Which of the following is an example of a storage form of glucose in the human body?
A. Starch
B. Glycogen
C. Fructose
D. Cellulose
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the human body.
It is a polysaccharide that is stored primarily in the liver and muscle tissue and can be broken down into glucose when the body needs energy.
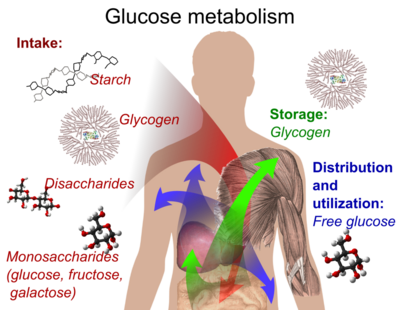 |
Choice A is incorrect because starch is a storage form of glucose in plants, not in the human body.
Choice C is incorrect because fructose is a simple sugar, not a storage form of glucose.
Choice D is incorrect because cellulose is a structural carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, not a storage form of glucose in the human body.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
Which type of bond is responsible for the unique properties of water and plays a crucial role in the structure of DNA and proteins?
A. Hydrogen bonds.
B. Covalent bonds.
C. Ionic bonds.
D. Van der Waals forces.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the unique properties of water and play a crucial role in the structure of DNA and proteins.
Hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Choice B.
Covalent bonds is incorrect because covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Choice C.
Ionic bonds is incorrect because ionic bonds are chemical bonds formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
Choice D.
Van der Waals forces is incorrect because Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that arise from temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules.
Question 2:
What is the function of inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection?
A. Enhancing the phagocytosis of pathogens and disrupting the infection
B. Attacking invading pathogens
C. Initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation
D. Secreting antibodies to neutralize pathogens .
The Correct Answer is C.Inflammatory cytokines released during the early response to bacterial infection play a crucial role in initiating cell recruitment and local inflammation 1.
They induce the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells and promote the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of inflammation 1.
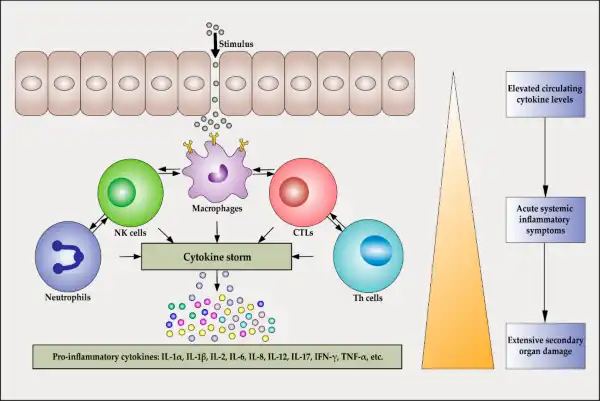
Choice A is incorrect because while inflammatory cytokines may enhance phagocytosis, they do not directly disrupt the infection.
Choice B is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not directly attack invading pathogens.
Choice D is incorrect because inflammatory cytokines do not secrete antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
Question 3:
Which of the following statements about bacteria and archaea is true?
A. A. Bacteria have a true nucleus while archaea do not
B. B. Archaea reproduce by spores while some bacteria reproduce by fission.
C. C. Bacteria can perform photosynthesis while archaea cannot.
D. D. Archaeal and bacterial flagella are constructed similarly.
The Correct Answer is C.Bacteria can perform photosynthesis while archaea cannot. Many types of bacteria can generate oxygen from sunlight through photosynthesis, while archaea cannot perform this process.
Choice A is incorrect because neither bacteria nor archaea have a true nucleus. Both are prokaryotic organisms. Choice B is incorrect because archaea reproduce by fission, fragmentation, or budding, while bacteria can produce spores and divide sexually or asexually. Choice D is incorrect because archaeal and bacterial flagella are constructed differently.
Question 4:
In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between what?.
A. Control group and treatment group.
B. Independent variable and dependent variable.
C. Experimental group and non-experimental group.
D. High level and low level of the independent variable.
The Correct Answer is A.In a well-designed experiment, all variables apart from the treatment should be kept constant between the control group and treatment group.
This means researchers can correctly measure the entire effect of the treatment without interference from confounding variables.
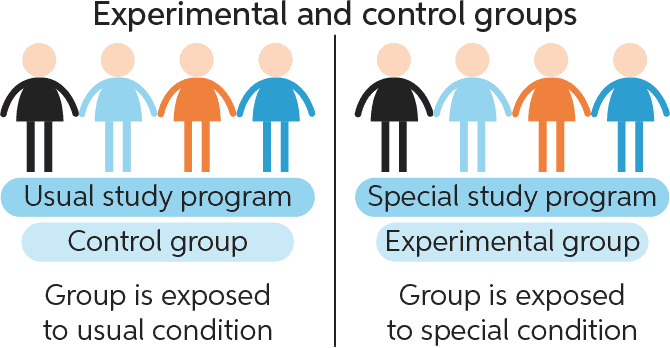
Choice B) Independent variable and dependent variable is incorrect because these are not groups but rather variables.
The independent variable is manipulated by the experimenters while the dependent variable is measured to see if it changes as a result of the manipulation.
Choice C) Experimental group and non-experimental group is incorrect because a non-experimental group is not a term used in experimental design.
The correct term for the group that does not receive the treatment is control group.
Choice D) High level and low level of the independent variable is incorrect because these are levels of the independent variable, not groups.
In an experiment, there can be multiple levels of the independent variable, but they are applied to different groups (e.g.
control group, treatment group).
Question 5:
Which of the following is a consequence of increased viscosity of a fluid?
A. Particles have a decrease in mobility.
B. The fluid will have a lower density.
C. The fluid will have a higher flow rate.
D. The fluid will have a higher pressure.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
Question 6:
What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
The Correct Answer is A.Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
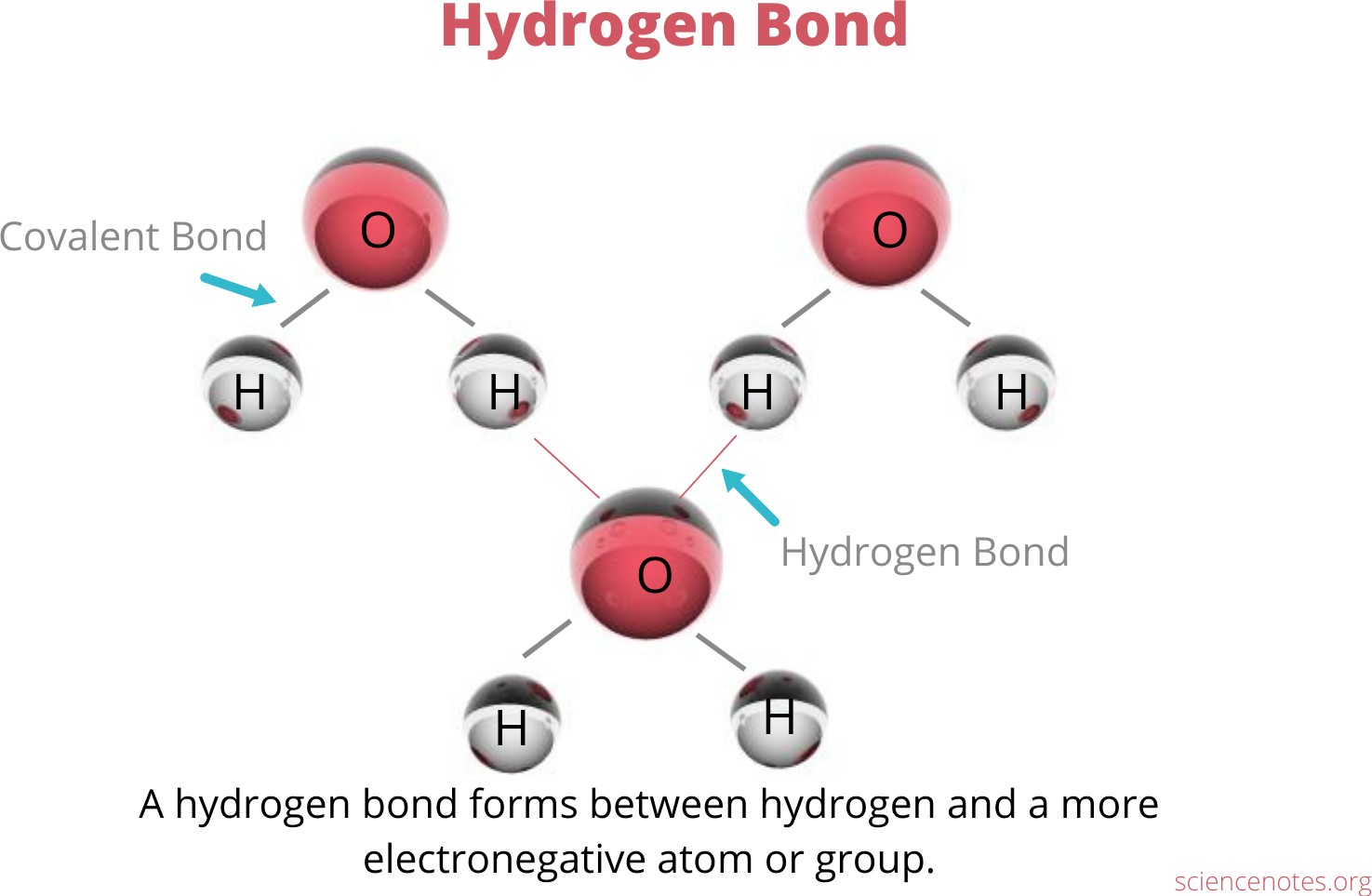 |
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
Question 7:
Which of the following is a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning?
A. Conversion to carbon monoxide.
B. Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
C. Increased production of red blood cells.
D. Decreased pulmonary function.
The Correct Answer is B.Formation of carboxyhemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin to create a molecule called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which interferes with the body’s ability to transport and use oxygen, especially in the brain.
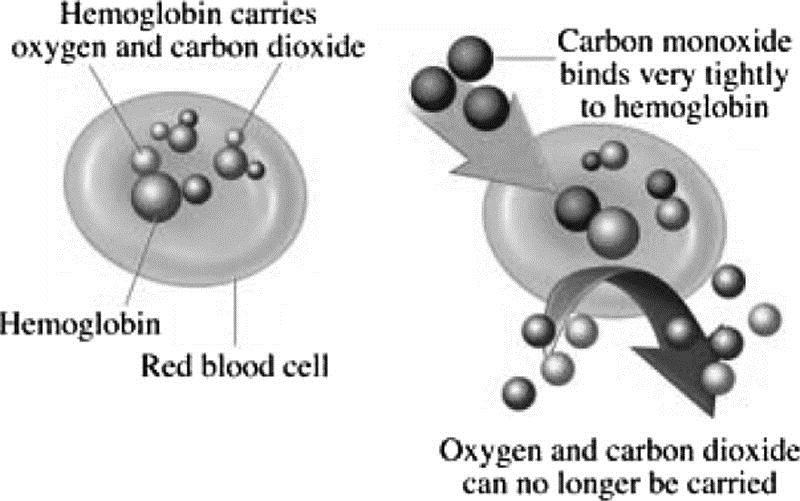 |
Choice A is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide builds up in your bloodstream.
Choice C is incorrect because carbon monoxide poisoning does not increase the production of red blood cells.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased pulmonary function is not a potential complication of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 8:
Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
Question 9:
What is a control group used for in scientific studies?
A. To establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
B. To establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
C. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable.
D. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
The Correct Answer is A.A control group is used in scientific studies to establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
The control group serves as a baseline or comparison group that does not receive the treatment or intervention being tested.
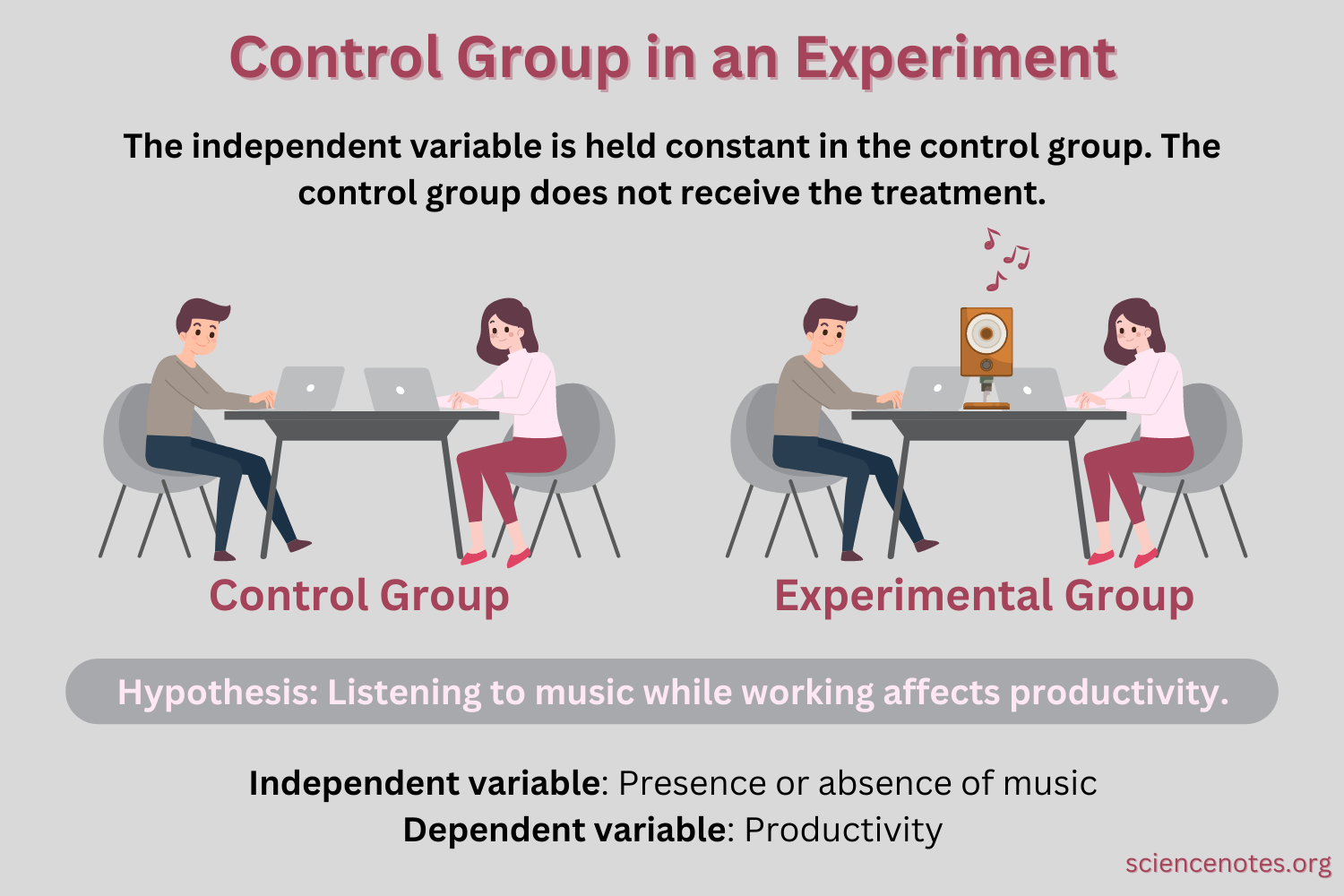 |
By comparing the results of the control group to the experimental group, researchers can determine if any observed changes are due to the independent variable or if they are due to chance or other factors.
Choice B is incorrect because a control group is not used to establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
Choice C is incorrect because while a control group can help control for the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable, its primary purpose is to isolate the effect of the independent variable.
Choice D is incorrect because a control group is not used to control for the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
Question 10:
A patient with a history of heart failure is prescribed a medication that increases urine output to reduce fluid buildup.
Which of the following statements best describes the mechanism of action of the prescribed medication?
A. Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
B. Blocks beta receptors.
C. Increases sodium and water reabsorption.
D. Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The Correct Answer is D.The correct answer is choice D - Enhances glomerular filtration rate.
The medication prescribed to the patient is a diuretic, which removes water and electrolytes from the body by increasing urination 1.
This helps reduce fluid buildup in the body.
Choice A, Inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice B, Blocks beta receptors, is not the correct answer because it describes a different mechanism of action.
Choice C, Increases sodium and water reabsorption, is not the correct answer because it would have the opposite effect of reducing fluid buildup.