Which type of lymphocyte is capable of killing tumor cells and infected cells without prior sensitization?.
A. Helper T cells.
B. B cells.
C. Natural killer cells.
D. Cytotoxic T cells .
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Test 4
Question 1:
A patient with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis.
What process allows for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the patient's bloodstream during hemodialysis?
A. Active transport.
B. Osmosis
C. Diffusion
D. Facilitated diffusion.
The Correct Answer is C.Diffusion.
During hemodialysis, waste products and excess fluids are removed from the blood by diffusion 1.
Diffusion is a separation process in which particles that are dissolved in a solution are relocated from an area of higher concentration in the blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate.
Choice A.
Active transport is incorrect because active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient.
Choice B.
Osmosis is incorrect because osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
Choice D.
Facilitated diffusion is incorrect because facilitated diffusion is a process where molecules move down their concentration gradient with the help of carrier proteins.
Question 2:
Which type of bond is responsible for the unique properties of water and plays a crucial role in the structure of DNA and proteins?
A. Hydrogen bonds.
B. Covalent bonds.
C. Ionic bonds.
D. Van der Waals forces.
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the unique properties of water and play a crucial role in the structure of DNA and proteins.
Hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Choice B.
Covalent bonds is incorrect because covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Choice C.
Ionic bonds is incorrect because ionic bonds are chemical bonds formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
Choice D.
Van der Waals forces is incorrect because Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that arise from temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules.
Question 3:
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been declared brain dead and is awaiting organ donation.
Which of the following interventions is most important to preserve the viability of the organs?
A. Administering antibiotics to prevent infection.
B. Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
C. Providing emotional support to the family members.
D. Applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying.
The Correct Answer is B.The correct answer is choice B.
Maintaining normal body temperature and blood pressure.
Early identification and management of potential organ donors must take into consideration specific pathophysiologic changes for medical optimization 1.
The VIPPS (ventilation, infusion and pumping, pharmacological treatment, and specificities) strategy is a mnemonic method that brings together key aspects of the restoration of oxygen delivery to tissues during hemodynamic instability plus organ optimization strategies.
Choice A is incorrect because administering antibiotics to prevent infection is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Choice C is incorrect because providing emotional support to family members, while important, is not an intervention that directly affects organ viability.
Choice D is incorrect because applying eye drops and ointment to prevent corneal drying is not the most important intervention to preserve organ viability.
Question 4:
What is the relationship between atomic mass and mass number?
A. They are the same.
B. Atomic mass is always greater than mass number.
C. Atomic mass and mass number are not related.
D. Atomic mass is very close to mass number but with some deviation in the decimal places.
The Correct Answer is D.Atomic mass is very close to mass number but with some deviation in the decimal places.
Atomic mass is also known as atomic weight and is the weighted average mass of an atom of an element based on the relative natural abundance of that element’s isotopes.
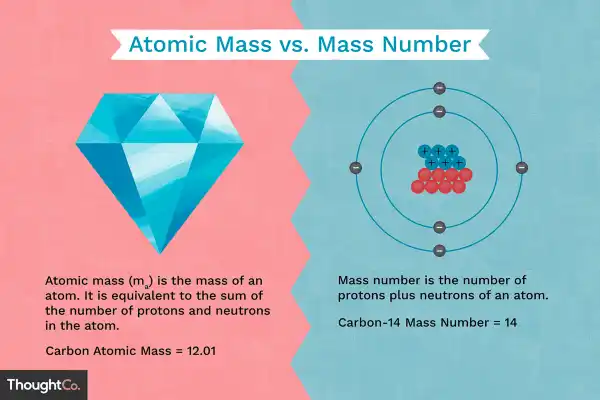 |
The mass number, on the other hand, is a count of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Choice A is incorrect because atomic mass and mass number do not mean the same thing.
Choice B is incorrect because atomic mass is not always greater than mass number.
Choice C is incorrect because atomic mass and mass number are related.
Question 5:
Which of the following organelles is responsible for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The correct answer is choice A. Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations.
Choice B is incorrect because mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Choice C is incorrect because ribosomes are responsible for protein production.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production and protein production, but not for modifying, sorting and packaging proteins and lipids.
Question 6:
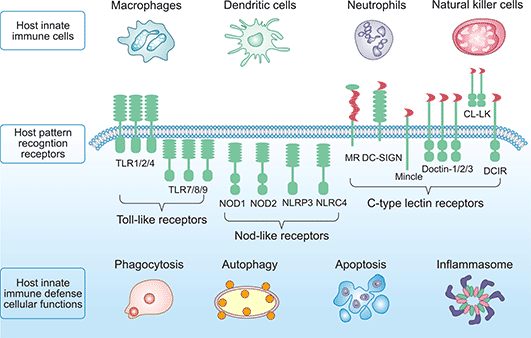
Which of the following allows a limited range of immune cells to detect and respond rapidly to a wide range of pathogens that share common structures?
A. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
B. Cytokines
C. Chemokines
D. T cells .
The Correct Answer is A.Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are a class of receptors that can directly recognize the specific molecular structures on the surface of pathogens.
PRRs play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system and are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens.
 |
Choice B is incorrect because cytokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that regulate immunity.
Choice C is incorrect because chemokines are not receptors but rather signaling molecules that attract immune cells to sites of infection.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are not receptors but rather white blood cells that assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Question 7:
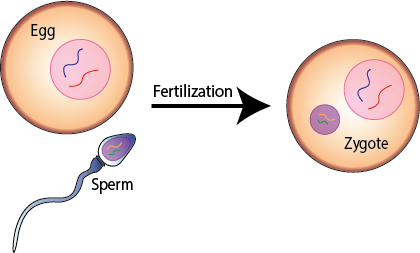
Which process involves the fusion of male and female gametes resulting in the formation of a zygote?
A. Oogenesis.
B. Fertilization.
C. Meiosis.
D. Mitosis.
The Correct Answer is B.Fertilization.
Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
 |
Oogenesis (choice A) is the process by which female gametes, or eggs, are produced.
Meiosis (choice C) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of gametes.
Mitosis (choice D) is a type of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
Question 8:
Which of the following represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen?
A. Adaptive immunity
B. Antibodies
C. Innate immunity
D. T cells .
The Correct Answer is C.Innate immunity represents the first line of defense to an intruding pathogen.
The innate immune system is a series of nonspecific defenses that make up the innate immune system.
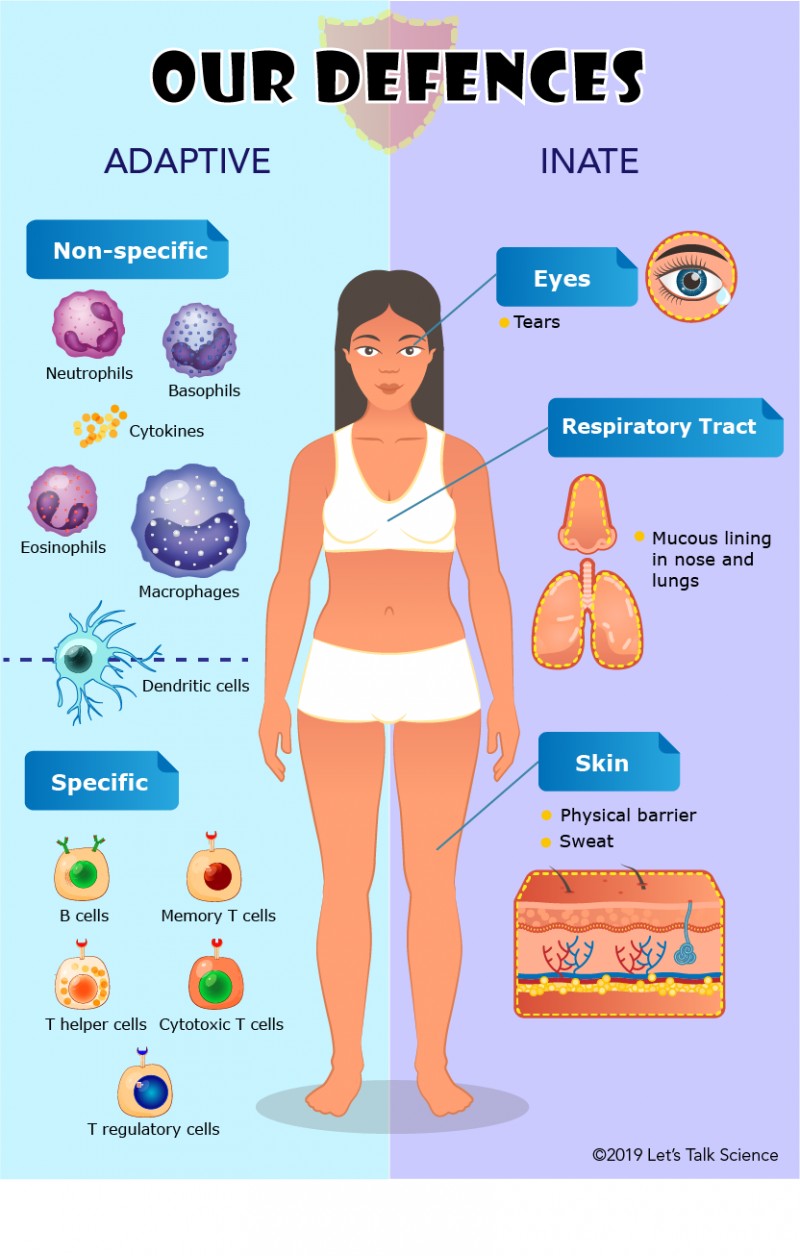
These defenses are not directed against any one pathogen but instead provide a guard against all infection.
Choice A is incorrect because adaptive immunity is activated when pathogens are able to bypass innate immune defenses.
Choice B is incorrect because antibodies are part of the adaptive immune system and are produced by B cells.
Choice D is incorrect because T cells are part of the adaptive immune system and assist B cells or directly kill infected cells.
Question 9:
During the menstrual cycle, which structure in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation?
A. Corpus luteum.
B. Fimbriae
C. Follicle
D. Ovarian ligament.
The Correct Answer is A.Corpus luteum.
During the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum in the ovary produces progesterone to prepare the endometrium for potential implantation.
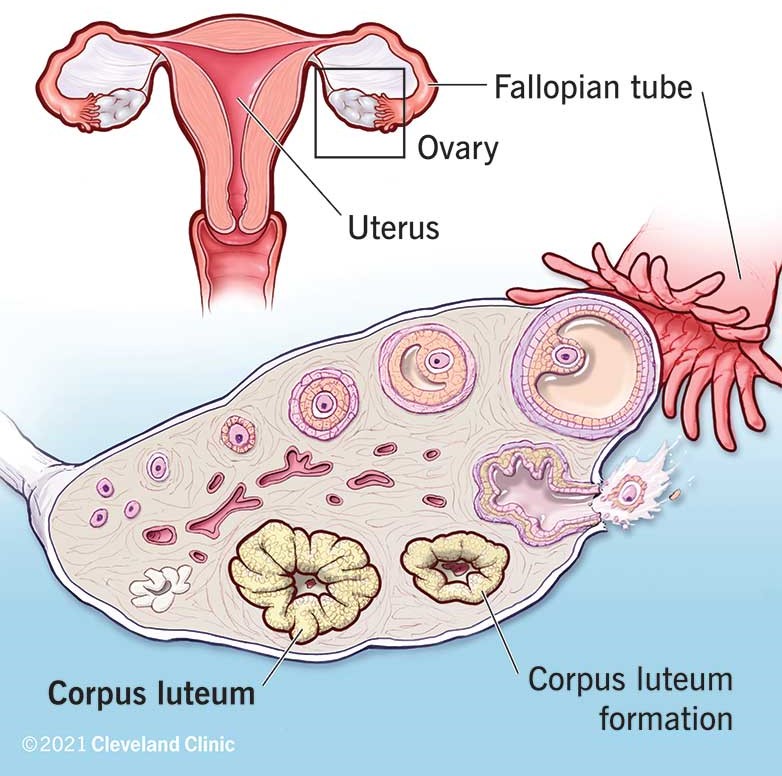
Choice B is incorrect because fimbriae are finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube.
Choice C is incorrect because a follicle is a sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Choice D is incorrect because the ovarian ligament is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the uterus.
Question 10:
What is a primer in DNA sequencing?
A. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
B. A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a "starter" for the template.
C. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a "starter" for the polymerase.
D. A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a "starter" for the template.
The Correct Answer is C.A primer is a short single-stranded DNA fragment used in certain laboratory techniques, such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
In the PCR method, a pair of primers hybridizes with the sample DNA and defines the region that will be amplified.
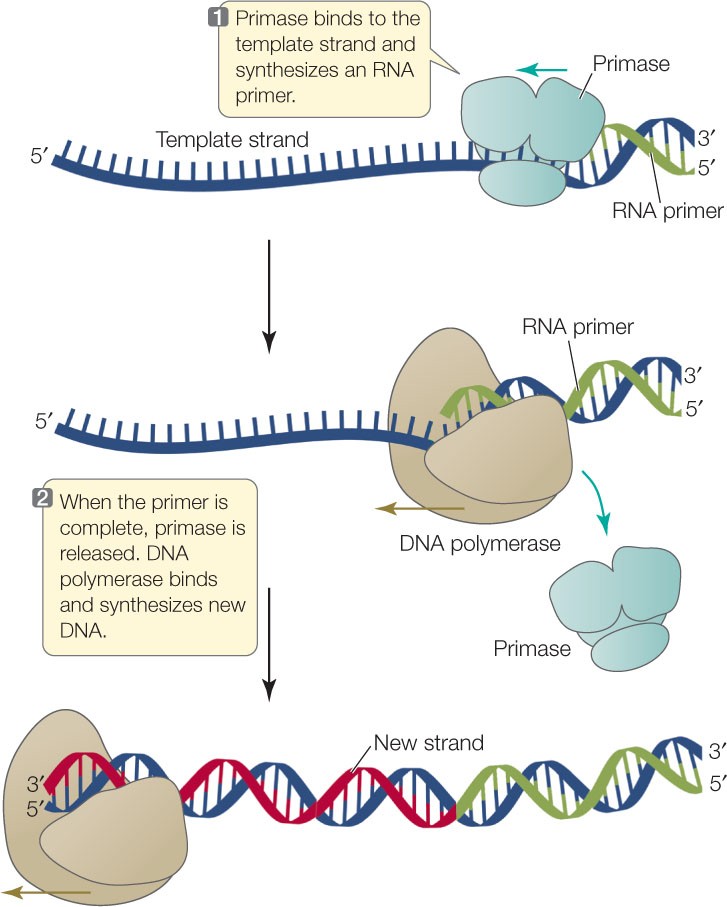
Choice A) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the template DNA and acts as a “starter” for the polymerase is incorrect because primers are single-stranded, not double-stranded.
Choice B) A short piece of double-stranded DNA that binds to the primer and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because it does not make sense for a primer to bind to itself.
Choice D) A short piece of single-stranded DNA that binds to the polymerase and acts as a “starter” for the template is incorrect because primers bind to the template DNA, not to the polymerase.
Note: DNA primers are used instead of RNA primers in DNA sequencing and PCR because DNA is more stable, specific, and compatible with the enzymes and processes involved in these techniques.