Common Respiratory Disorders
- Respiratory disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the organs and structures involved in breathing and gas exchange.
- These disorders can result from infections, allergies, environmental factors, genetic predisposition, and lifestyle choices.
1. Asthma
Definition: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing.
Pathophysiology:
- Airway inflammation leads to bronchoconstriction, narrowing of the airways, and increased mucus production, causing airflow obstruction.
- Triggers include allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, and stress.
Management:
- Short-acting bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) for acute relief of symptoms.
- Inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators for long-term control of inflammation and symptoms.
- Avoidance of triggers and use of peak flow meters to monitor lung function.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Definition: Progressive lung diseases, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, characterized by airflow limitation and breathing difficulties.
Pathophysiology:
- Chronic inflammation and narrowing of the airways (chronic bronchitis).
- Destruction of alveolar walls and loss of lung elasticity (emphysema).
- Main risk factor: Smoking, although exposure to air pollutants and genetic factors also play a role.
Management:
- Smoking cessation is essential to slow disease progression.
- Bronchodilators (short-acting and long-acting) and inhaled corticosteroids to relieve symptoms and reduce exacerbations.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and vaccination against respiratory infections.
3. Pneumonia
Definition: Infection of the lung parenchyma, often caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Pathophysiology:
- Inflammatory response leads to alveolar consolidation, edema, and exudate formation.
- Symptoms include fever, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and sputum production.
Management:
- Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia (guided by culture and sensitivity testing).
- Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia (e.g., oseltamivir for influenza).
- Supportive care, including rest, fluids, and fever control.
4. Influenza (Flu)
Definition: Viral infection of the respiratory system caused by influenza viruses (types A, B, and rarely C).
Pathophysiology:
- Highly contagious virus transmitted via respiratory droplets.
- Symptoms include sudden onset of fever, chills, sore throat, cough, muscle aches, and fatigue.
Management:
- Antiviral medications (e.g., oseltamivir, zanamivir) if started early in the course of illness to reduce severity and duration.
- Supportive care, including rest, fluids, and fever control.
- Annual influenza vaccination to prevent infection and reduce transmission.
5. Tuberculosis (TB)
Definition: Infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, usually affecting the lungs (pulmonary TB) but can involve other organs (extrapulmonary TB).
Pathophysiology:
- Spread via airborne droplets from coughing or sneezing by individuals with active TB.
- Primary TB infection occurs when the bacteria are inhaled, leading to formation of granulomas (tubercles) in the lungs.
- Reactivation TB may occur years later if the immune system weakens.
Management:
- Antibiotic therapy with multiple drugs (e.g., rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) for several months to eradicate the bacteria.
- Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) to ensure adherence to treatment.
- Infection control measures to prevent transmission, including isolation of contagious individuals and contact tracing.
More on AmplifyGlobe
Organs of the Respiratory System
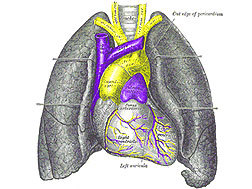 The respiratory system is crucial for the exchange of gases between the body and Read More
The respiratory system is crucial for the exchange of gases between the body and Read More
Physiology of Respiration
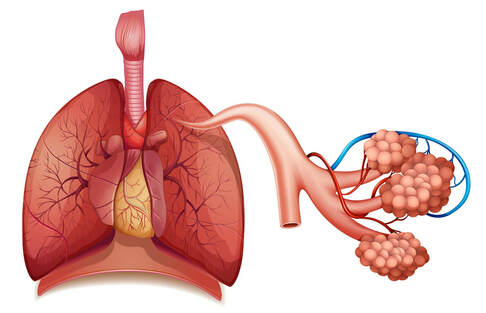 Respiration is the process by which the body takes in oxygen from the air and re Read More
Respiration is the process by which the body takes in oxygen from the air and re Read More
Factors Affecting Breathing
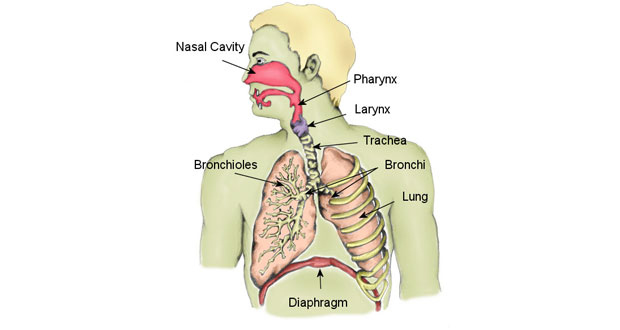 Breathing, or respiration, is a complex physiological process influenced by vari Read More
Breathing, or respiration, is a complex physiological process influenced by vari Read More
If you're looking to ace your ATI TEAS test and get accepted into the nursing program of your dreams, try ExamGates today. Tutors who have taken the exam before wrote and prepared the practice questions on ExamGates. Therefore, you have 100% relevant content, vivid images and illustrations, and in-depth explanations for right and wrong answers.