce movement.
B. Isotonic contractions produce movement while isometric contractions produce no movement.
C. Isotonic contractions generate tension in the muscle while isometric contractions involve shortening of the muscle fibers.
D. Isotonic contractions involve contraction of individual muscle fibers while isometric contractions involve the entire muscle.
The Correct Answer is B.Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
 |
Question 5:
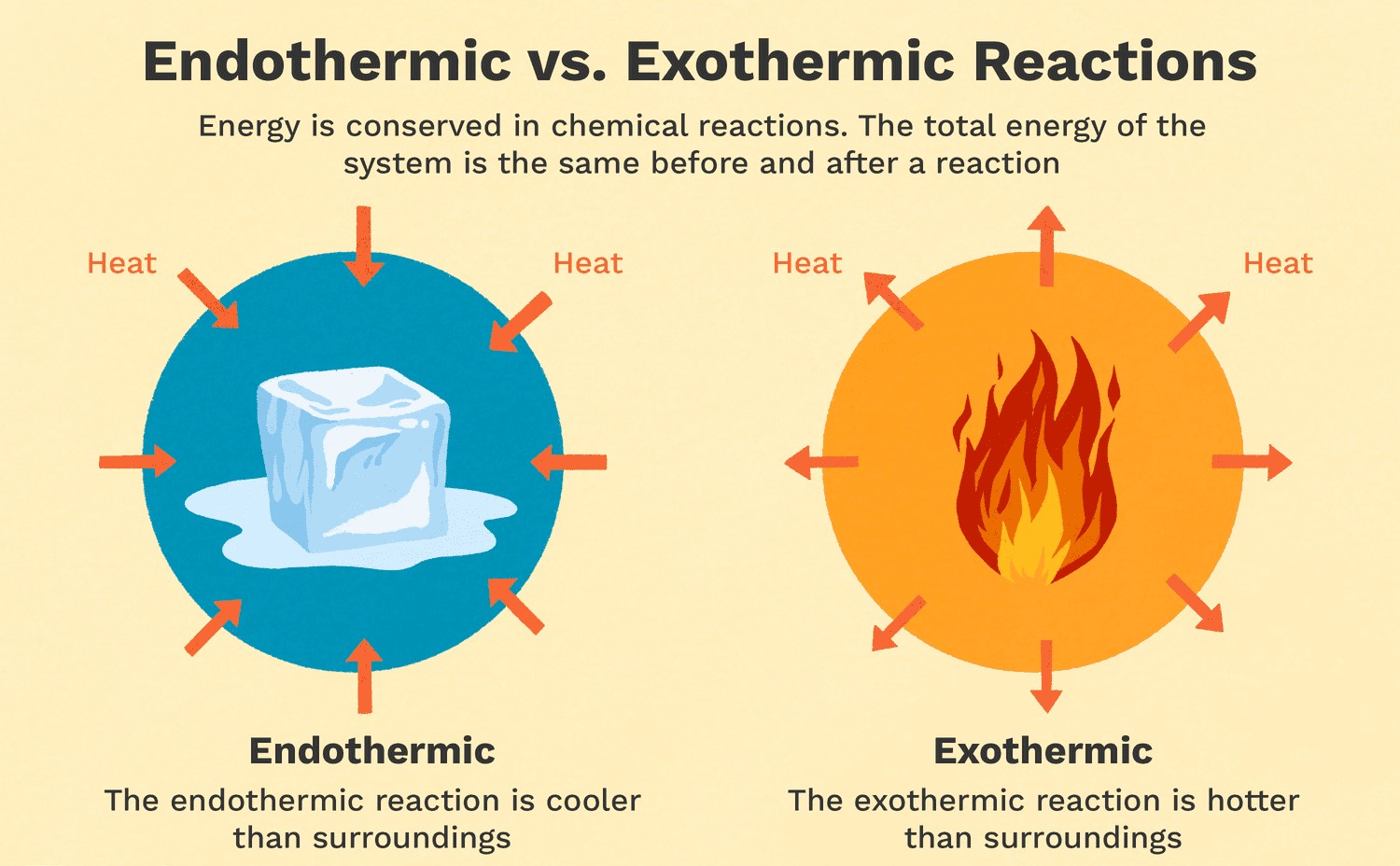
Which of the following is an example of an exothermic reaction?
A. Melting ice
B. Burning wood
C. Cooking an egg
D. Dissolving sugar in water
The Correct Answer is B.Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. Burning wood is an example of an exothermic reaction because it releases heat and light. As the wood reacts with oxygen in the air, it undergoes a combustion reaction that releases energy in the form of heat and light. Melting ice is an endothermic reaction because it requires energy input to melt the solid ice into liquid water. Cooking an egg is a chemical reaction that involves denaturing the proteins in the egg, but it is not necessarily exothermic or endothermic. Dissolving sugar in water is also not an example of an exothermic reaction because it does not release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound.
Question 6:
What is the chemical formula for water?
A. H2O
B. CO2
C. NaCl
D. C6H12O6
The Correct Answer is A.The chemical formula for water is H2O. It consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
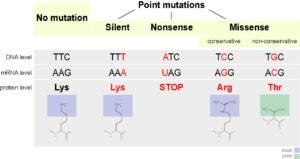
Question 7:
Which of the following is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence?
A. Silent mutation
B. Nonsense mutation
C. Frameshift mutation
D. Missense mutation
The Correct Answer is C.A frameshift mutation is a type of genetic mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides in a DNA sequence. This can cause a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein. Frameshift mutations can have significant effects on the function of the protein and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
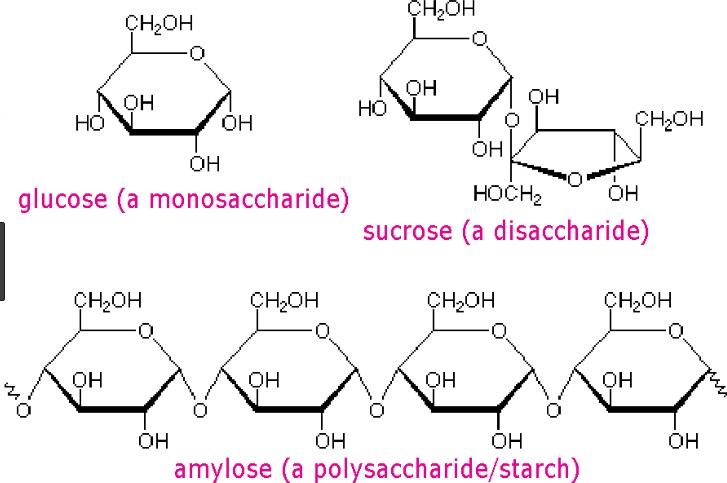
Question 8:
What is the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide?
A. Monosaccharides are composed of two sugar molecules while disaccharides are composed of a single sugar molecule.
B. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars while disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars.
C. Monosaccharides are only found in plants while disaccharides are only found in animals.
D. Monosaccharides are used for energy storage while disaccharides are used for structural purposes.
The Correct Answer is B.Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
 |
Question 9:
What is the name of the joint that allows for rotation of the arm at the shoulder?
A. Elbow joint
B. Hip joint
C. Knee joint
D. Shoulder joint
The Correct Answer is D.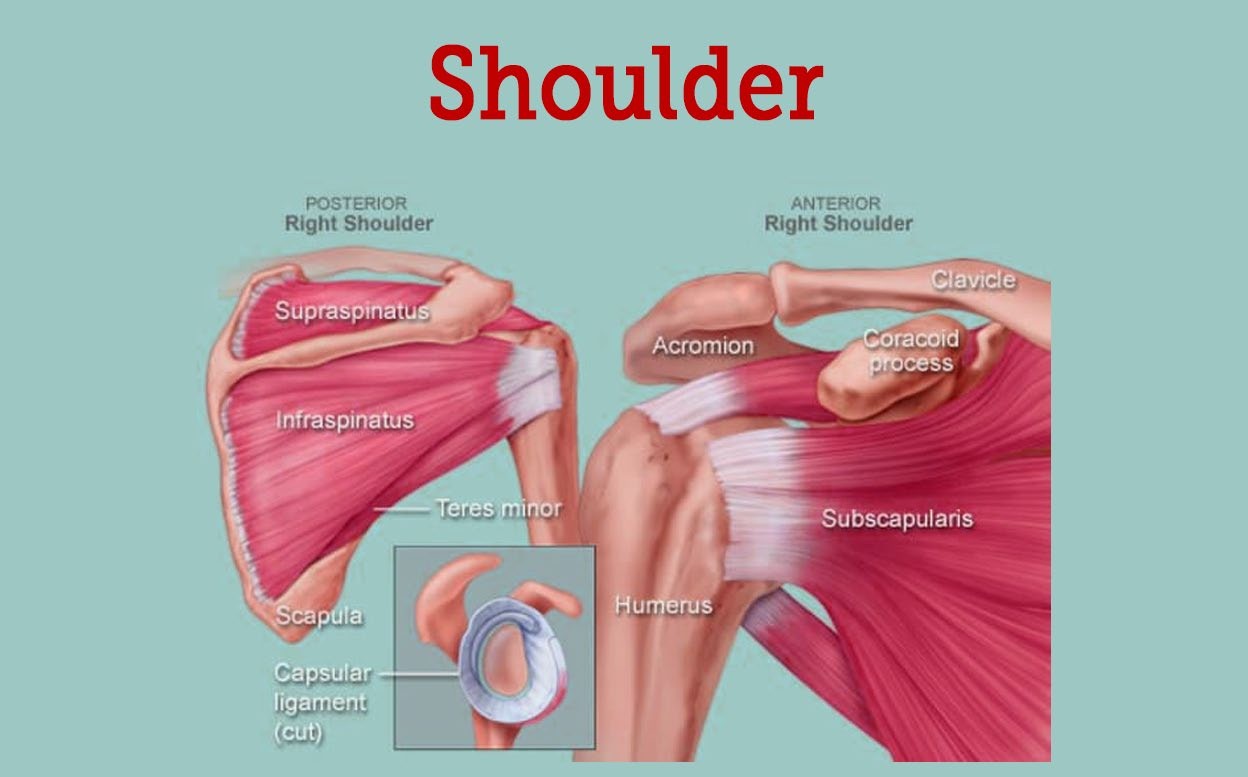 |
Question 10:
Which of the following types of RNA carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis?
A. Messenger RNA
B. Ribosomal RNA
C. Transfer RNA
D. Small nuclear RNA
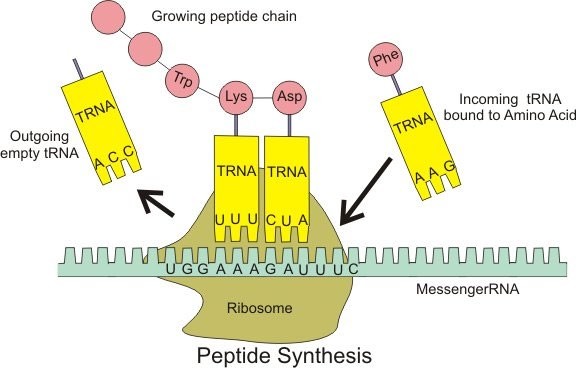
The Correct Answer is C.Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific sequence of three nucleotides called an anticodon, which pairs with a complementary codon in the messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence. Each tRNA also carries a specific amino acid that corresponds to the codon it recognizes, allowing the ribosome to link the amino acids together in the correct order to form a protein.
In contrast, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosome itself, where it helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is involved in splicing of pre-mRNA molecules during post-transcriptional processing.
 |