Which part of the digestive system comes before the stomach?
A. mouth
B. esophagus
C. ileum
D. colon
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
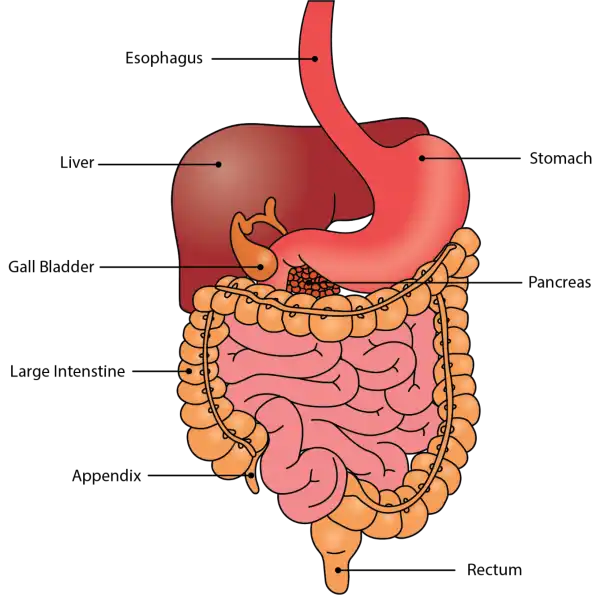
Oral Cavity is the first part of the digestive system. It is bounded by the lips and cheeks and contains the teeth and tongue. Its primary function is to masticate, or chew, and moisten the food.
Pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Food travels down it to the cardiac sphincter of the stomach.
Pyloric sphincter. The exit of the stomach.
Small intestine is about 6 meters long and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Large intestine, consists of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. The cecum is located where the small and large intestine meet. The primary function of the large intestine is to compress the waste and collect any excess water that can be recycled.
Colon is about 1.5 to 1.8 meters long and consists of four parts: the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Practice Test 2
Question 1:
Which of the following atoms is a cation?
A. 14 protons, 14 neutrons, 18 electrons
B. 34 protons, 45 neutrons, 36 electrons
C. 35 protons, 44 neutrons, 35 electrons
D. 82 protons, 125 neutrons, 78 electrons
The Correct Answer is D.Because it has more protons than electrons, this atom has a positive charge and can be classified as a cation. When a metal such as sodium reacts to become stable, it loses its valence electrons. At first, it is a neutral atom with 11 protons and 11 electrons. When it loses an electron, the number of protons does not change, and the atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons. Because there is one more positively charged proton, a cation forms. A cation is an ion with a net positive charge.
Question 2:
Which blood group is a universal donor?
A. A
B. B
C. AB
D. O
The Correct Answer is D.A person can be a universal blood donor or acceptor. A universal blood donor has type O blood, while a universal blood acceptor has type AB blood.
There are several different types or groups of blood, and the major groups are A, B, AB, and O. Blood group is a way to classify blood according to inherited differences of red blood cell antigens found on the surface of a red blood cell. The type of antibody in blood also identifies a particular blood group. Antibodies are proteins found in the plasma. They function as part of the body’s natural defense to recognize foreign substances and alert the immune system.
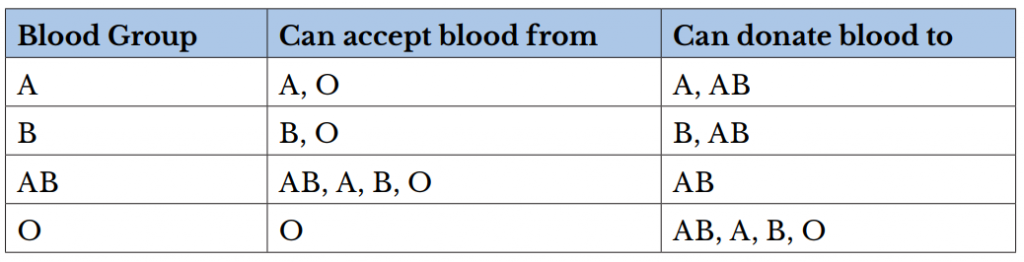
Depending on which antigen is inherited, parental offspring will have one of the four major blood groups. Collectively, the following major blood groups comprise the ABO system:
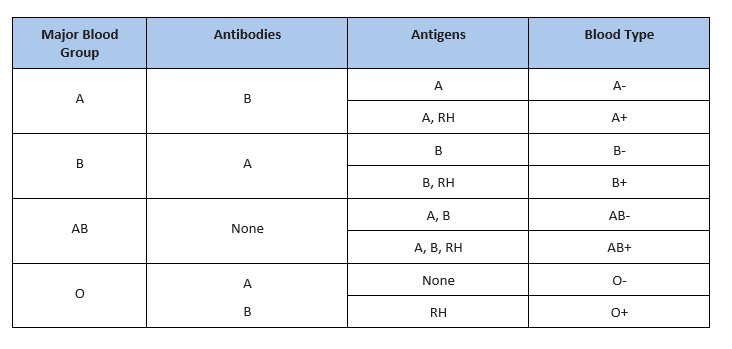
- Blood group A: Displays type A antigens on the surface of a red blood cell and contains B antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group B: Displays type B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface and contains A antibodies in the plasma.
- Blood group O: Does not display A or B antigens on the surface of a red blood cell. Both A and B antibodies are in the plasma.
- Blood group AB: Displays type A and B antigens on the red blood cell’s surface, but neither A nor B antibodies are in the plasma
In addition to antigens, the Rh factor protein may exist on a red blood cell’s surface. Because this protein can be either present (+) or absent (-), it increases the number of major blood groups from four to eight: A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, and AB-.
Question 3:
A student notices a pattern of stripes on five tigers. Each of the five tigers has the same stripe pattern. Using his inductive reasoning, what does he logically assume based on this information?
A. The pattern continues to change over time.
B. Natural adaptations cause this pattern to occur
C. Each offspring will have the same stripe pattern
D. Ancestors of the tigers have different stripe patterns
The Correct Answer is C.Inductive reasoning involves making specific observations and using them to make broad statements. The student observes that all of the tigers have the same stripe pattern. He can use this observation to make the broad statement that all the tigers’ offspring will have the same stripe pattern.
Inductive reasoning involves drawing a general conclusion from specific observations. This form of reasoning is referred to as the “from the bottom up” approach. Information gathered from specific observations can be used to make a general conclusion about the topic under investigation. In other words, conclusions are based on observed patterns in data.
Question 4:
What standard is used to make comparisons in experiments?
A. Sample size
B. Control group
C. Dependent variable
D. Independent variable
The Correct Answer is B.A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up the scientific method, described below:
- Problem: The question created because of an observation. Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research: Reliable information available about what is observed. Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis: A predicted solution to the question or problem. Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment: A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of an independent variable that the researcher modifies and a dependent variable that changes due to the independent variable. They also include a control group used as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe: Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion: State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate: Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Question 5:
In which state of matter are the intermolecular forces between particles in a substance the strongest?
A. Gas
B. Liquid
C. Plasma
D. Solid
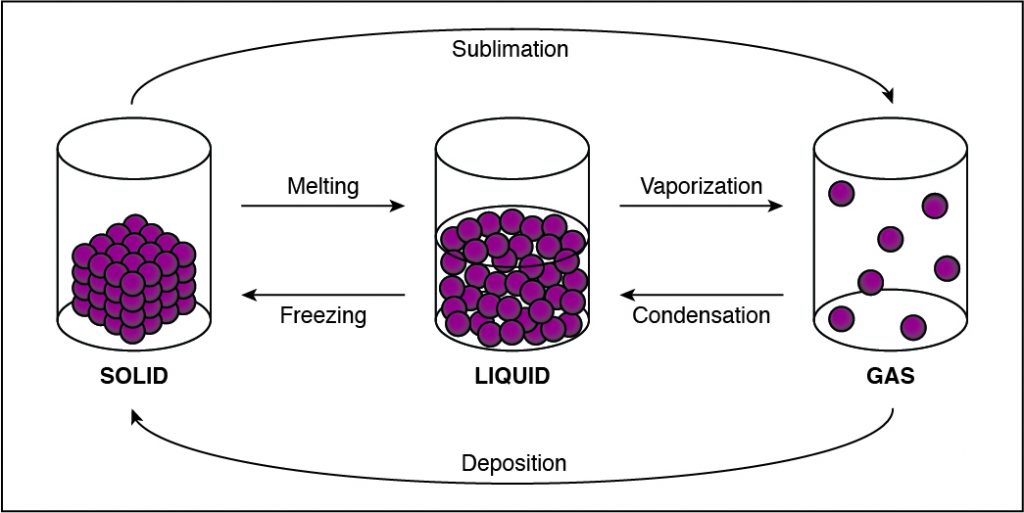
The Correct Answer is D.In solids, particles are usually closer together than in other states of matter because of the strong cohesive forces between the particles.
- Solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas differ from one another in the amount of energy that the particles have and the strength of the cohesive forces that hold the particles together.
- Cohesion is the tendency of particles of the same kind to stick to each other.
- A solid has the lowest amount of energy because its particles are packed close together. Liquids have more energy than a solid, and gases have more energy than solids or liquids because the cohesive forces are very weak.
Question 6:
Mendel discovered the pattern associated with _____after developing a series of rules in genetics.
A. epigenetics
B. heredity
C. heterogeneity
D. taxonomy
The Correct Answer is B.Mendel was accurately able to predict the patterns of heredity by studying rules related to genetics. These rules helped shape his theory of heredity. Heredity is the characteristics offspring inherit from their parents.
From experiments with garden peas, Mendel developed a simple set of rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity. He discovered that plants either self-pollinate or cross-pollinate, when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the pistil of another plant. He also discovered that traits are either dominant or recessive. Dominant traits are expressed, and recessive traits are hidden.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information called genes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual is homozygous for that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual is heterozygous for that trait. Each copy of a factor, or gene, is called an allele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, or phenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is its genotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed.
Question 7:
What structure plays a role in air conduction?
A. Alveolus
B. Capillary
C. Lung
D. Trachea
The Correct Answer is D.The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from the body. In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system enables a person to breathe. Breathing, or inhalation, is essential to life. It is the mechanism that provides oxygen to the body. Without oxygen, cells are unable to perform their functions necessary to keep the body alive. The primary muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm. Known as the chest cavity, this dome shaped structure flattens when it contracts. The rib cage moves outward, allowing outside air to be drawn into the lungs. During relaxation, the diaphragm returns to its dome shape and the rib cage moves back to its natural position. This causes the chest cavity to push air out of the lungs.
The respiratory system can be functionally divided into two parts:
- Air-conducting portion: Air is delivered to the lungs. This region consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract—specifically, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas exchange portion: Gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. This portion includes the lungs, alveoli, and capillaries.
Question 8: A person is diagnosed as having acidosis, a condition in which the blood pH is below 7.45. What does the doctor most likely conclude?
A. Too much carbon dioxide is found in the blood.
B. Highly oxygenated blood circulates through the body
C. A blockage prevents blood from leaving the pulmonary artery
D. The nasal cavity has a difficult time clearing particles from the air.
The Correct Answer is A. Acidosis is when the body fluids contain too much acid, or low pH. The kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body’s pH in balance. Acidosis is the result when there is too much loss of bicarbonate from the blood known as metabolic acidosis, or due to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood due to poor lung function, known as respiratory acidosis. It is the opposite of alkalosis, which is a condition in which there is too much base in the body fluids.Question 9:
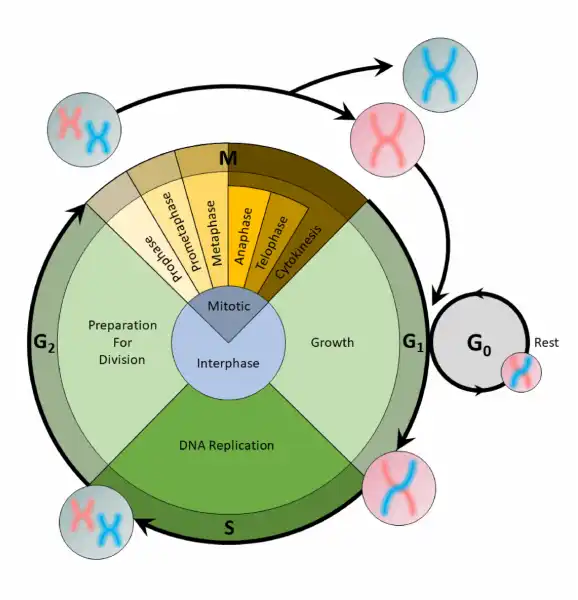
What phase is the cell cycle part of?
A. Interphase
B. Metaphase
C. Prophase
D. Telophase
The Correct Answer is A.Before mitosis or meiosis occurs, interphase must happen. This is when the cell cycle takes place. The cell cycle is an organized process divided into two phases: interphase and the M (mitotic) phase. During interphase, the cell grows and copies its DNA. After the cell reaches the M phase, division of the two new cells can occur. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
Question 10:
While hiking, a person is startled after encountering a bear. Her palms get sweaty and her heart starts racing. Which part of her nervous system was directly stimulated?
A. Central
B. Parasympathetic
C. Somatic
D. Sympathetic
The Correct Answer is D.The autonomic nervous system is responsible for activities that are nonvoluntary and under unconscious control. This system controls glands and the smooth muscles of internal organs, heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the following:
- Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system focuses on emergency situations by preparing the body for fight or flight. (Sympathetic = Stress)
- Parasympathetic nervous system: The parasympathetic nervous system controls involuntary processes unrelated to emergencies. This system deals with “rest or digest” activities. (Parasympathetic = Peace)
The somatic nervous system primarily controls voluntary activities such as walking and riding a bicycle. Thus, this system sends information to the CNS and motor nerve fibers that are attached to skeletal muscle.