Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
Which cytotoxic lymphocyte granules contain serine proteases that induce apoptosis in target cells?.
A. Perforins.
B. Cytokines.
C. Granzymes.
D. Interferons.
The Correct Answer is C.Granzymes.
Granzymes are a family of serine proteases that are stored in and secreted from the cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells.
They work in synergy with perforin, a pore-forming toxin, to induce apoptosis in target cells.
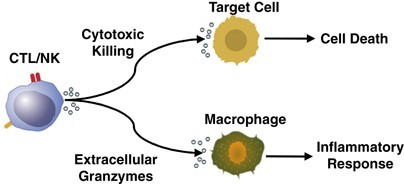
Perforin is necessary for the delivery of granzyme B to the target cell cytosol where caspase-dependent and -independent pathways to apoptosis are activated.
Perforins (choice A) are pore-forming toxins that work in synergy with granzymes to induce apoptosis in target cells.
Cytokines (choice B) are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
Interferons (choice D) are a type of cytokine that play a role in immune responses but do not directly induce apoptosis in target cells.
Question 2:
What is a primer in DNA sequencing?
A. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
B. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a "starter" for the template.
C. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
D. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a "starter" for the template.
The Correct Answer is C.A primer is a short single-stranded DNA fragment used in certain laboratory techniques, such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
In the PCR method, a pair of primers hybridizes with the sample DNA and defines the region that will be amplified.
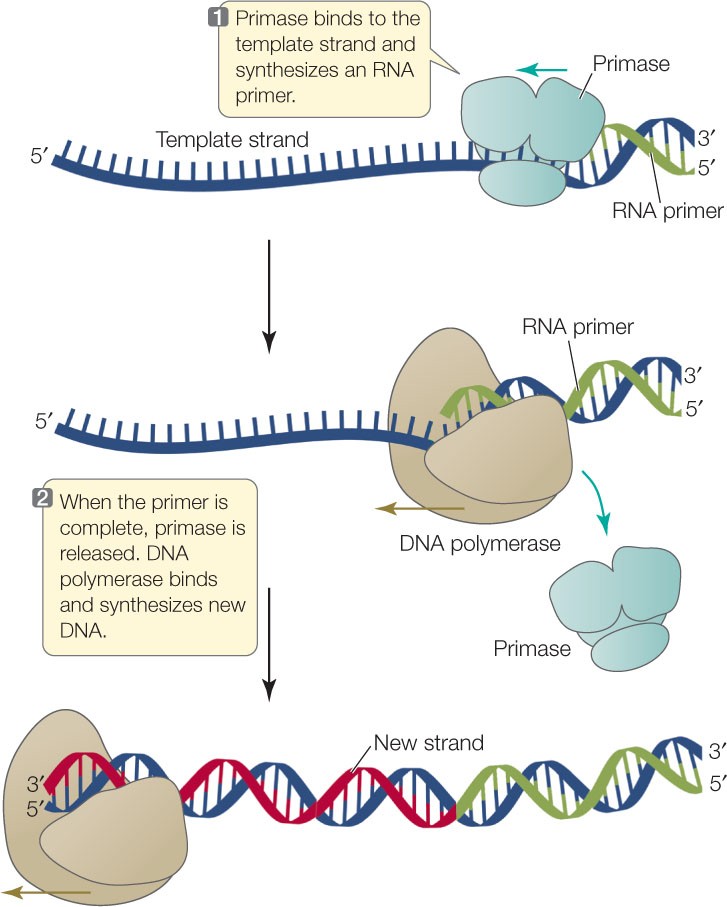
Choice A) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a “starter” for the polymerase is incorrect because primers are single-stranded, not double-stranded.
Choice B) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because it does not make sense for a primer to bind to itself.
Choice D) A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because primers bind to the template DNA, not to the polymerase.
Note: DNA primers are used instead of RNA primers in DNA sequencing and PCR because DNA is more stable, specific, and compatible with the enzymes and processes involved in these techniques.
Question 3:
Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
Question 4:
What is the hallmark of adaptive immunity?
A. Rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation
B. Antigen-independent defense mechanism
C. Immunologic memory
D. Non-specific host-defense mechanisms .
The Correct Answer is C.Immunologic memory is the hallmark of adaptive immunity.
Immunologic memory enables the host to mount a more rapid and efficient immune response upon subsequent exposure to the antigen.
Choice A is incorrect because rapid recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection and inflammation is a characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice B is incorrect because antigen-independent defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Choice D is incorrect because non-specific host-defense mechanisms are characteristic of innate immunity.
Question 5:
What is a control group used for in scientific studies?
A. To establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
B. To establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
C. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable.
D. To control the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
The Correct Answer is A.A control group is used in scientific studies to establish causality by isolating the effect of an independent variable.
The control group serves as a baseline or comparison group that does not receive the treatment or intervention being tested.
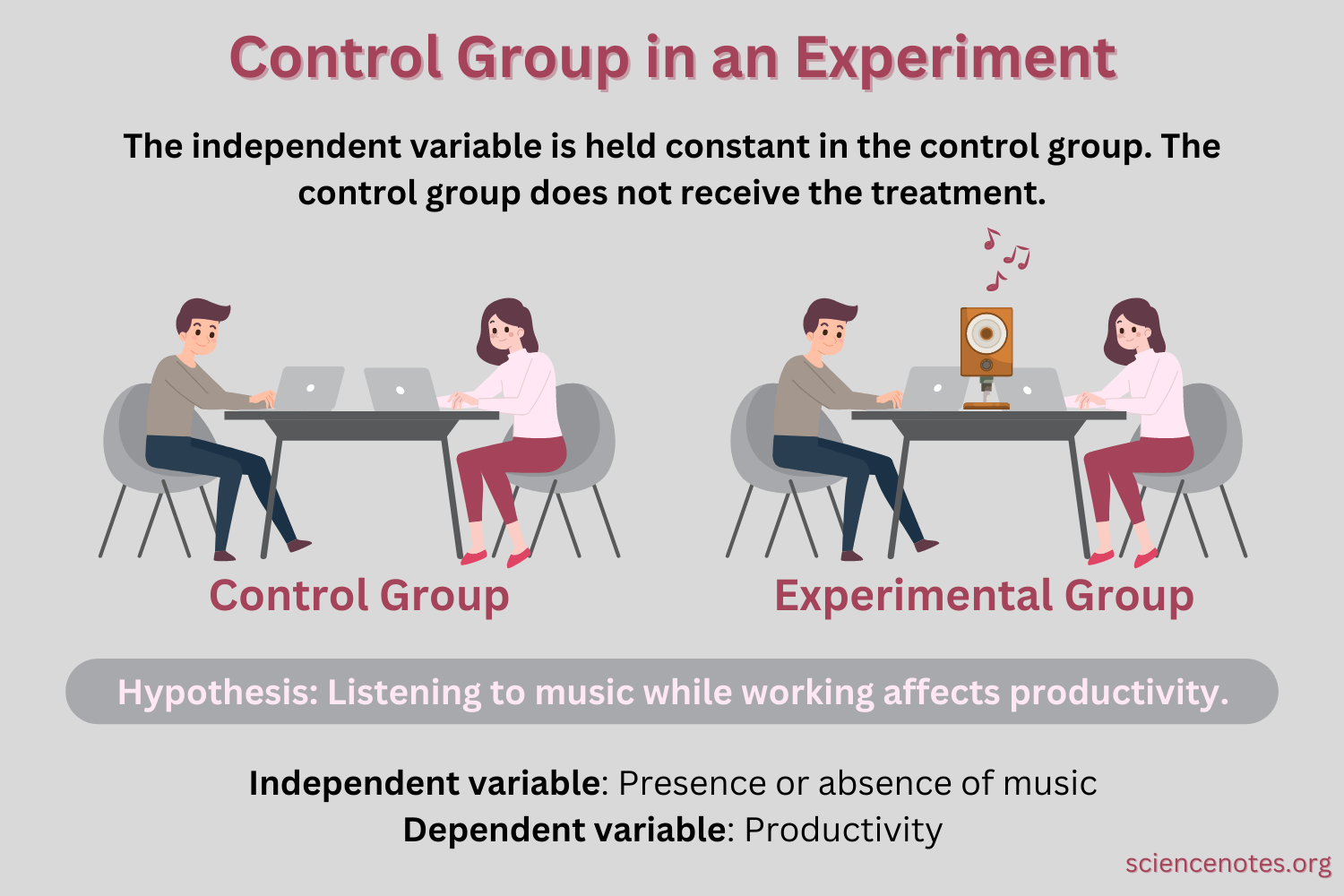 |
By comparing the results of the control group to the experimental group, researchers can determine if any observed changes are due to the independent variable or if they are due to chance or other factors.
Choice B is incorrect because a control group is not used to establish the effect of a dependent variable on an independent variable.
Choice C is incorrect because while a control group can help control for the impact of extraneous variables on the dependent variable, its primary purpose is to isolate the effect of the independent variable.
Choice D is incorrect because a control group is not used to control for the impact of extraneous variables on the independent variable.
Question 6:
Which of the following is a mechanism that the body uses to regulate blood pH levels?
A. Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
B. Decreased respiration rate to retain CO2.
C. Increased water intake to dilute the blood.
D. Decreased water intake to concentrate the blood.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
Increased respiration rate to remove excess CO2.
The body regulates blood pH through several mechanisms, including chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the urinary system.
The respiratory system can adjust blood pH by changing the rate of respiration to remove or retain CO2.
When there is excess acid in the blood, the respiratory rate increases to remove more CO2, which helps to raise blood pH.
Choice B is incorrect because decreasing the respiration rate would retain CO2, which would lower blood pH.
Choice C is incorrect because increased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Choice D is incorrect because decreased water intake would not directly affect blood pH levels.
Question 7:
Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
The Correct Answer is C.Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
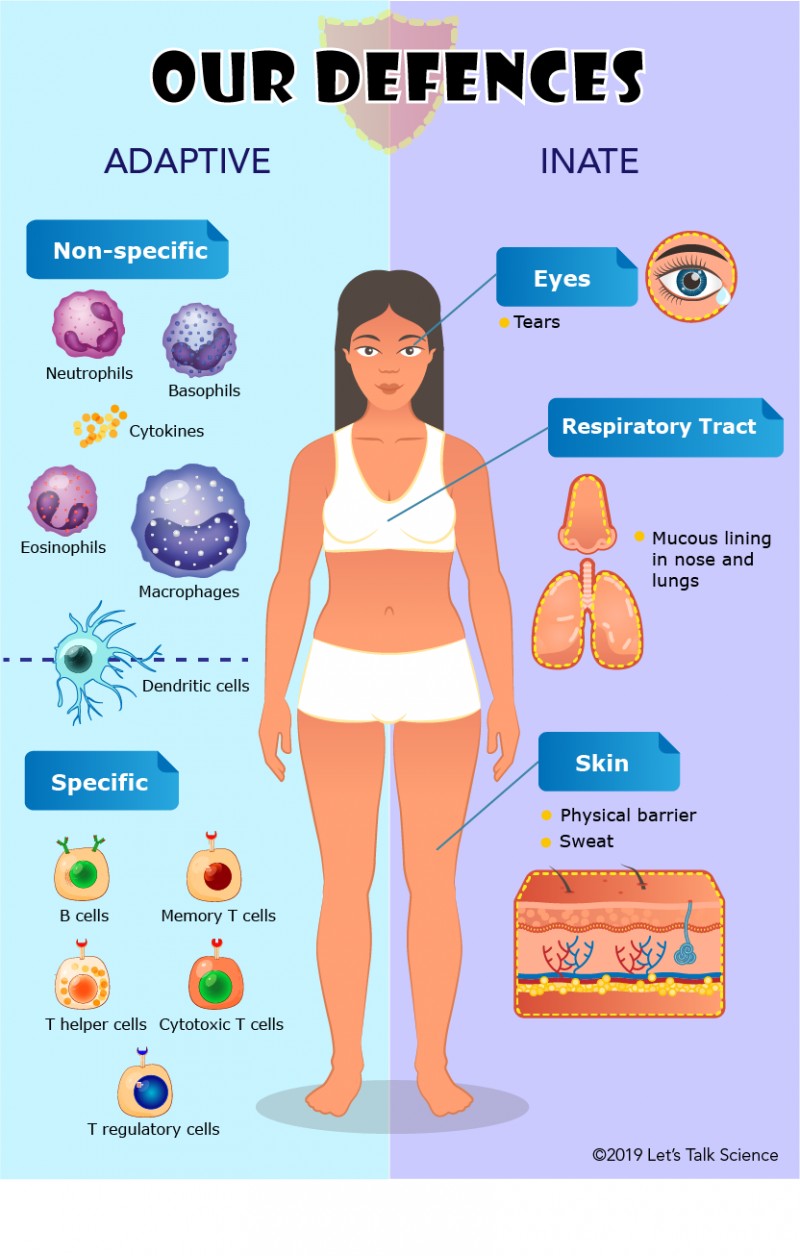
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Question 8:
Which of the following allows a limited range of immune cells to detect and respond rapidly to a wide range of pathogens that share common structures?
A. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
B. Cytokines
C. Chemokines
D. T cells .
The Correct Answer is A.Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are a class of receptors that can directly recognize the specific molecular structures on the surface of pathogens.
PRRs play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system and are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens.
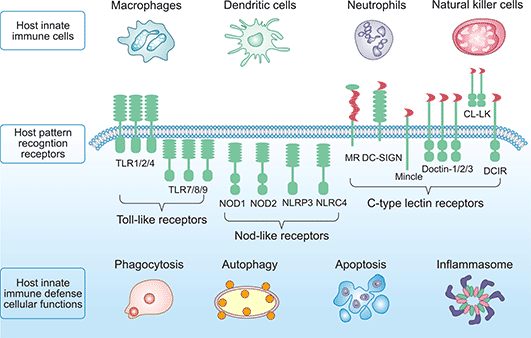 |
Choice B is incorrect because cytokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that regulate immunity.
Choice C is incorrect because chemokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that attract immune cells to sites of infection.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are not receptors but rather white blood cells that assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Question 9:
How does the use of a catalyst affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
A. It increases the activation energy required for the reaction.
B. It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
C. It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction.
D. It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
It decreases the activation energy required for the reaction.
A catalyst provides a new reaction pathway in which a lower activation energy is offered.
This allows more reactant molecules to collide with enough energy to surmount the smaller energy barrier, increasing the rate of reaction 2.
Choice A, It increases the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because it describes the opposite effect of a catalyst.
Choice C, It has no effect on the activation energy required for the reaction, is not the correct answer because a catalyst does have an effect on activation energy.
Choice D, It increases the rate of reaction but has no effect on the activation energy, is not the correct answer because a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
Question 10:
Which organ in the human body is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells?
A. Spleen
B. Kidneys
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A.
The spleen is an organ in the human body that is responsible for the removal of damaged red blood cells and the production of certain types of white blood cells.
Choice B is incorrect because the kidneys are responsible for filtering waste from the blood and regulating electrolyte balance.
Choice C is incorrect because the pancreas produces hormones and enzymes that aid in digestion.
Choice D is incorrect because the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism.