Why is it important for new scientific findings to be published?
A. Scientists will get paid if their findings are published.
B. Publishing findings will help scientists become more biased.
C. Other scientists can validate or disprove the findings
D. This prevents other scientists from performing similar tests
For those aiming to excel in their ATI TEAS test and secure admission into their desired nursing program, ExamGates offers an invaluable resource. Our platform features practice questions meticulously crafted by tutors who have previously aced the exam themselves. With ExamGates, you can access content that is 100% relevant to the test, accompanied by vivid images and illustrations. Additionally, our platform provides comprehensive explanations for both correct and incorrect answers, empowering you to fully grasp the material and optimize your study efforts. Take the first step towards your nursing aspirations with ExamGates today.
Other scientists can validate or disprove the findings.
It is important for new scientific findings to be published so that other scientists can review the research and either validate or disprove the findings.
This process of peer-review helps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of scientific research.
Choice A.
Scientists will get paid if their findings are published is not correct because while some scientists may receive funding or grants for their research, the primary goal of publishing scientific findings is not for financial gain.
Choice B.
Publishing findings will help scientists become more biased is not correct because the goal of publishing scientific findings is to share information and promote transparency, not to promote bias.
Choice D.
This prevents other scientists from performing similar tests is not correct because publishing scientific findings allows other scientists to build upon the research and perform further tests to validate or disprove the findings.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.
More Questions on TEAS 7 Science Exam 2
Question 1:
Which of the following is the atomic number of an atom that has 12 protons and 12 neutrons?
A. 24
B. 12
C. 1
D. 144
The Correct Answer is B.The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus.
In this case, the atom has 12 protons, so its atomic number is 12.
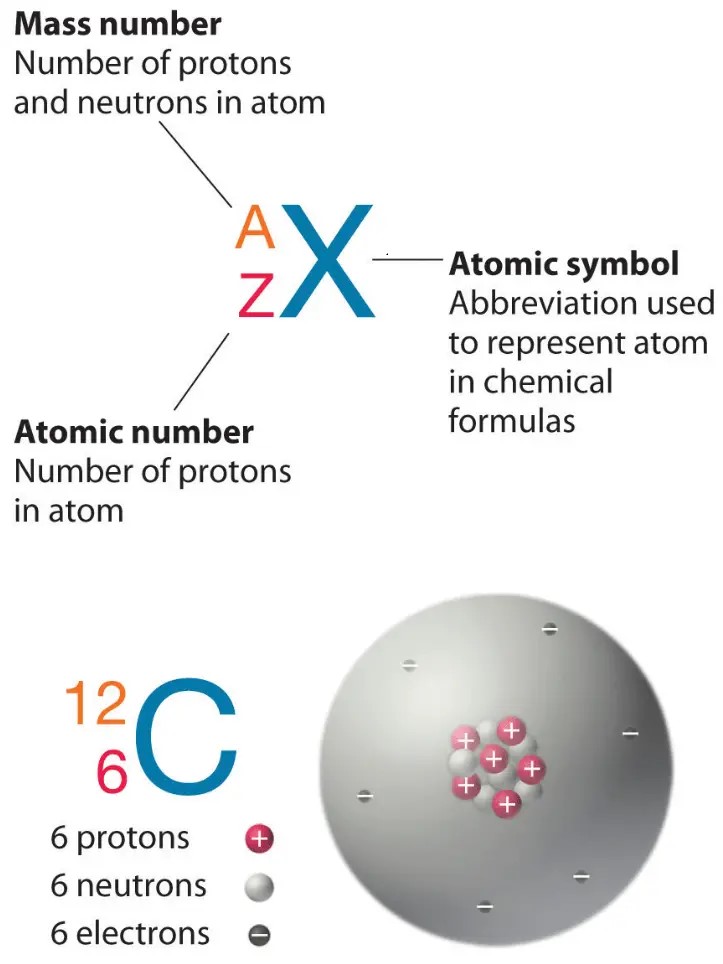
Choice A, 24, is not the correct answer because it represents the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus, which is known as the mass number.
Choice C, 1, is not the correct answer because it does not represent the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus.
Choice D, 144, is not the correct answer because it represents the square of the mass number and does not represent any property of the atom.
Question 2:
Which of the following is correct regarding the pH scale?
A. A substance with a pH of 3 is two times more alkaline than a substance with a pH of 4
B. A substance with a pH of 3 is two times more acidic than a substance with a pH of 4
C. A substance with a pH of 3 is 10 times more acidic than a substance with a pH of 4
D. A substance with a pH of 3 is 10 times more alkaline than a substance with a pH of 4
The Correct Answer is C.The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
A solution with a pH of 7 is neutral, while a solution with a pH less than 7 is acidic and a solution with a pH greater than 7 is alkaline.
Because the pH scale is logarithmic, each whole number change in pH represents a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity.
Therefore, a substance with a pH of 3 is 10 times more acidic than a substance with a pH of 4.
Choice A.
A substance with a pH of 3 is two times more alkaline than a substance with a pH of 4 is not correct because it incorrectly states that the substance with a lower pH is more alkaline and also incorrectly states the magnitude of the difference in acidity or alkalinity.
Choice B.
A substance with a pH of 3 is two times more acidic than a substance with a pH of 4 is not correct because it correctly states that the substance with a lower pH is more acidic but incorrectly states the magnitude of the difference in acidity.
Choice D.
A substance with a pH of 3 is 10 times more alkaline than a substance with a pH of 4 is not correct because it incorrectly states that the substance with a lower pH is more alkaline.
Question 3:
In a plant in which fuzzy leaves (F) are dominant over smooth leaves (f), which of the following crosses will produce only offspring with smooth leaves?
A. FF x FF
B. Ff x Ff
C. ff x ff
D. Ff x ff
The Correct Answer is C.ff.
In this cross, both parents are homozygous recessive for the smooth leaf trait
(ff).
This means that all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the recessive allele (f) and will therefore have smooth leaves.
Choice A.
FF x FF is not correct because both parents are homozygous dominant for the fuzzy leaf trait (FF) and all of their offspring will inherit two copies of the dominant allele (F) and will therefore have fuzzy leaves.
Choice B.
Ff x Ff is not correct because both parents are heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) and their offspring can inherit either one dominant allele (F) or one recessive allele (f) from each parent, resulting in a 3:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves. Choice D.
Ff x ff is not correct because one parent is heterozygous for the leaf trait (Ff) while the other is homozygous recessive (ff), resulting in a 1:1 ratio of fuzzy to smooth leaves in their offspring.
Question 4:
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood?
A. Superior vena cava
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary artery
D. Pulmonary vein
The Correct Answer is D.The pulmonary veins are the vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
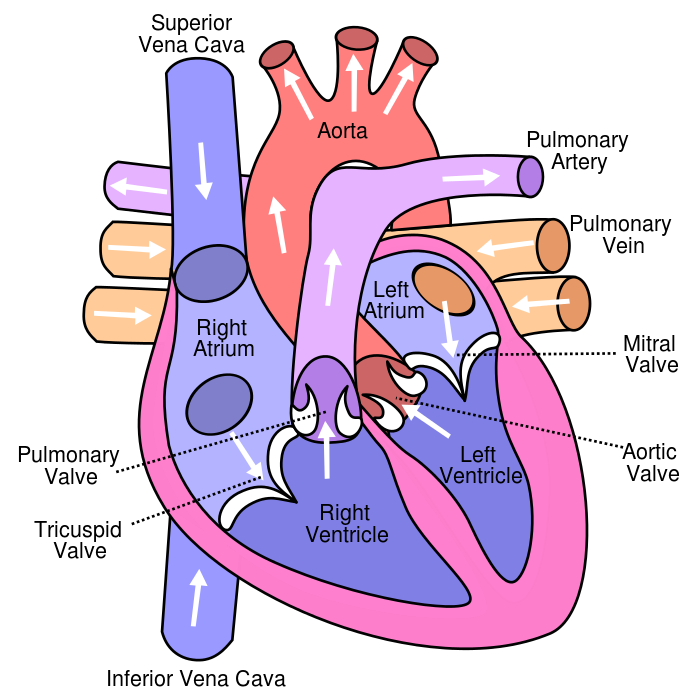
Choice A is not correct because the superior vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice B is not correct because the inferior vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is not correct because the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs.
Question 5:
In a hypertonic solution, water flows through aquaporins embedded in the plasma membrane of the cell.
This type of transport is best known as which of the following?
A. Facilitated diffusion
B. Active transport
C. Osmosis
D. Diffusion
The Correct Answer is C.Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration.
In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell, so water flows out of the cell through aquaporins embedded in the plasma membrane to balance the concentration gradient.
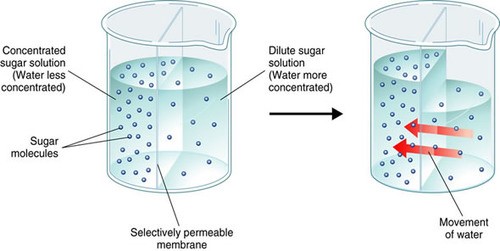
Choice A.
Facilitated diffusion is not correct because it is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of molecules across a membrane through specific transport proteins, but it does not specifically refer to the movement of water molecules.
Choice B.
Active transport is not correct because it is a type of transport that involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient and requires energy in the form of ATP, but osmosis is a passive process that does not require energy.
Choice D.
Diffusion is not correct because it refers to the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, but it does not specifically refer to the movement of water molecules.
Question 6:
Nitrogen gas is an extremely stable molecule because of which of the following?
A. Ionic bonds
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Resonance bonds
D. Triple covalent bonds
The Correct Answer is D.Triple covalent bonds.
Nitrogen gas (N2) is an extremely stable molecule because it consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together by a triple covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons to form a molecule.
In a triple covalent bond, three pairs of electrons are shared between the two atoms, resulting in a very strong bond that makes the molecule extremely stable.
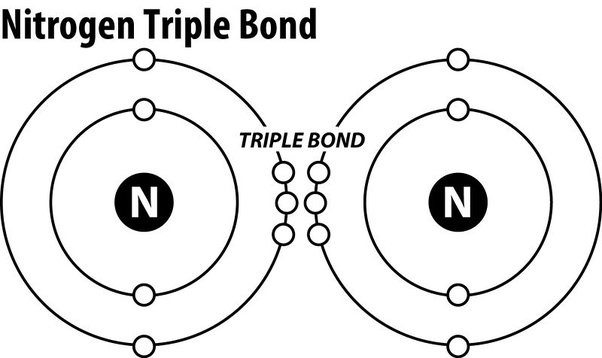
Choice A.
Ionic bonds is not correct because ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another to form ions, which are then attracted to each other due to their opposite charges.
Nitrogen gas does not contain ions and is not held together by ionic bonds.
Choice B.
Hydrogen bonds is not correct because hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between molecules that contain hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Nitrogen gas does not contain hydrogen atoms and is not held together by hydrogen bonds.
Choice C.
Resonance bonds is not correct because resonance refers to the delocalization of electrons in a molecule where multiple Lewis structures can be drawn to represent the molecule.
Nitrogen gas has a single Lewis structure and does not exhibit resonance.
Question 7:
Which of the following organic molecules contain both an amine and carboxyl group?
A. Lipids
B. Chitin
C. Cellulose
D. Proteins
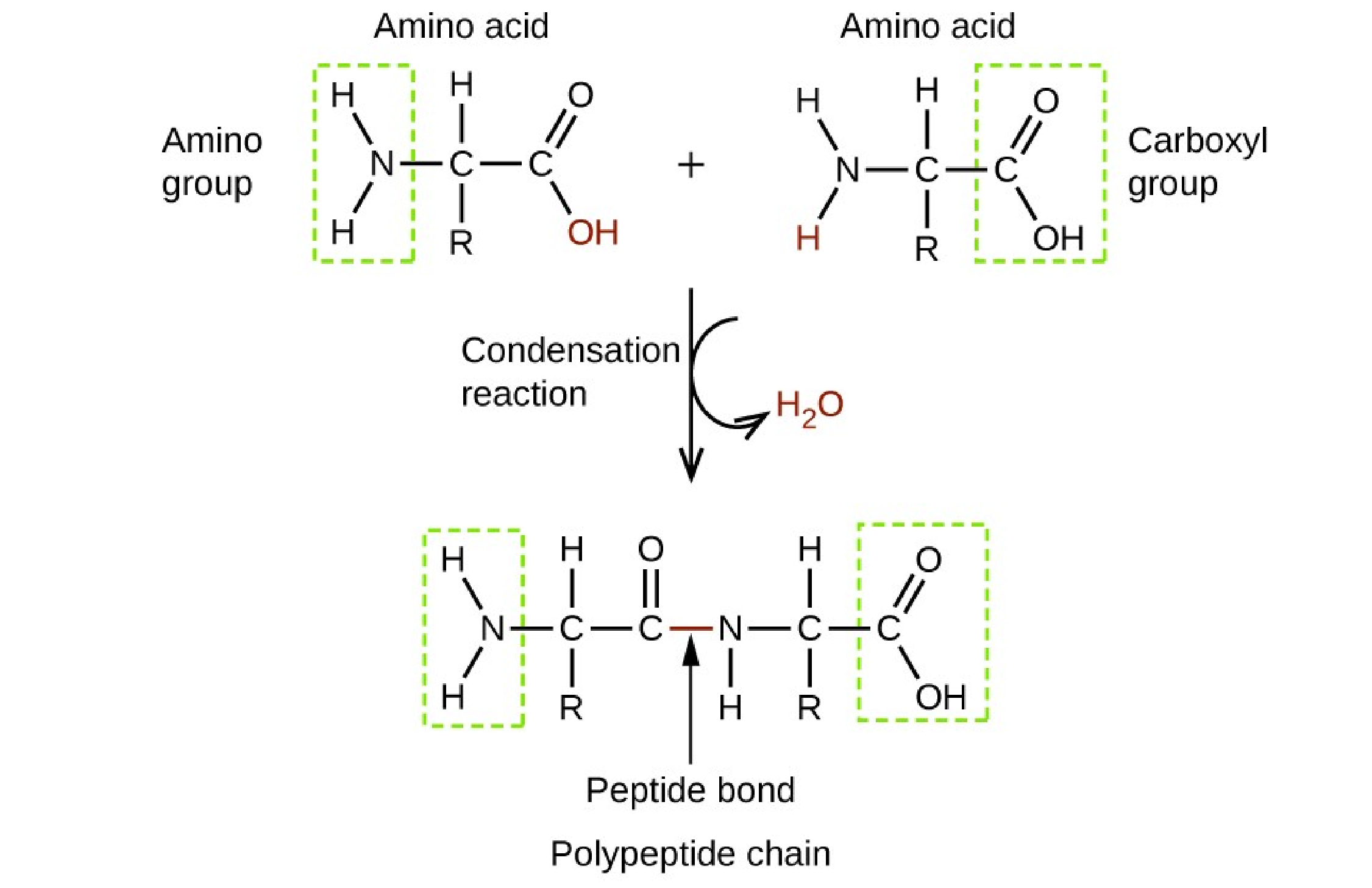
The Correct Answer is D.Proteins.
Proteins are made up of amino acids which are organic molecules that contain both an amine functional group (–NH2) and a carboxylic acid functional group (– COOH).
 |
Choice A, Lipids, is not the correct answer because lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others.
They do not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice B, Chitin, is not the correct answer because chitin is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Choice C, Cellulose, is not the correct answer because cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C6H10O5)n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units.
It does not contain both an amine and carboxyl group.
Question 8:
Hikers who found a human body at high altitude in the Italian Alps thought the man had died recently, but tests indicated he was shot with an arrow more than 5,300 years ago.
Which of the following would be the best reason for prolonged preservation of the body? .
A. The food that the person ate contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body
B. The arrow wound caused blood to flow out of the body, which led the enzymes that would break down tissue to be cleared from the body
C. The body was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found
D. The ultraviolet rays at such a high altitude caused all the body's molecules to be preserved.
The Correct Answer is C.The best reason for the prolonged preservation of the body is that it was frozen in the cold temperature of the Alps shortly after he died and remained frozen until it was found.
Freezing can preserve a body by slowing down or stopping the decomposition process.
Choice A is not correct because the food that the person ate would not have contained toxins that killed the bacteria that would have otherwise destroyed the body.
Choice B is not correct because the arrow wound would not have caused blood to flow out of the body in a way that would have cleared enzymes that break down tissue from the body.
Choice D is not correct because ultraviolet rays at high altitude would not have caused all of the body’s molecules to be preserved.
Question 9:
Which of the following structures is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Cell membrane
B. Golgi apparatus
C. Chloroplasts
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
The Correct Answer is A.The cell membrane is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment.
It is composed of a lipid bilayer and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
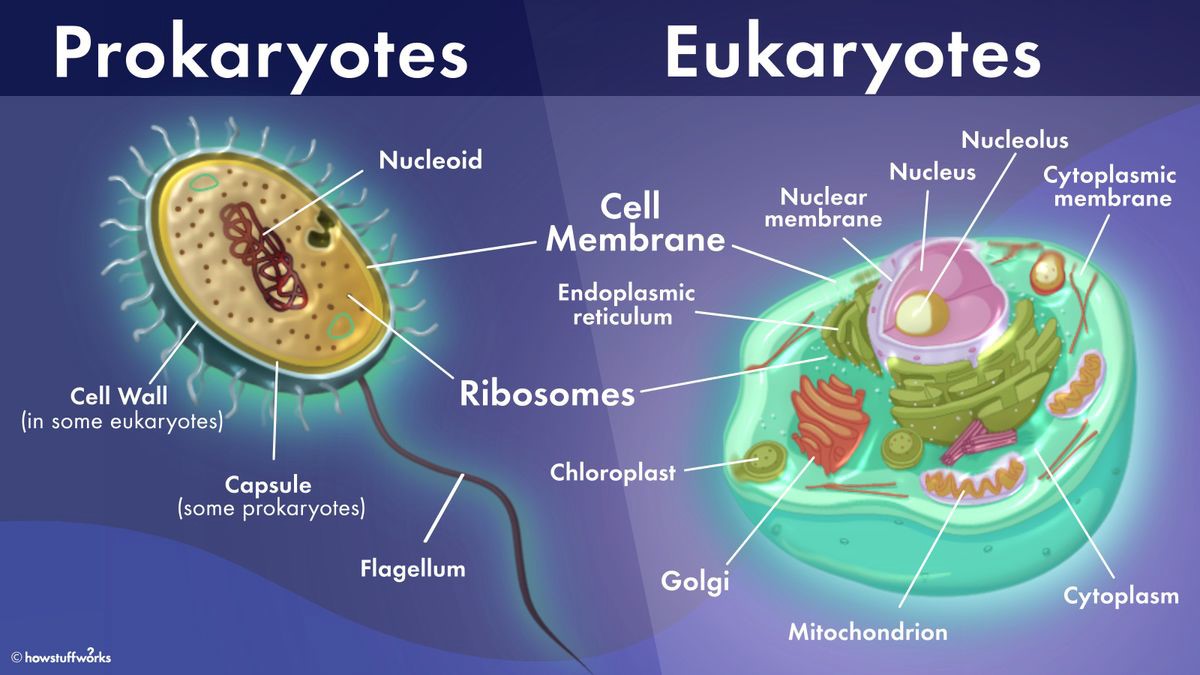
Choice B is incorrect because the Golgi apparatus is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transport to other parts of the cell or to be secreted outside the cell.
Choice C is incorrect because chloroplasts are not present in prokaryotic cells.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae that are responsible for photosynthesis.
Choice D is incorrect because the endoplasmic reticulum is not present in prokaryotic cells.
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
Question 10:
Which of the following indicates the function of sodium bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas?
A. Sodium bicarbonate is a protease that digests carbohydrates.
B. Sodium bicarbonate stimulates the pyloric sphincter.
C. Sodium bicarbonate inhibits peristalsis.
D. Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
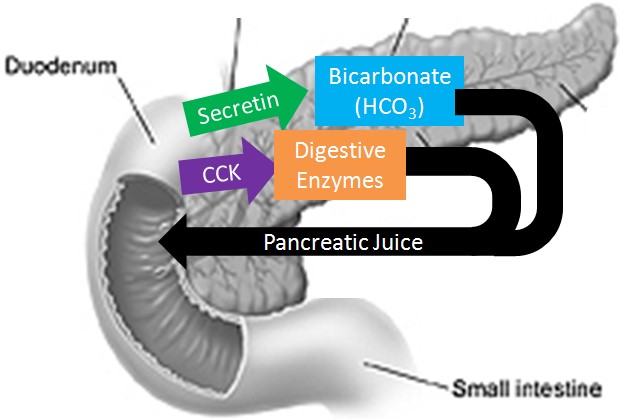
The Correct Answer is D.Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity of chyme.
The pancreas secretes large amounts of sodium bicarbonate, which protects the duodenum by neutralizing the acid that comes from the stomach.
This compound helps neutralize stomach acid generated during the digestive process.
Choice A is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate is not a protease that digests carbohydrates.
Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins, while sodium bicarbonate is a chemical compound that helps neutralize stomach acid.
Choice B is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not stimulate the pyloric sphincter.
The pyloric sphincter is a ring of smooth muscle that separates the stomach from the duodenum and regulates the passage of partially digested food (chyme) into the small intestine.
Choice C is incorrect because sodium bicarbonate does not inhibit peristalsis.
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.